Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
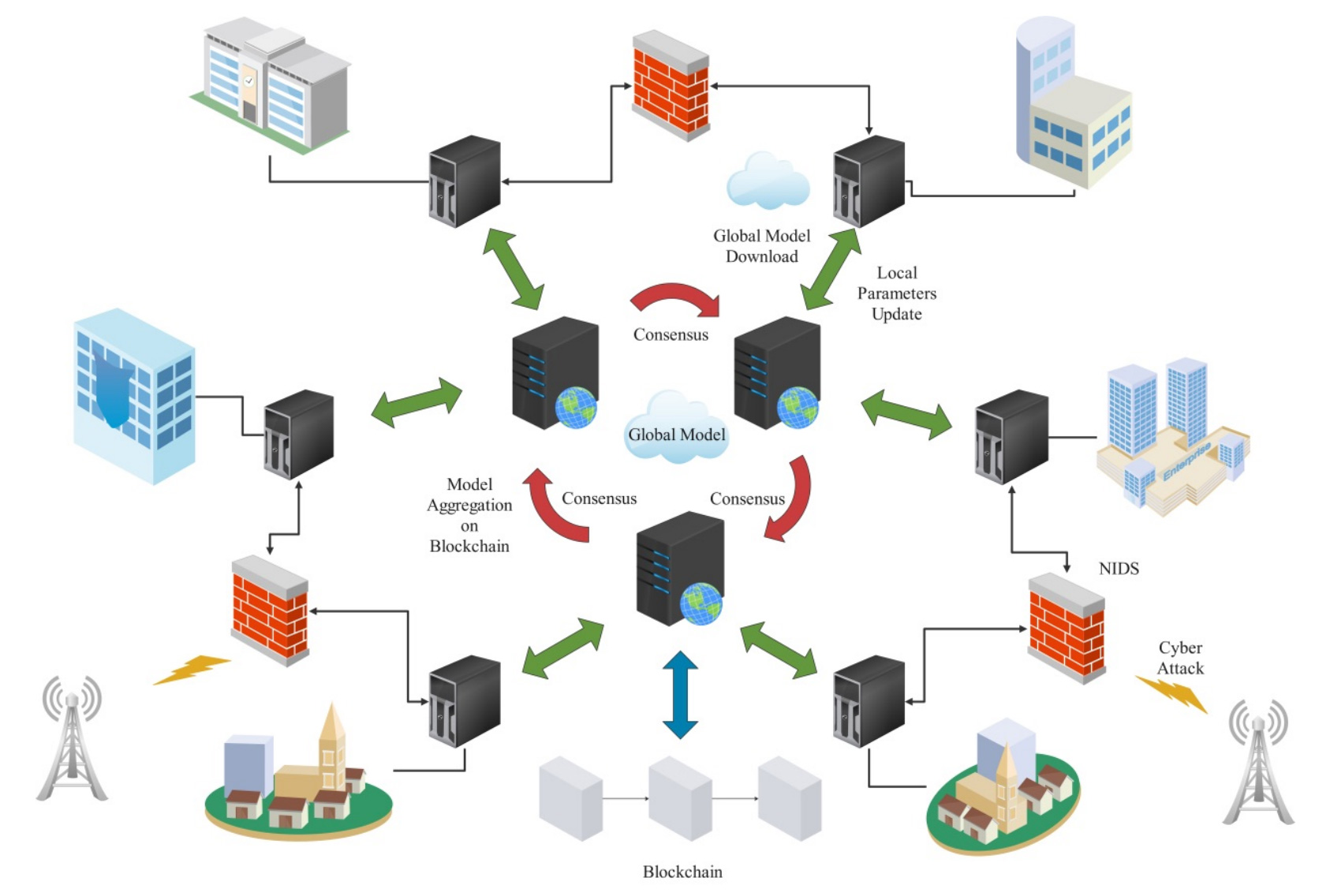
TY - JOUR AU - Cao, Yuan AU - Ku, Chin Soon AU - Kumar, Rahul AU - Khan, Arshad PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/02 TI - Privacy and Trust in Blockchain-Federated Intrusion Detection Systems: Taxonomy, Challenges and Perspectives JO - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing T2 - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing JF - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 4 EP - 24 DO - 10.62762/JRSC.2025.399812 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.399812 KW - intrusion detection systems KW - federated learning KW - blockchain KW - privacy KW - trust AB - Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a critical role in protecting modern networks, but traditional centralized designs raise serious concerns regarding data privacy, trust, and scalability. Federated Learning (FL) reduces privacy risks through decentralized model training, and blockchain enhances trust by providing immutability and transparency. Combining these technologies creates a promising paradigm for secure and trustworthy IDS. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of blockchain-federated IDS with a particular focus on privacy and trust. The key contribution is a multi-dimensional taxonomy that integrates IDS architectures, FL strategies, blockchain types, and consensus mechanisms, providing a clear and structured view of this emerging field. We categorize threats into data, communication, and model levels, and map representative defense mechanisms to each. We also review applications in vehicular networks, industrial and medical Internet of Things (IoT), and metaverse scenarios. Finally, we highlight key challenges, including non-IID data, lightweight consensus, incentive mechanisms, and poisoning-resilient aggregation, and outline future research directions. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Cao2025Privacy,
author = {Yuan Cao and Chin Soon Ku and Rahul Kumar and Arshad Khan},
title = {Privacy and Trust in Blockchain-Federated Intrusion Detection Systems: Taxonomy, Challenges and Perspectives},
journal = {Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {4-24},
doi = {10.62762/JRSC.2025.399812},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.399812},
abstract = {Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a critical role in protecting modern networks, but traditional centralized designs raise serious concerns regarding data privacy, trust, and scalability. Federated Learning (FL) reduces privacy risks through decentralized model training, and blockchain enhances trust by providing immutability and transparency. Combining these technologies creates a promising paradigm for secure and trustworthy IDS. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of blockchain-federated IDS with a particular focus on privacy and trust. The key contribution is a multi-dimensional taxonomy that integrates IDS architectures, FL strategies, blockchain types, and consensus mechanisms, providing a clear and structured view of this emerging field. We categorize threats into data, communication, and model levels, and map representative defense mechanisms to each. We also review applications in vehicular networks, industrial and medical Internet of Things (IoT), and metaverse scenarios. Finally, we highlight key challenges, including non-IID data, lightweight consensus, incentive mechanisms, and poisoning-resilient aggregation, and outline future research directions.},
keywords = {intrusion detection systems, federated learning, blockchain, privacy, trust},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/