ICCK Journal of Software Engineering
ISSN: 3069-1834 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
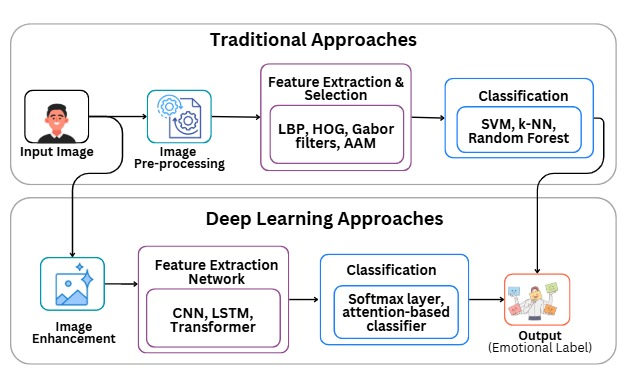
TY - JOUR AU - Farooq, Amna AU - Wattoo, Waqas Ahmad AU - Farooq, Wajiha AU - Mukhtar, Aiza AU - Zahid, Momina AU - Iqra PY - 2025 DA - 2025/10/31 TI - A Comprehensive Review on Software Architectures for Facial Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Techniques JO - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering T2 - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering JF - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 75 EP - 89 DO - 10.62762/JSE.2025.285106 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.285106 KW - convolutional neural network KW - long-short-term memory KW - facial emotion recognition AB - Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) software is an important part of modern software applications. It is used for intelligent user interfaces, diagnostics in psychiatry or psychology, human-computer interaction, and even in surveillance. The recent advancements in the use of deep learning, and the advanced architectures based on them, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and transformer models have made the development of FER software much efficient and scalable. This review paper contributes to the existing literature by providing a comprehensive synthesis of Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) systems from a software engineering perspective spanning the period from 2015 to the present. Unlike prior surveys, our analysis emphasizes the software engineering perspective, covering aspects such as software architectures, system integration, deployment on edge devices, and MLOps practices for continuous testing and monitoring. It specifically targets software construction, software architecture, software systems integration, training frameworks, datasets employment, and also deployment challenges. It explores common datasets like FER2013, RAF-DB and AffectNet and the prevailing model architectures, which include CNN, Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM), hybrid and transformers. Importantly, over half of the surveyed studies continue to rely on demographically narrow datasets (e.g., FER2013, JAFFE, CK+), which limits generalizability and raises fairness concerns across ethnicity, age, and gender. This review contributes by providing a comprehensive and up-to-date synthesis of FER systems while providing directions to the development of fair, lightweight, and robust FER systems suitable for real-world deployment. SN - 3069-1834 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Farooq2025A,
author = {Amna Farooq and Waqas Ahmad Wattoo and Wajiha Farooq and Aiza Mukhtar and Momina Zahid and Iqra},
title = {A Comprehensive Review on Software Architectures for Facial Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Techniques},
journal = {ICCK Journal of Software Engineering},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {75-89},
doi = {10.62762/JSE.2025.285106},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.285106},
abstract = {Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) software is an important part of modern software applications. It is used for intelligent user interfaces, diagnostics in psychiatry or psychology, human-computer interaction, and even in surveillance. The recent advancements in the use of deep learning, and the advanced architectures based on them, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and transformer models have made the development of FER software much efficient and scalable. This review paper contributes to the existing literature by providing a comprehensive synthesis of Facial Emotion Recognition (FER) systems from a software engineering perspective spanning the period from 2015 to the present. Unlike prior surveys, our analysis emphasizes the software engineering perspective, covering aspects such as software architectures, system integration, deployment on edge devices, and MLOps practices for continuous testing and monitoring. It specifically targets software construction, software architecture, software systems integration, training frameworks, datasets employment, and also deployment challenges. It explores common datasets like FER2013, RAF-DB and AffectNet and the prevailing model architectures, which include CNN, Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM), hybrid and transformers. Importantly, over half of the surveyed studies continue to rely on demographically narrow datasets (e.g., FER2013, JAFFE, CK+), which limits generalizability and raises fairness concerns across ethnicity, age, and gender. This review contributes by providing a comprehensive and up-to-date synthesis of FER systems while providing directions to the development of fair, lightweight, and robust FER systems suitable for real-world deployment.},
keywords = {convolutional neural network, long-short-term memory, facial emotion recognition},
issn = {3069-1834},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/