ICCK Journal of Software Engineering
ISSN: 3069-1834 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
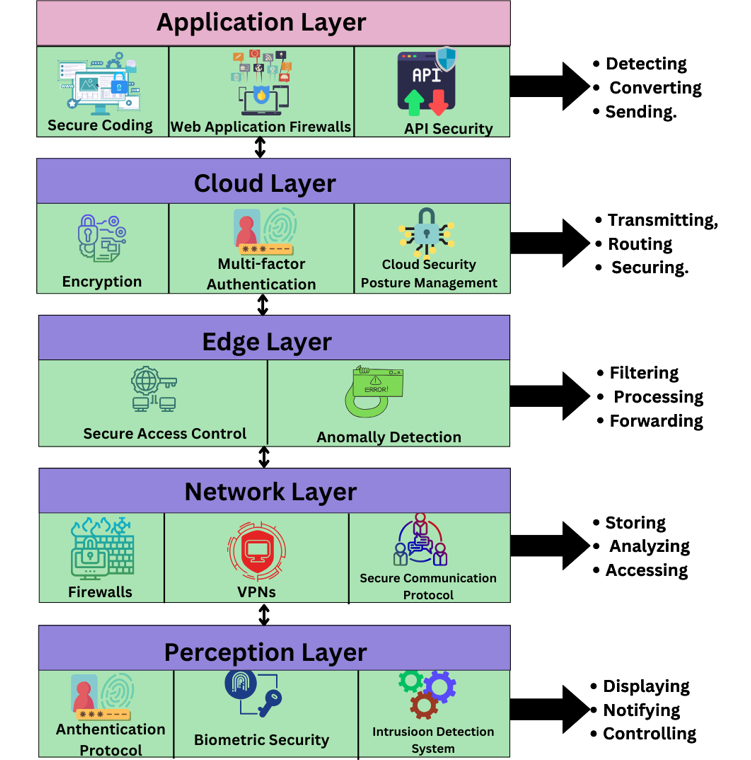
TY - JOUR AU - Arif, Haroon AU - Ali, Abdul Karim Sajid AU - Nabi, Hussain Abdul PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/02 TI - IoT Security through ML/DL: Software Engineering Challenges and Directions JO - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering T2 - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering JF - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 90 EP - 108 DO - 10.62762/JSE.2025.372865 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.372865 KW - internet of things (IoT) KW - cybersecurity KW - machine learning (ML) KW - deep learning (DL) KW - intrusion detection system (IDS) KW - anomaly detection KW - IoT security KW - adversarial attacks AB - The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly integrated into modern software-driven systems across consumer, industrial, and healthcare domains. The heterogeneity of IoT devices, combined with their resource constraints, often renders conventional software security mechanisms insufficient, exposing systems to breaches and exploitation. This study examines recent IoT security incidents to illustrate common vulnerabilities in software-intensive IoT ecosystems, highlighting the resulting risks to critical applications. In response, we review emerging machine learning (ML)-driven security modules and deep learning (DL)-based intrusion detection software, positioning them as adaptive components that can be integrated into IoT system architectures. This review highlights recent peer-reviewed contributions, ensuring alignment with the most current developments in IoT security using ML and DL, and follows a systematic review methodology based on IEEE Xplore (2020--2024). The study further identifies software engineering challenges in integrating these intelligent modules into resource-constrained IoT environments and outlines future directions for building secure-by-design, AI-driven IoT software frameworks. Results demonstrate that ML- and DL-enhanced security modules strengthen software resilience by enabling real-time detection of cyber-attacks, reducing false alarms, and adapting to evolving threat landscapes. The review is structured to first discuss notable case studies of IoT security breaches, followed by an analysis of ML- and DL-based security modules, a comparative evaluation of their effectiveness, and finally, a discussion of key challenges and future research opportunities. SN - 3069-1834 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Arif2025IoT,
author = {Haroon Arif and Abdul Karim Sajid Ali and Hussain Abdul Nabi},
title = {IoT Security through ML/DL: Software Engineering Challenges and Directions},
journal = {ICCK Journal of Software Engineering},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {90-108},
doi = {10.62762/JSE.2025.372865},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.372865},
abstract = {The Internet of Things (IoT) is increasingly integrated into modern software-driven systems across consumer, industrial, and healthcare domains. The heterogeneity of IoT devices, combined with their resource constraints, often renders conventional software security mechanisms insufficient, exposing systems to breaches and exploitation. This study examines recent IoT security incidents to illustrate common vulnerabilities in software-intensive IoT ecosystems, highlighting the resulting risks to critical applications. In response, we review emerging machine learning (ML)-driven security modules and deep learning (DL)-based intrusion detection software, positioning them as adaptive components that can be integrated into IoT system architectures. This review highlights recent peer-reviewed contributions, ensuring alignment with the most current developments in IoT security using ML and DL, and follows a systematic review methodology based on IEEE Xplore (2020--2024). The study further identifies software engineering challenges in integrating these intelligent modules into resource-constrained IoT environments and outlines future directions for building secure-by-design, AI-driven IoT software frameworks. Results demonstrate that ML- and DL-enhanced security modules strengthen software resilience by enabling real-time detection of cyber-attacks, reducing false alarms, and adapting to evolving threat landscapes. The review is structured to first discuss notable case studies of IoT security breaches, followed by an analysis of ML- and DL-based security modules, a comparative evaluation of their effectiveness, and finally, a discussion of key challenges and future research opportunities.},
keywords = {internet of things (IoT), cybersecurity, machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), intrusion detection system (IDS), anomaly detection, IoT security, adversarial attacks},
issn = {3069-1834},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/