ICCK Journal of Software Engineering
ISSN: 3069-1834 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
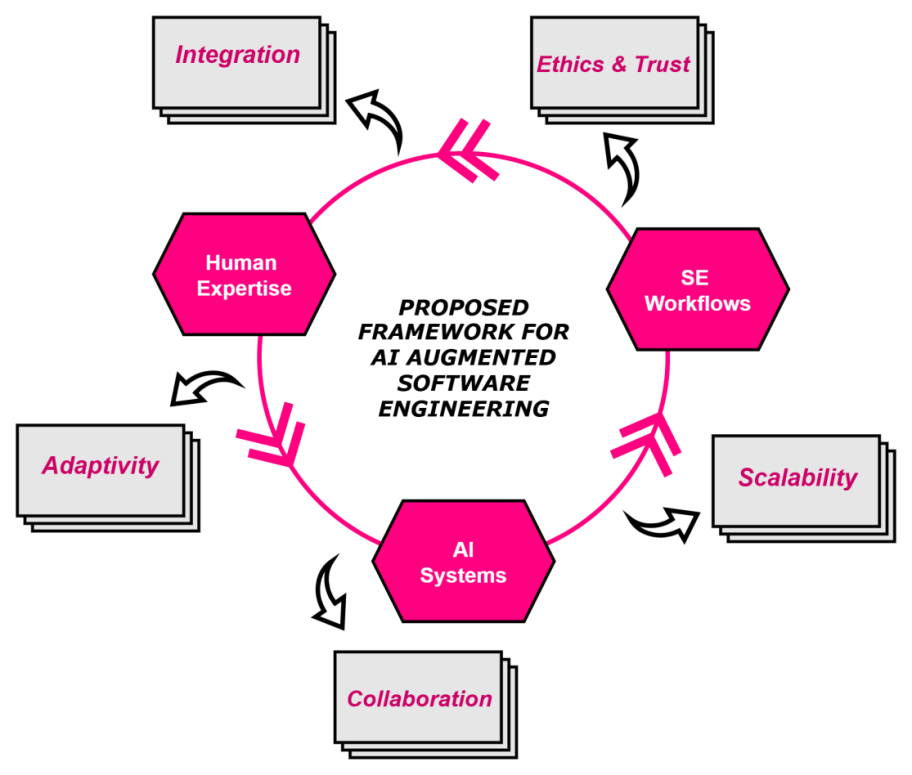
TY - JOUR AU - Akhtar, Samia AU - Aftab, Shabib PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/11 TI - Towards AI-Augmented Software Engineering: A Theoretical Framework JO - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering T2 - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering JF - ICCK Journal of Software Engineering VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 124 EP - 138 DO - 10.62762/JSE.2025.407864 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.407864 KW - software engineering KW - generative AI KW - machine learning KW - deep learning KW - software quality AB - Software Engineering (SE) has traditionally relied on rule-based methods and human expertise to deliver reliable systems. As software systems grow more complex and the demand for intelligent and scalable solutions increases, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative approach. In particular, Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) play a central role in this shift. This paper proposes a theoretical framework for AI-augmented Software Engineering. It emphasizes the role of machine learning and deep learning across the entire software engineering lifecycle including requirement analysis, design, development, testing, maintenance, project management, and process improvement. The framework is further illustrated with recent case studies demonstrating practical applications of AI in real-world SE contexts. Instead of presenting experimental analysis, this study introduces a conceptual framework that shows how AI can enhance automation, improve predictive accuracy, and support better decision-making in SE practices. The discussion highlights both opportunities and challenges. Opportunities include improved productivity, higher software quality, and better adaptability to emerging domains such as Industry 4.0, IoT, and edge computing. Challenges include limited data availability, issues of interpretability, ethical concerns, and difficulties in integrating with legacy systems. The paper also outlines future directions, envisioning AI-driven paradigms such as generative design models, autonomous self-evolving systems, and human--AI collaborative development environments. This theoretical perspective is intended to guide researchers and practitioners in rethinking conventional approaches and adopting AI-augmented strategies for the next generation of Software Engineering. SN - 3069-1834 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Akhtar2025Towards,
author = {Samia Akhtar and Shabib Aftab},
title = {Towards AI-Augmented Software Engineering: A Theoretical Framework},
journal = {ICCK Journal of Software Engineering},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {124-138},
doi = {10.62762/JSE.2025.407864},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JSE.2025.407864},
abstract = {Software Engineering (SE) has traditionally relied on rule-based methods and human expertise to deliver reliable systems. As software systems grow more complex and the demand for intelligent and scalable solutions increases, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative approach. In particular, Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) play a central role in this shift. This paper proposes a theoretical framework for AI-augmented Software Engineering. It emphasizes the role of machine learning and deep learning across the entire software engineering lifecycle including requirement analysis, design, development, testing, maintenance, project management, and process improvement. The framework is further illustrated with recent case studies demonstrating practical applications of AI in real-world SE contexts. Instead of presenting experimental analysis, this study introduces a conceptual framework that shows how AI can enhance automation, improve predictive accuracy, and support better decision-making in SE practices. The discussion highlights both opportunities and challenges. Opportunities include improved productivity, higher software quality, and better adaptability to emerging domains such as Industry 4.0, IoT, and edge computing. Challenges include limited data availability, issues of interpretability, ethical concerns, and difficulties in integrating with legacy systems. The paper also outlines future directions, envisioning AI-driven paradigms such as generative design models, autonomous self-evolving systems, and human--AI collaborative development environments. This theoretical perspective is intended to guide researchers and practitioners in rethinking conventional approaches and adopting AI-augmented strategies for the next generation of Software Engineering.},
keywords = {software engineering, generative AI, machine learning, deep learning, software quality},
issn = {3069-1834},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/