ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
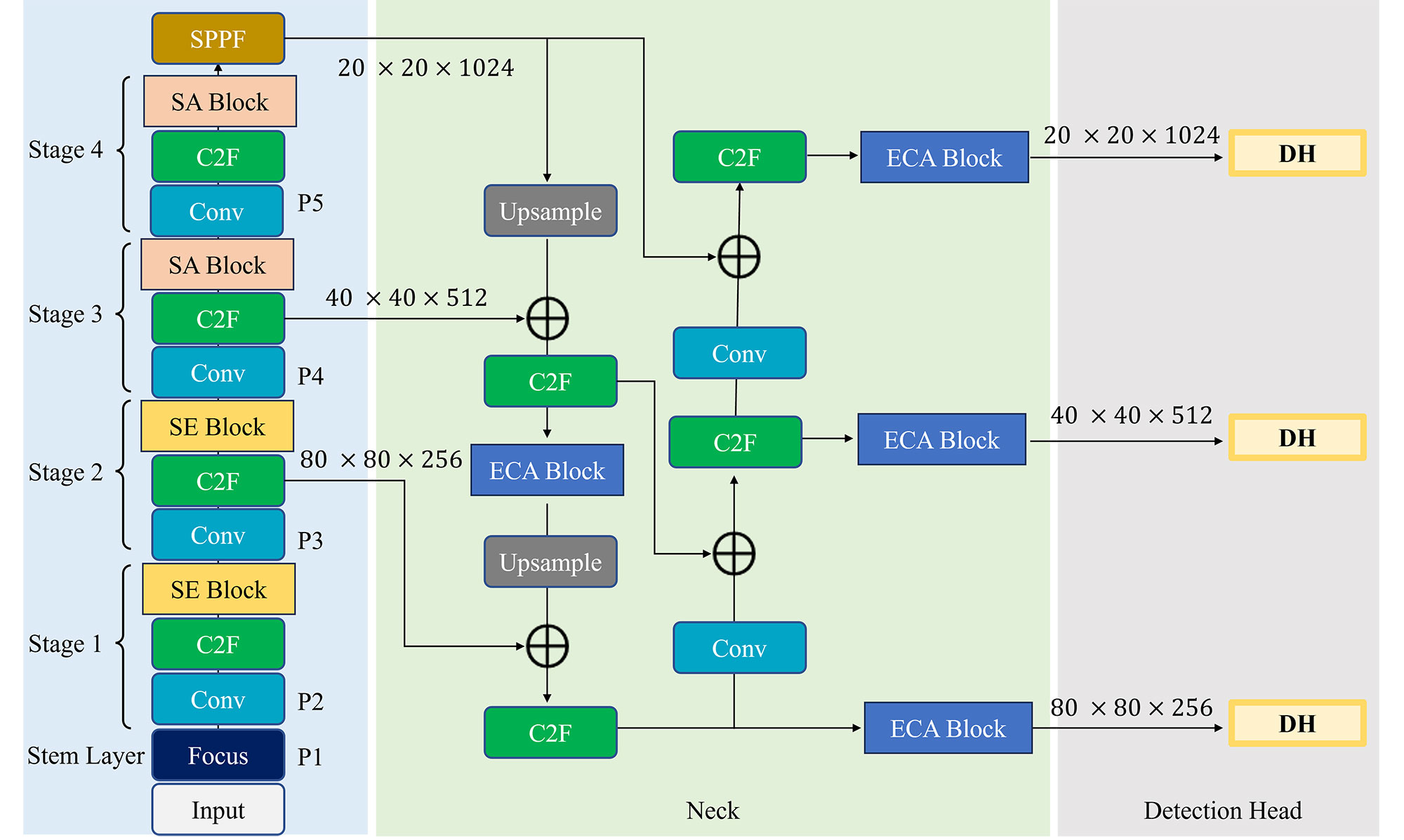
TY - JOUR AU - Ali, Farhan AU - Gazis, Alexandros AU - Zahoor, Faryal PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/06 TI - Lightweight Cascaded Feature Reweighting for Fall Detection through Context-Aware YOLOv8 Architecture JO - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics T2 - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics JF - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics VL - 2 IS - 4 SP - 224 EP - 237 DO - 10.62762/TIS.2025.196437 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.196437 KW - fall detection KW - lightweight architecture KW - feature reweighting KW - healthcare monitoring KW - elderly care KW - elderly fall detection KW - computer vision in healthcare AB - Falls represent a significant global health concern, particularly among older adults, with delayed detection often leading to severe medical complications. Although computer vision-based fall detection systems offer promising solutions, they usually struggle with diverse real-world scenarios and computational efficiency. This paper introduces a novel lightweight cascaded feature reweighting approach that enhances YOLOv8 for reliable fall detection through a context-aware architecture. We strategically integrate three complementary attention mechanisms: Squeeze-and-Excitation blocks in the early stages, Spatial Attention modules in the later stages, and Efficient Channel Attention in the neck section, creating a progressive feature refinement pipeline that leverages the bilateral symmetry properties of human posture. Our approach achieves significant performance improvements, with an mAP of 0.878, an increase of 1.5% over the baseline YOLOv8, while maintaining minimal computational overhead. This makes it well-suited for real-world deployment in resource-constrained environments. Comprehensive evaluations across two diverse datasets, including DiverseFall and CAUCAFall, demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) detectors, including Faster R-CNN and earlier YOLO variants. Our approach shows particularly pronounced advantages under challenging and varied environmental conditions. Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of our architectural design choices, demonstrating that each attention mechanism makes a unique contribution to overall performance improvement. The proposed lightweight architecture represents a significant advancement in vision-based fall detection, striking a balance between high accuracy and computational efficiency while maintaining robust performance in diverse real-world scenarios. SN - 3068-5079 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ali2025Lightweigh,
author = {Farhan Ali and Alexandros Gazis and Faryal Zahoor},
title = {Lightweight Cascaded Feature Reweighting for Fall Detection through Context-Aware YOLOv8 Architecture},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {224-237},
doi = {10.62762/TIS.2025.196437},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.196437},
abstract = {Falls represent a significant global health concern, particularly among older adults, with delayed detection often leading to severe medical complications. Although computer vision-based fall detection systems offer promising solutions, they usually struggle with diverse real-world scenarios and computational efficiency. This paper introduces a novel lightweight cascaded feature reweighting approach that enhances YOLOv8 for reliable fall detection through a context-aware architecture. We strategically integrate three complementary attention mechanisms: Squeeze-and-Excitation blocks in the early stages, Spatial Attention modules in the later stages, and Efficient Channel Attention in the neck section, creating a progressive feature refinement pipeline that leverages the bilateral symmetry properties of human posture. Our approach achieves significant performance improvements, with an mAP of 0.878, an increase of 1.5\% over the baseline YOLOv8, while maintaining minimal computational overhead. This makes it well-suited for real-world deployment in resource-constrained environments. Comprehensive evaluations across two diverse datasets, including DiverseFall and CAUCAFall, demonstrate that our model outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) detectors, including Faster R-CNN and earlier YOLO variants. Our approach shows particularly pronounced advantages under challenging and varied environmental conditions. Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of our architectural design choices, demonstrating that each attention mechanism makes a unique contribution to overall performance improvement. The proposed lightweight architecture represents a significant advancement in vision-based fall detection, striking a balance between high accuracy and computational efficiency while maintaining robust performance in diverse real-world scenarios.},
keywords = {fall detection, lightweight architecture, feature reweighting, healthcare monitoring, elderly care, elderly fall detection, computer vision in healthcare},
issn = {3068-5079},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/