ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
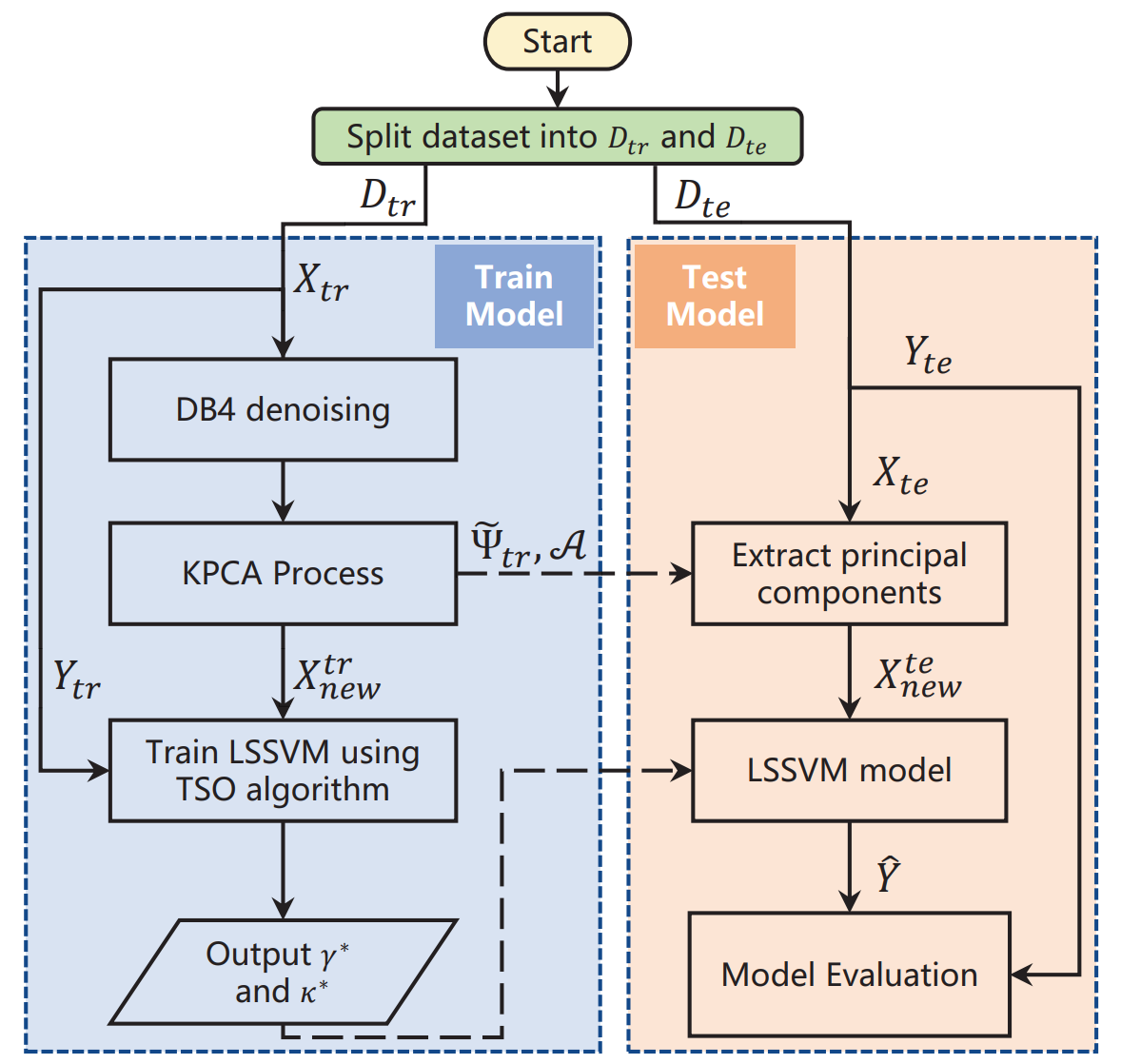
TY - JOUR AU - Peng, Qiang AU - Li, Gengen AU - Yang, Chunxi AU - Zhang, Xiufeng AU - Na, Jing AU - Li, Mou PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/30 TI - RUL Prediction of the Injection Lance in Copper Top-Blown Smelting Using KPCA and TSO-Optimized LSSVM JO - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control T2 - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control JF - ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control VL - 2 IS - 4 SP - 238 EP - 249 DO - 10.62762/TSCC.2025.978286 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.978286 KW - injection lance KW - least square support vector machine (LSSVM) KW - tuna swarm optimization (TSO) algorithm KW - remaining useful life (RUL) AB - As the core component of the copper top-blown smelting, the service life of the injection lance critically affects production stability. To monitor the operating condition of the injection lance, a data-driven model is proposed to predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) or service life, namely, the DKT-LSSVM model. Firstly, to reduce noise interference, the Daubechies wavelet with four vanishing moments (DB4) denoising is used to process the raw data. Then, the Kernel Principal Component Analysis (KPCA) method is utilized to extract the principal components from the denoised data, which retains at least 90% information content (18 principal components are obtained). These principal components are used as inputs to a Least Square Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) model to predict the RUL of the injection lance, and a Tuna Swarm Optimization (TSO) algorithm is proposed to optimize the hyperparameters of the LSSVM. The results show that the proposed algorithm performs well in RUL prediction of the injection lance, with RMSE=1.2274 (day), MAE=0.6623 (day) and R$^2$=0.9308. Therefore, the proposed algorithm can provide effective RUL prediction for the injection lance, reduce its operational risks, and improve the stability and reliability of the copper top-blown smelting system. SN - 3068-9287 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Peng2025RUL,
author = {Qiang Peng and Gengen Li and Chunxi Yang and Xiufeng Zhang and Jing Na and Mou Li},
title = {RUL Prediction of the Injection Lance in Copper Top-Blown Smelting Using KPCA and TSO-Optimized LSSVM},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {4},
pages = {238-249},
doi = {10.62762/TSCC.2025.978286},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSCC.2025.978286},
abstract = {As the core component of the copper top-blown smelting, the service life of the injection lance critically affects production stability. To monitor the operating condition of the injection lance, a data-driven model is proposed to predict the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) or service life, namely, the DKT-LSSVM model. Firstly, to reduce noise interference, the Daubechies wavelet with four vanishing moments (DB4) denoising is used to process the raw data. Then, the Kernel Principal Component Analysis (KPCA) method is utilized to extract the principal components from the denoised data, which retains at least 90\% information content (18 principal components are obtained). These principal components are used as inputs to a Least Square Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) model to predict the RUL of the injection lance, and a Tuna Swarm Optimization (TSO) algorithm is proposed to optimize the hyperparameters of the LSSVM. The results show that the proposed algorithm performs well in RUL prediction of the injection lance, with RMSE=1.2274 (day), MAE=0.6623 (day) and R\$^2\$=0.9308. Therefore, the proposed algorithm can provide effective RUL prediction for the injection lance, reduce its operational risks, and improve the stability and reliability of the copper top-blown smelting system.},
keywords = {injection lance, least square support vector machine (LSSVM), tuna swarm optimization (TSO) algorithm, remaining useful life (RUL)},
issn = {3068-9287},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control
ISSN: 3068-9287 (Online) | ISSN: 3068-9279 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/