Journal of Nonlinear Dynamics and Applications | Volume 1, Issue 2: 112-126, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JNDA.2025.753314
Abstract
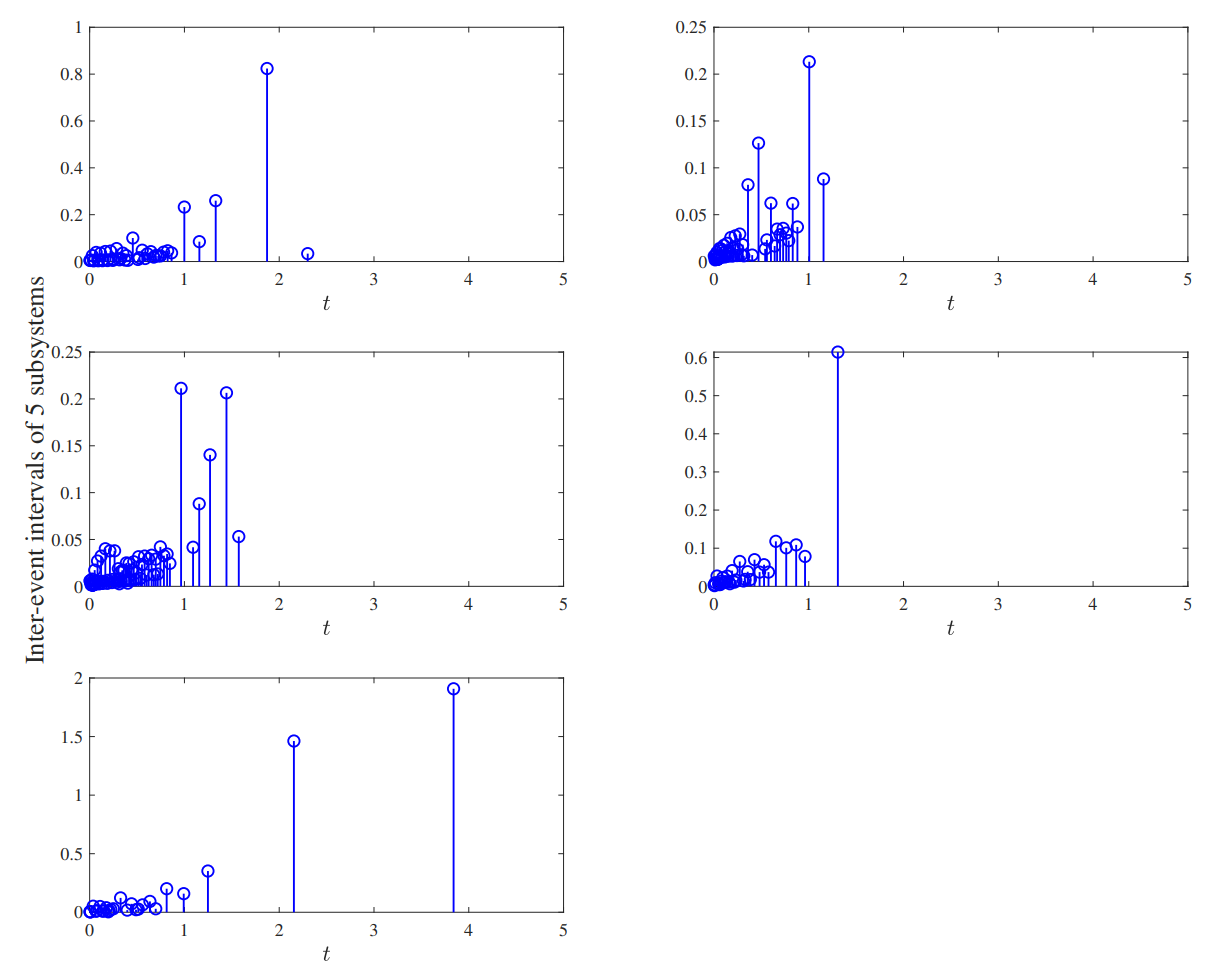
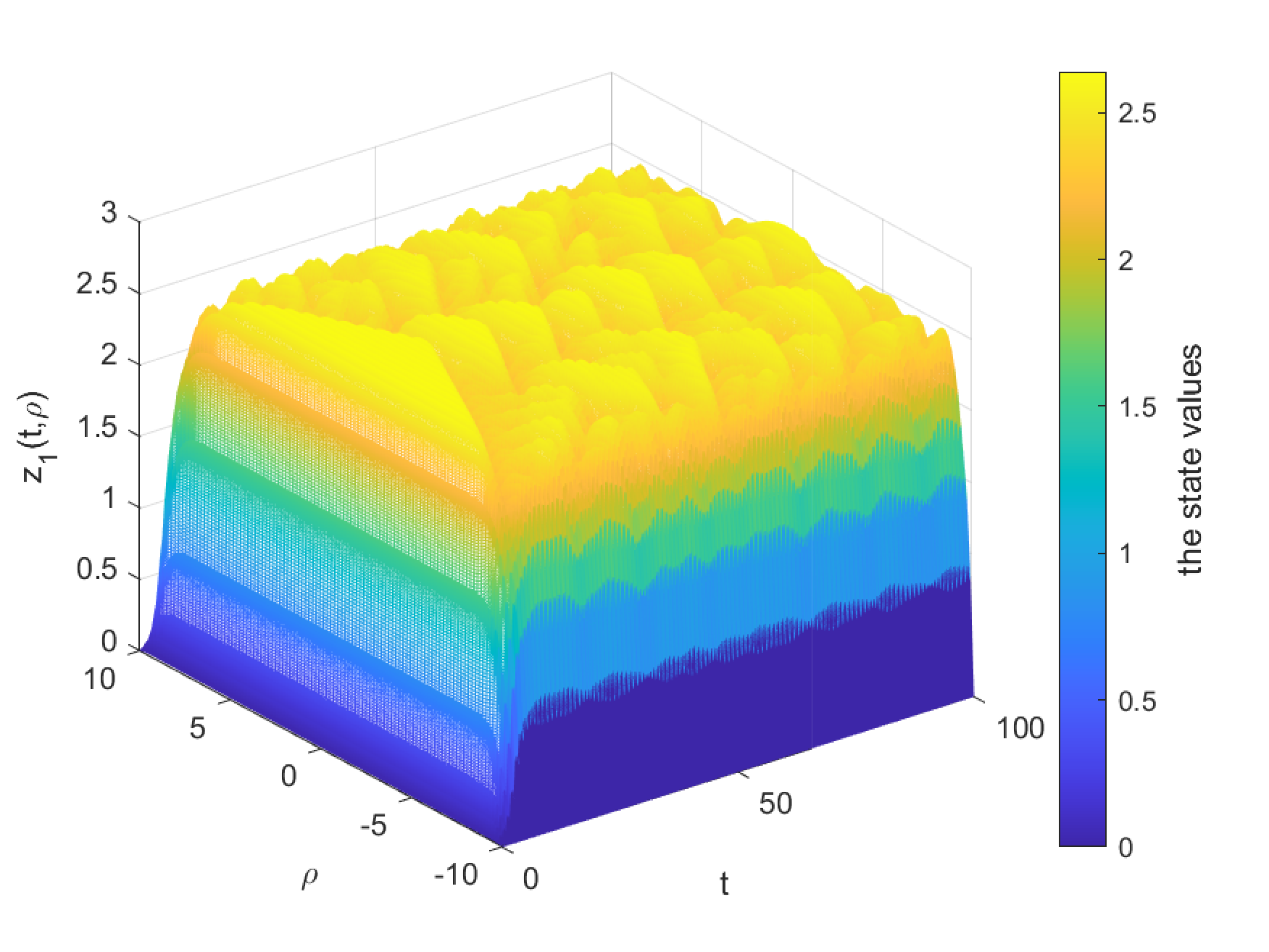
This paper investigates a class of coupled stochastic strict-feedback nonlinear systems under asynchronous intermittent event-triggered control (AIETC). Initially, stochastic analysis technique, Lyapunov method and backstepping design method are employed to design the virtual and actual controllers. AIETC is achieved by an auxiliary timer that grants each subsystem its own control and rest time. In the meantime the control input is applied only at the last node of each subsystem. Then, a global Lyapunov function is constructed. By utilizing graph theory, the global exponential ultimate boundedness in mean square of the systems can be obtained and Zeno behavior is eliminated successfully. Fin... More >
Graphical Abstract