ICCK Transactions on Emerging Topics in Artificial Intelligence | Volume 3, Issue 1: 1-8, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TETAI.2025.518010
Abstract
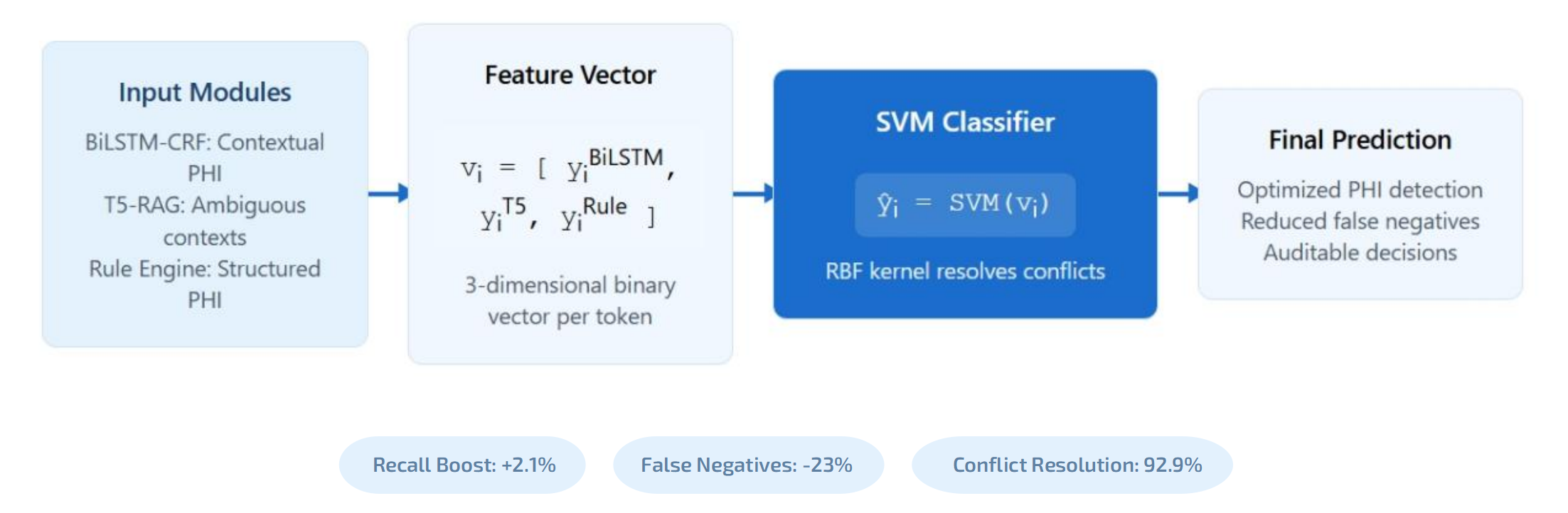
The growing demand for secondary use of electronic health records (EHRs) in clinical research has amplified the importance of effective de-identification of protected health information (PHI) to comply with privacy regulations such as HIPAA. Manual annotation remains error-prone, time-consuming, and inconsistent across healthcare institutions, while existing automated systems often face trade-offs between accuracy, interpretability, and computational cost. This study proposes a novel hybrid de-identification framework that integrates neural, statistical, and rule-based approaches to achieve high recall, operational efficiency, and deployment feasibility in real-world healthcare settings. More >
Graphical Abstract