ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography | Volume 2, Issue 1: 1-15, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TISC.2025.775760
Abstract
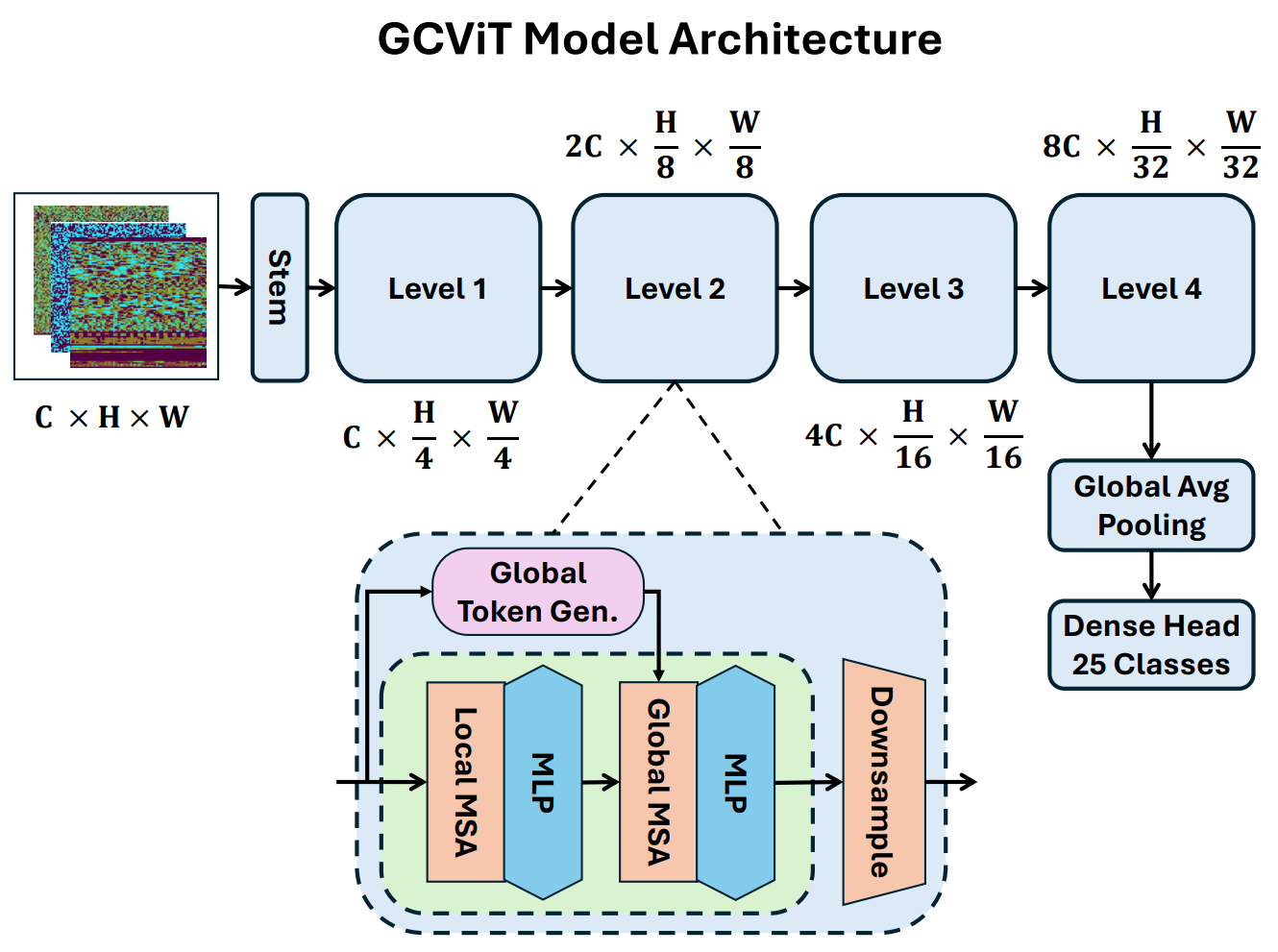
The continuous threat of malware against digital systems exists because its attack methods develop rapidly, reducing the effectiveness of traditional detection systems. Current static and dynamic analysis methods for malware detection face challenges with scalability and robustness when handling large and complex malware samples. Computer vision now shows that malware binaries contain specific structural patterns when displayed as grayscale images, which can be used for classification. This study investigates GCViT for malware detection through its application to the Malimg dataset, which contains 9,337 samples from 25 malware families. The dataset underwent preprocessing through a two-step... More >
Graphical Abstract