ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
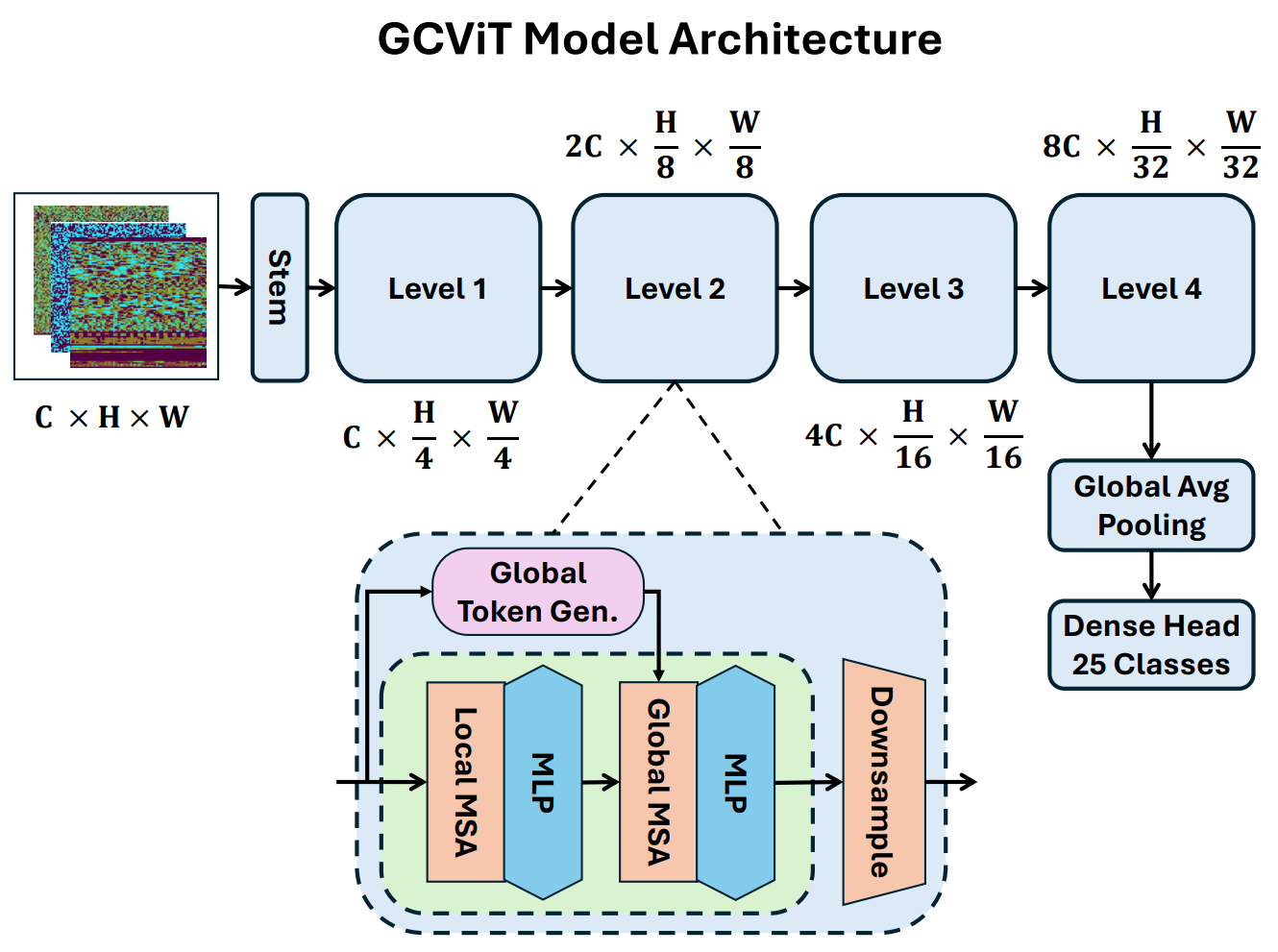
TY - JOUR AU - Masab, Muhammad AU - Ahmad, Khubab AU - Hussain, Muzammil AU - Khan, Muhammad Shahbaz PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/20 TI - Malware Image Classification Using Global Context Vision Transformers for Information Security JO - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography T2 - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography JF - ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 1 EP - 15 DO - 10.62762/TISC.2025.775760 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.775760 KW - malware classification KW - global context vision transformer KW - deep learning KW - information security KW - malimg dataset AB - The continuous threat of malware against digital systems exists because its attack methods develop rapidly, reducing the effectiveness of traditional detection systems. Current static and dynamic analysis methods for malware detection face challenges with scalability and robustness when handling large and complex malware samples. Computer vision now shows that malware binaries contain specific structural patterns when displayed as grayscale images, which can be used for classification. This study investigates GCViT for malware detection through its application to the Malimg dataset, which contains 9,337 samples from 25 malware families. The dataset underwent preprocessing through a two-step process that involved converting binary files into grayscale images followed by applying viridis colormap transformation and normalization for better visual discrimination. The GCViT model trained using ImageNet-pretrained weights while keeping its backbone fixed and modifying only the classifier head for malware family classification. The model reached 99.46% test accuracy and showed high effectiveness across most malware families, with only a few errors among structurally similar variants. The results demonstrate that GCViT achieves better performance by detecting both local and global dependencies in images, leading to improved malware image classification. The research sets a new benchmark for the Malimg dataset and highlights the potential of Vision Transformers in cybersecurity. SN - 3070-2429 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Masab2025Malware,
author = {Muhammad Masab and Khubab Ahmad and Muzammil Hussain and Muhammad Shahbaz Khan},
title = {Malware Image Classification Using Global Context Vision Transformers for Information Security},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography},
year = {2025},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {1-15},
doi = {10.62762/TISC.2025.775760},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TISC.2025.775760},
abstract = {The continuous threat of malware against digital systems exists because its attack methods develop rapidly, reducing the effectiveness of traditional detection systems. Current static and dynamic analysis methods for malware detection face challenges with scalability and robustness when handling large and complex malware samples. Computer vision now shows that malware binaries contain specific structural patterns when displayed as grayscale images, which can be used for classification. This study investigates GCViT for malware detection through its application to the Malimg dataset, which contains 9,337 samples from 25 malware families. The dataset underwent preprocessing through a two-step process that involved converting binary files into grayscale images followed by applying viridis colormap transformation and normalization for better visual discrimination. The GCViT model trained using ImageNet-pretrained weights while keeping its backbone fixed and modifying only the classifier head for malware family classification. The model reached 99.46\% test accuracy and showed high effectiveness across most malware families, with only a few errors among structurally similar variants. The results demonstrate that GCViT achieves better performance by detecting both local and global dependencies in images, leading to improved malware image classification. The research sets a new benchmark for the Malimg dataset and highlights the potential of Vision Transformers in cybersecurity.},
keywords = {malware classification, global context vision transformer, deep learning, information security, malimg dataset},
issn = {3070-2429},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Information Security and Cryptography
ISSN: 3070-2429 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/