Journal of Advanced Materials Research | Volume 1, Issue 1: 37-55, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JAMR.2025.925427
Abstract
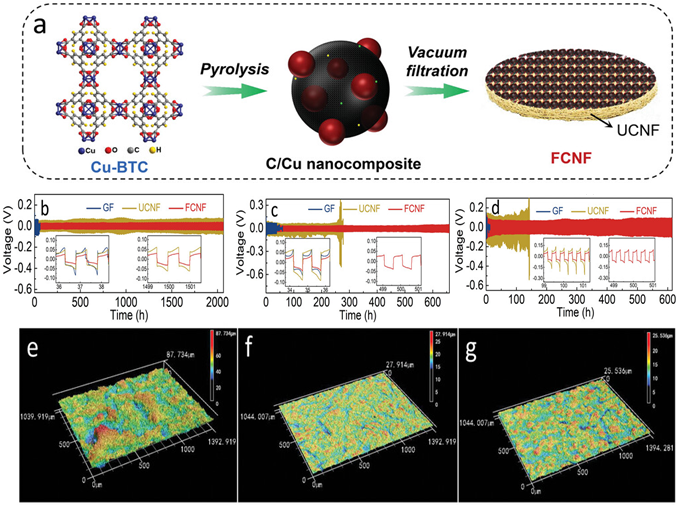
Aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs) are considered one of the most promising candidates for next-generation energy storage systems, owing to the high safety, low cost, high theoretical capacity (820 mAh g\(^{-1}\)), and environmental compatibility. However, the practical implementation of zinc metal anodes still faces challenges such as dendrite growth, hydrogen evolution reaction, and corrosion, which significantly restrict the cycling life and practical usability. To address these issues, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) with tunable pore structures and ultrahigh specific surface areas have been widely employed for protecting zinc anodes. Therefore, this review systematically summarizes the... More >
Graphical Abstract