Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 2, Issue 3: 253-274, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2025.151851
Abstract
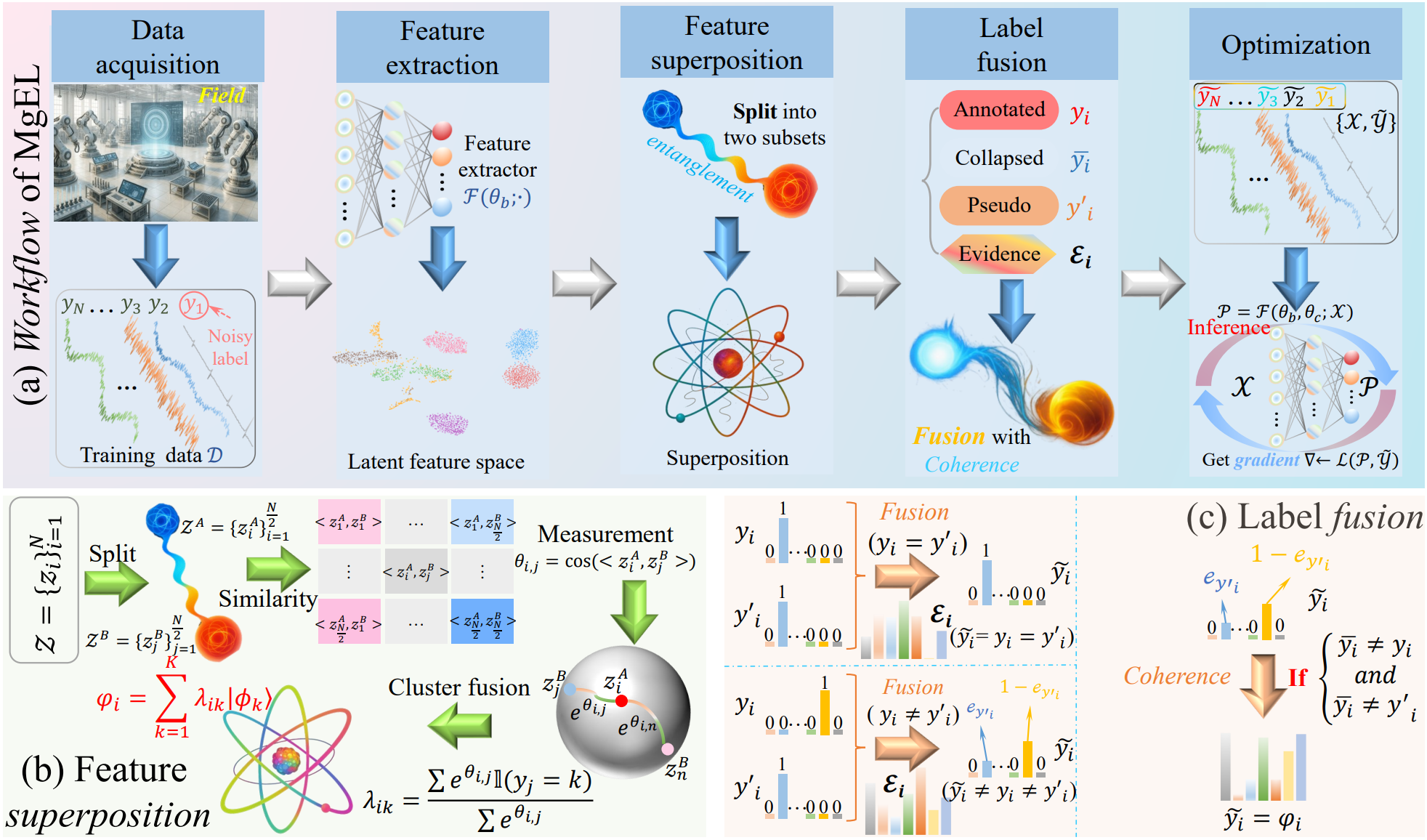
With the rise of data engineering-driven automatic annotation strategies, deep learning has demonstrated remarkable performance and strong competitiveness in intelligent fault diagnosis. However, the inherent limitations of automatic annotators inevitably introduce noisy labels, which in turn hinder the generalization and accuracy of diagnostic models. Although numerous Learning with Noisy Labels (LNL) methods attempt to alleviate the impact of label noise through sample selection or label correction, most rely heavily on model predictions to guide training. This self-reinforcing mechanism frequently leads to confirmation bias, especially under high-noise conditions, thereby limiting their e... More >
Graphical Abstract