Sustainable Energy Control and Optimization | Volume 1, Issue 2: 67-76, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/SECO.2025.538779
Abstract
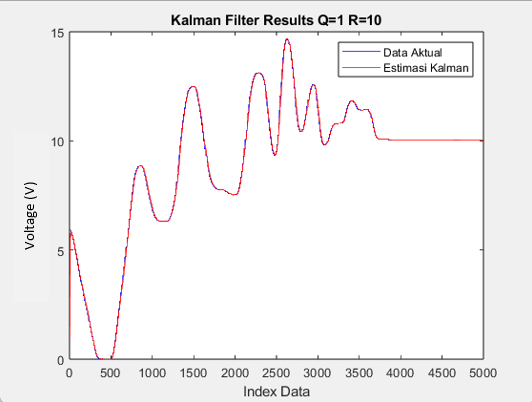
This work compared the effectiveness of the Kalman Filter and Moving Average Filter methods in minimizing noise and improving the stability of signal readings on a load-cell sensor simulation. The two filtering methods were applied to process the sensor data, to enhance both the precision and stability of the signal readings. According to the test results, the Kalman filter produced a lower average error of 0.0236, compared to 0.0244 when no filter was used, demonstrating its strong ability to reduce noise and signal fluctuations. On the other hand, the Moving Average Filter recorded a slightly higher error of 0.0238. Although it effectively smooths the signal, its performance is less reliab... More >
Graphical Abstract