Journal of Geo-Energy and Environment | Volume 1, Issue 2: 96-105, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JGEE.2025.365363
Abstract
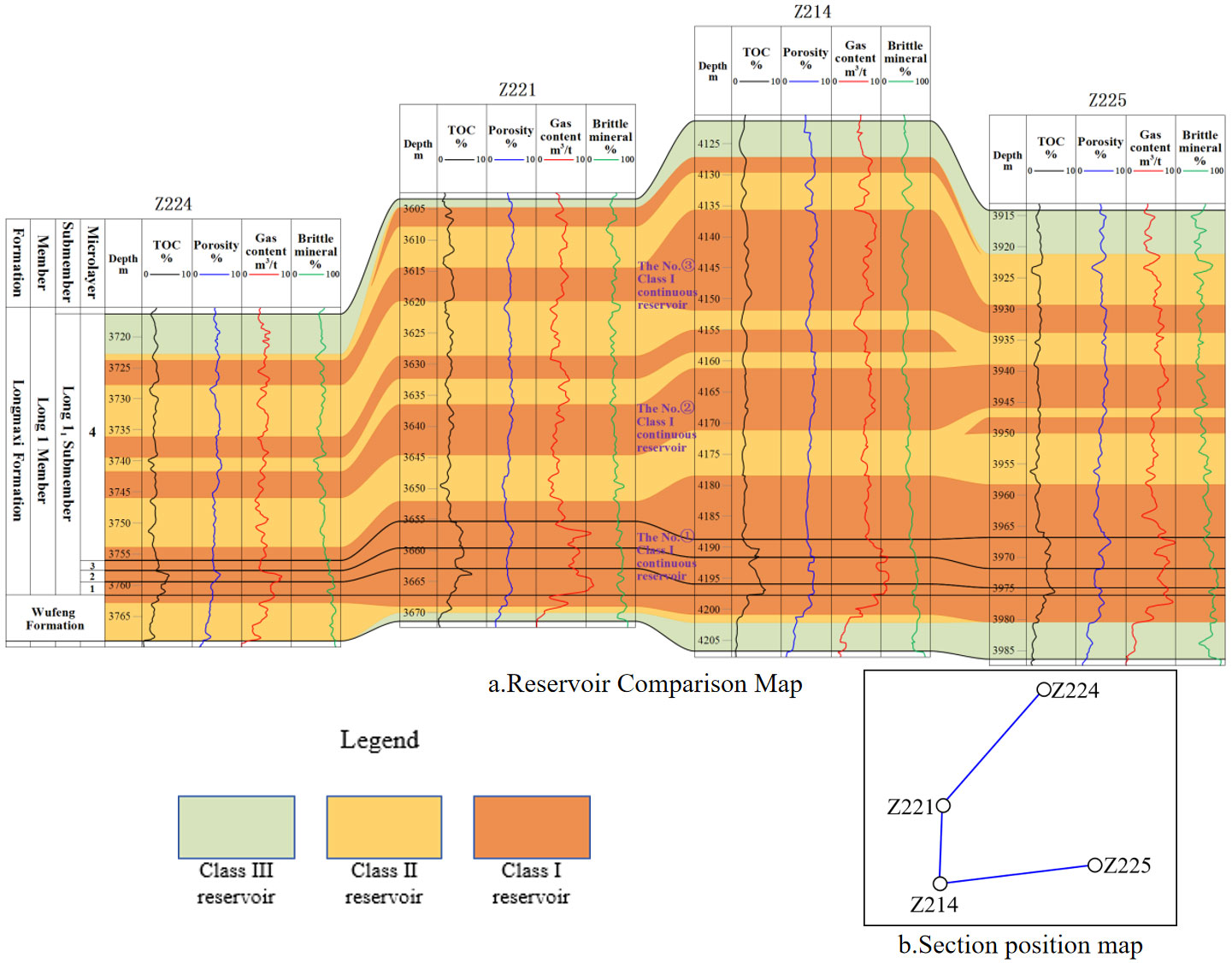
The deep shale gas ($\geq 3500$ m) in the Z205 well area is a critical exploration and development target in the Sichuan Basin. The shale gas reservoirs of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation -- Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation (Long 1$_1$ submember) in this area are characterized by deep burial and significant vertical and lateral heterogeneity. The Long 1$_1$ submember is subdivided into the Wufeng Formation, Long 1$_1^1$, Long 1$_1^2$, Long 1$_1^3$, and Long 1$_1^4$. This study conducts a detailed stratigraphic comparison based on integrated logging, core analysis, and analytical test data from the well area, clarifying the longitudinal and lateral distribution patterns of the reservoi... More >
Graphical Abstract