International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy | Volume 1, Issue 2: 83-95, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.318713
Abstract
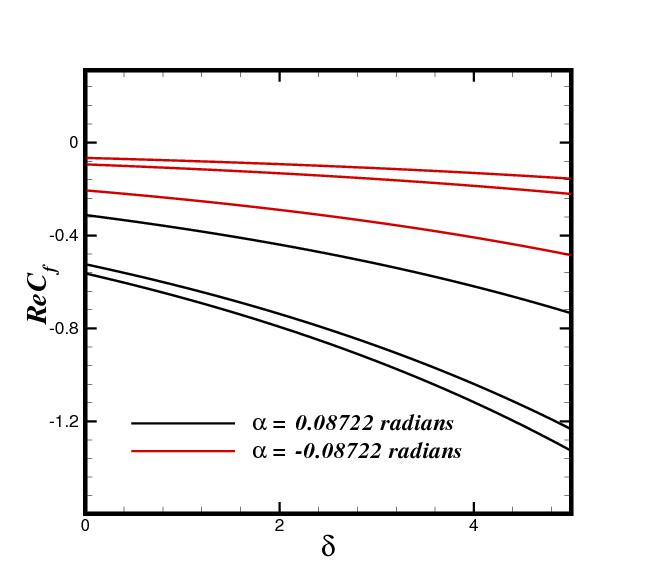
The laminar bioconvection flow of a nanofluid in a convergent/divergent channel is computationally analyzed. The channel features impervious, adiabatic walls. A physics-based model couples the mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations. A thermal-hydraulic and entropy production analysis is performed using the first and second laws of thermodynamics to identify ideal parameters that maximize thermal performance while minimizing system irreversibility. Fluid flow, heat-mass transfer, motile microorganism density, and system entropy are investigated as functions of the channel angle. The governing equations are reduced via scaling and solved numerically using the Keller-Box method. Resu... More >
Graphical Abstract