International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy
ISSN: 3069-1877 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
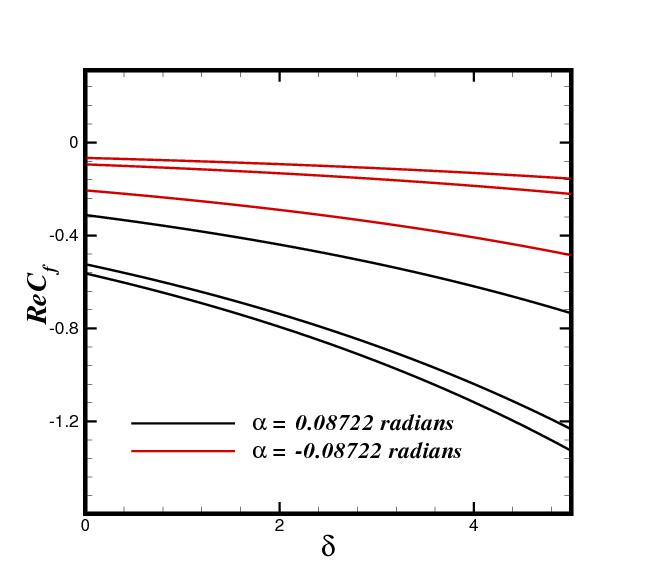
TY - JOUR AU - Eisa, Muhammad AU - Rehman, Sohail AU - Khan, Yasir AU - Maryam AU - Khan, Gulzar Ali PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/22 TI - Thermal Cooling and System Irreversibilities of A Divergent/Convergent Channel with The Bioconvection Flow of Non-Newtonian Nanofluid JO - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy T2 - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy JF - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 83 EP - 95 DO - 10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.318713 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/IJTSSE.2025.318713 KW - non-Newtonian fluid KW - converging/diverging flow KW - frictional drag KW - thermodynamic analysis KW - keller-Box approach KW - thermal cooling AB - The laminar bioconvection flow of a nanofluid in a convergent/divergent channel is computationally analyzed. The channel features impervious, adiabatic walls. A physics-based model couples the mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations. A thermal-hydraulic and entropy production analysis is performed using the first and second laws of thermodynamics to identify ideal parameters that maximize thermal performance while minimizing system irreversibility. Fluid flow, heat-mass transfer, motile microorganism density, and system entropy are investigated as functions of the channel angle. The governing equations are reduced via scaling and solved numerically using the Keller-Box method. Results indicate that higher Reynolds numbers and cross-viscosity reduce frictional drag, while motile density decreases with the Péclet number. Heat and mass transfer rates decline with increased Brownian motion, whereas thermophoresis shows opposing effects. Nanoparticle diffusion mitigates channel overheating, aiding thermal cooling. System irreversibilities dominate in narrower sections, and entropy generation near the wall increases with thermophoresis. SN - 3069-1877 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Eisa2025Thermal,
author = {Muhammad Eisa and Sohail Rehman and Yasir Khan and Maryam and Gulzar Ali Khan},
title = {Thermal Cooling and System Irreversibilities of A Divergent/Convergent Channel with The Bioconvection Flow of Non-Newtonian Nanofluid},
journal = {International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {83-95},
doi = {10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.318713},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/IJTSSE.2025.318713},
abstract = {The laminar bioconvection flow of a nanofluid in a convergent/divergent channel is computationally analyzed. The channel features impervious, adiabatic walls. A physics-based model couples the mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations. A thermal-hydraulic and entropy production analysis is performed using the first and second laws of thermodynamics to identify ideal parameters that maximize thermal performance while minimizing system irreversibility. Fluid flow, heat-mass transfer, motile microorganism density, and system entropy are investigated as functions of the channel angle. The governing equations are reduced via scaling and solved numerically using the Keller-Box method. Results indicate that higher Reynolds numbers and cross-viscosity reduce frictional drag, while motile density decreases with the Péclet number. Heat and mass transfer rates decline with increased Brownian motion, whereas thermophoresis shows opposing effects. Nanoparticle diffusion mitigates channel overheating, aiding thermal cooling. System irreversibilities dominate in narrower sections, and entropy generation near the wall increases with thermophoresis.},
keywords = {non-Newtonian fluid, converging/diverging flow, frictional drag, thermodynamic analysis, keller-Box approach, thermal cooling},
issn = {3069-1877},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy
ISSN: 3069-1877 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/