International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy | Volume 1, Issue 2: 96-107, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.805399
Abstract
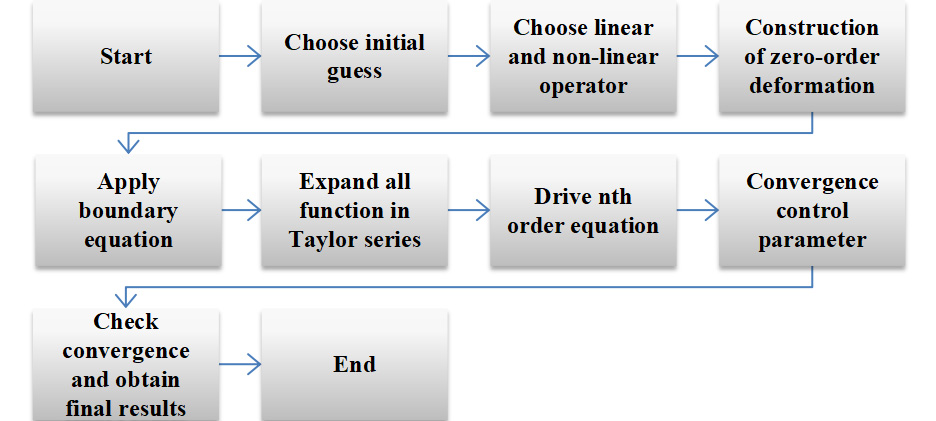
This study presents an analytical mathematical model for an integrated microbial fuel cell--oxic--anoxic bioreactor (MFC--OB--ANB) system designed for simultaneous slaughterhouse wastewater treatment and energy recovery. The model incorporates bioelectrochemical oxidation, nitrification, and denitrification processes using acetate as a representative substrate. Closed-form analytical solutions are derived for substrate degradation, nitrogen transformation, current density, and system voltage. The effects of biofilm thickness, membrane conductivity, and influent substrate concentration on treatment efficiency and power generation are systematically investigated. Results reveal that enhanced b... More >
Graphical Abstract