International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy
ISSN: 3069-1877 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
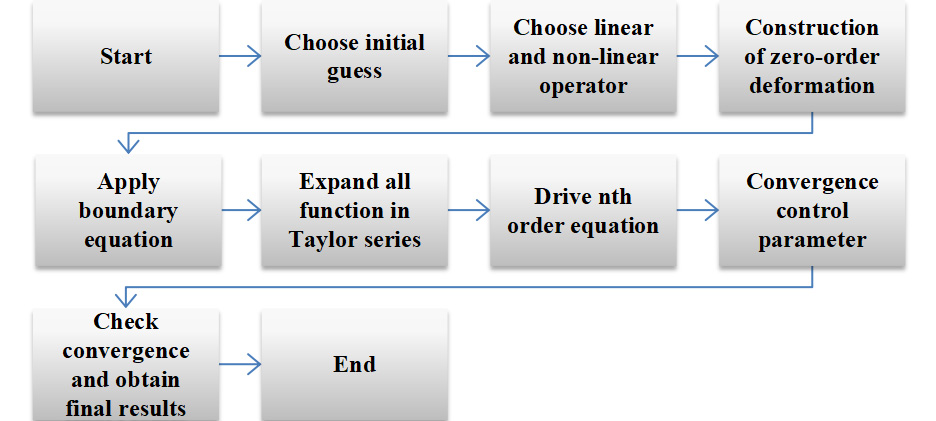
TY - JOUR AU - Riaz, Nimra AU - Sohail, Muhammad PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/22 TI - Thermal and Chemical Dynamics in Magnetohydrodynamic Williamson Fluid Flow over a Stretching Cylinder under Heat/Mass Flux Effects Using Optimal Homotopy Analysis Method JO - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy T2 - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy JF - International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 46 EP - 63 DO - 10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.383195 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/IJTSSE.2025.383195 KW - williamson fluid KW - Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) KW - hall effect KW - buongiorno model KW - cattaneo-christov flux KW - chemical reaction KW - nanofluid KW - stretched cylinder KW - optimal homotopy analysis method AB - The knowledge on understanding non-Newtonian fluid dynamics influences and behaviors in magnetic and nanoscale effects of transport is also important to the advanced processes of engineering. The current paper examines MHD flow and heat transfer of a Williamson nanofluid across a stretching cylindrical surface, taking into consideration Hall current and chemical reaction and non-Fourier heat and mass flux that is described by the Cattaneo Christov theory. The transport of Nanoparticles is explained in terms of Buongiorno model of thermophoresis and Brownian movement. Similarity variables are used to transform the governing nonlinear equations and then analytically solved via Optimal Homotopy Analysis Method. The parametric study of parameters like $M = 0.5 - 2.0$, $\gamma = 0.1 - 5.0$, $Nt = 0.1 - 0.5$, $Nb = 0.1 - 0.3$, $\delta t = \delta c = 0.1 - 0.5$, and $Kr = 0.1 - 1.0$ indicates that the values of the magnetic field, relaxation times, Hall currents, and diffusion of nanoparticles have a considerable effect on the flow, thermal, and concentration fields. The results have interesting applications in polymer extrusion, thermal control of nano-devices, magnetic drug delivery, and manufacturing smart materials. SN - 3069-1877 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Riaz2025Thermal,
author = {Nimra Riaz and Muhammad Sohail},
title = {Thermal and Chemical Dynamics in Magnetohydrodynamic Williamson Fluid Flow over a Stretching Cylinder under Heat/Mass Flux Effects Using Optimal Homotopy Analysis Method},
journal = {International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {46-63},
doi = {10.62762/IJTSSE.2025.383195},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/IJTSSE.2025.383195},
abstract = {The knowledge on understanding non-Newtonian fluid dynamics influences and behaviors in magnetic and nanoscale effects of transport is also important to the advanced processes of engineering. The current paper examines MHD flow and heat transfer of a Williamson nanofluid across a stretching cylindrical surface, taking into consideration Hall current and chemical reaction and non-Fourier heat and mass flux that is described by the Cattaneo Christov theory. The transport of Nanoparticles is explained in terms of Buongiorno model of thermophoresis and Brownian movement. Similarity variables are used to transform the governing nonlinear equations and then analytically solved via Optimal Homotopy Analysis Method. The parametric study of parameters like \$M = 0.5 - 2.0\$, \$\gamma = 0.1 - 5.0\$, \$Nt = 0.1 - 0.5\$, \$Nb = 0.1 - 0.3\$, \$\delta t = \delta c = 0.1 - 0.5\$, and \$Kr = 0.1 - 1.0\$ indicates that the values of the magnetic field, relaxation times, Hall currents, and diffusion of nanoparticles have a considerable effect on the flow, thermal, and concentration fields. The results have interesting applications in polymer extrusion, thermal control of nano-devices, magnetic drug delivery, and manufacturing smart materials.},
keywords = {williamson fluid, Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD), hall effect, buongiorno model, cattaneo-christov flux, chemical reaction, nanofluid, stretched cylinder, optimal homotopy analysis method},
issn = {3069-1877},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. International Journal of Thermo-Fluid Systems and Sustainable Energy
ISSN: 3069-1877 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/