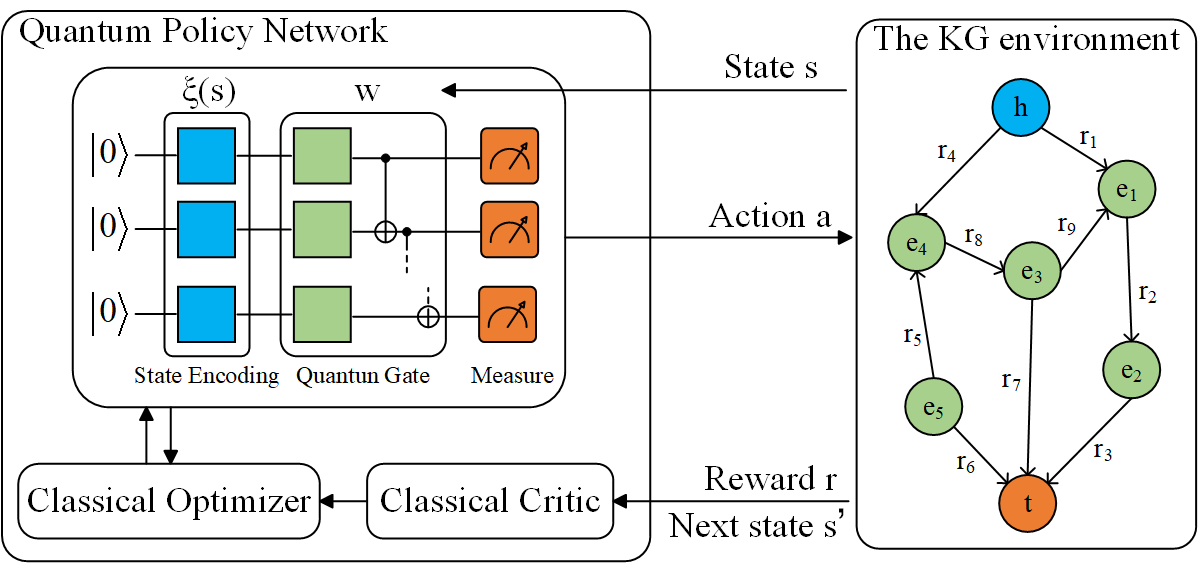
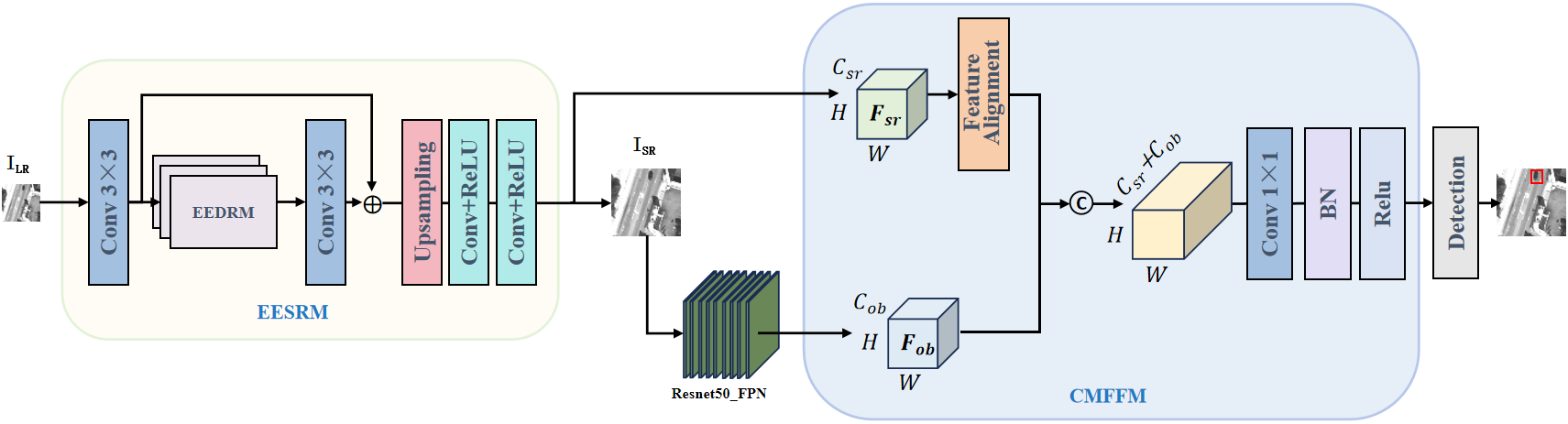
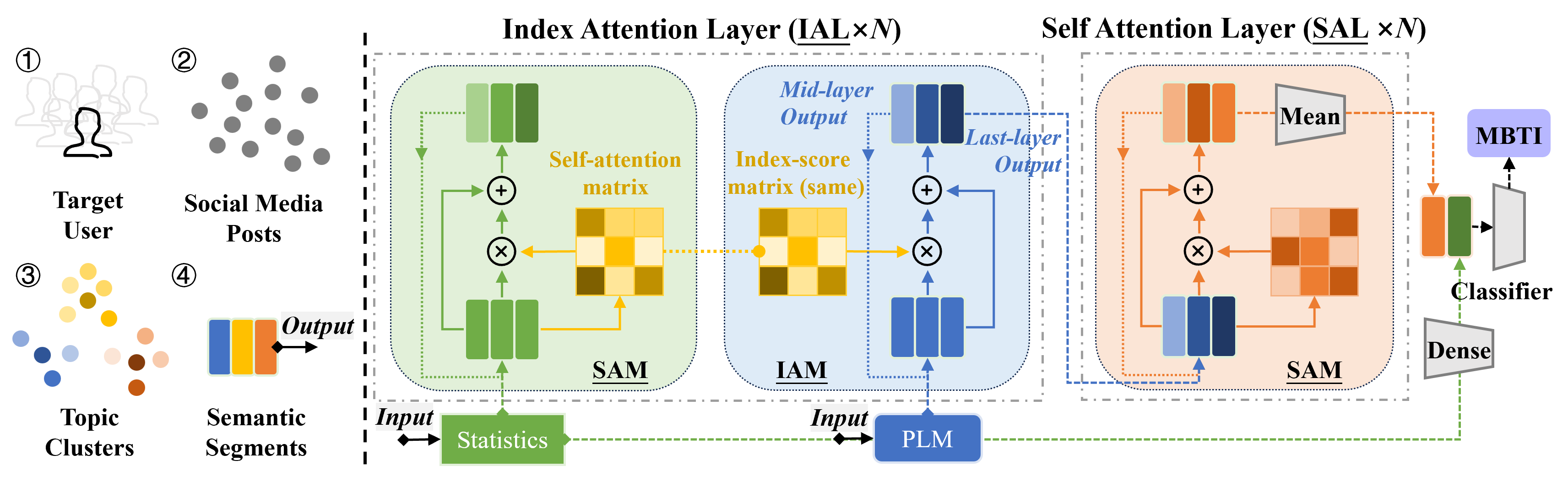
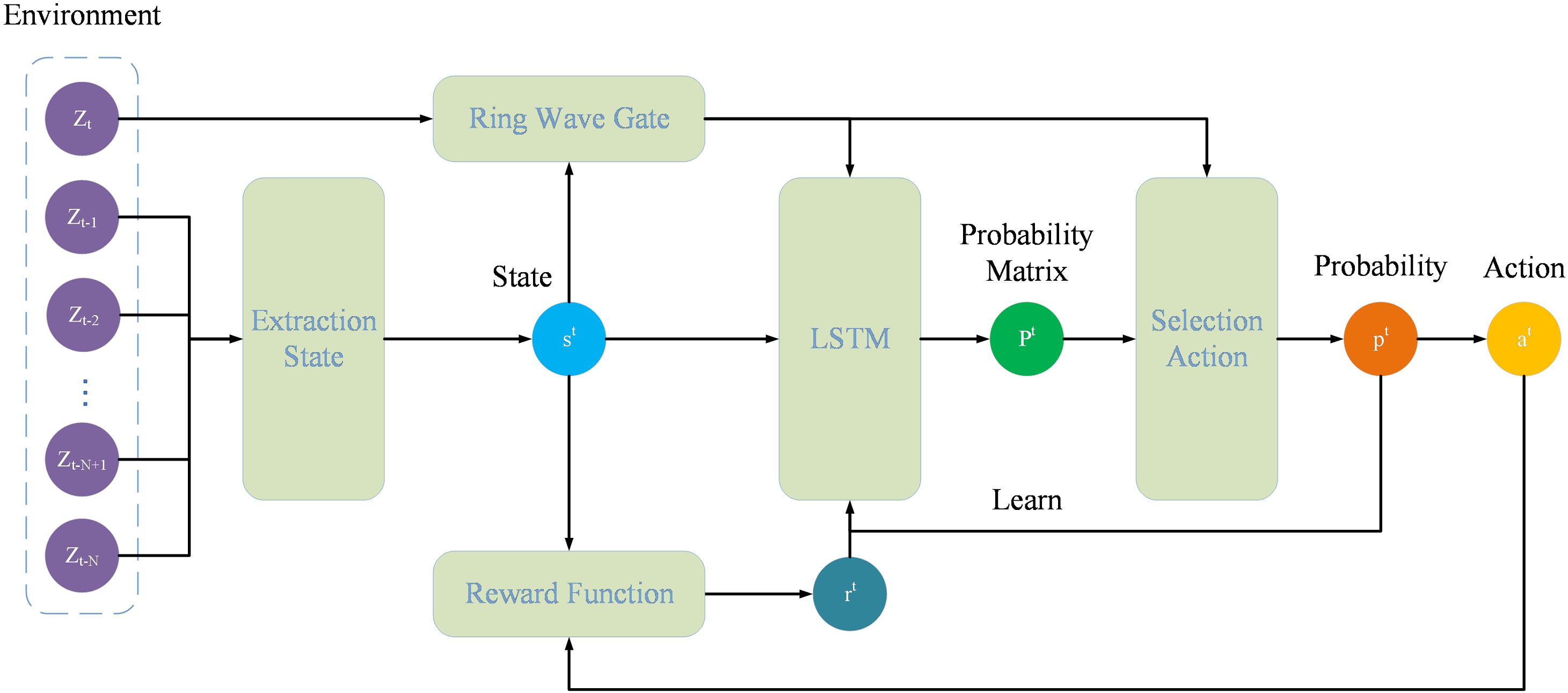
Chinese Journal of Information Fusion | Volume 2, Issue 2: 144-156, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/CJIF.2025.552445
Abstract
Knowledge reasoning is a critical task in information fusion systems, and its core step is reasoning missing information from existing facts to improve the knowledge graphs. Embedding-based reasoning methods and path-based reasoning methods are two mainstream knowledge reasoning methods. Embedding-based reasoning methods enable fast and direct reasoning but are limited to simple relationships between entities and exhibit poor performance in reasoning complex logical relationships. Path-based reasoning methods perform better in complex reasoning tasks, but suffer from high computational complexity, a large number of model parameters, and low reasoning efficiency. To address the aforementioned... More >
Graphical Abstract