ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 2, Issue 4: 248-258, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TIS.2025.756872
Abstract
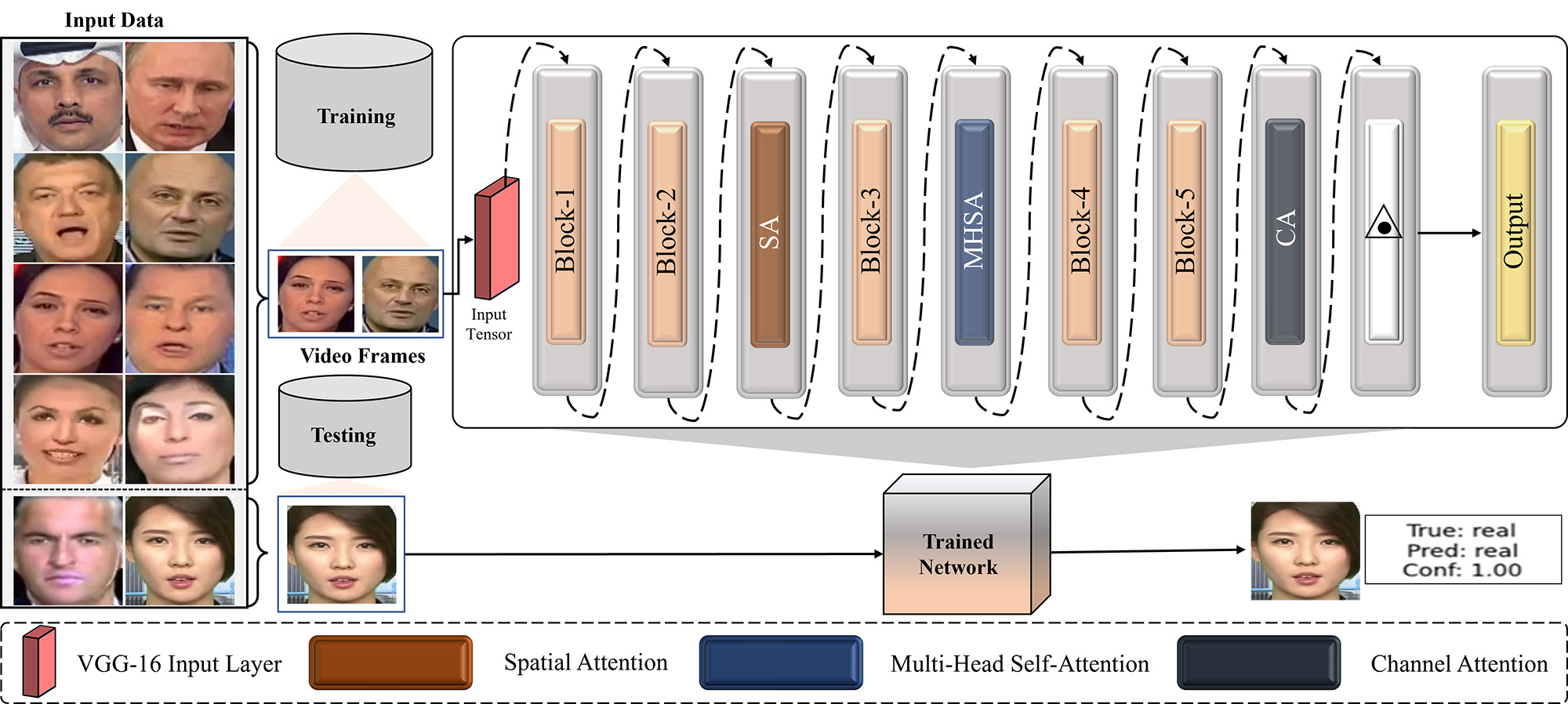
The proliferation of deepfake technology poses significant threats to digital media authenticity, necessitating robust detection systems to combat manipulated content. This paper presents a novel attention-based framework for deepfake detection that systematically integrates multiple complementary attention mechanisms to enhance discriminative feature learning. Our approach combines spatial attention, multi-head self-attention, and channel attention modules with a VGG-16 backbone to capture comprehensive representations across different feature spaces. The spatial attention mechanism focuses on discriminative facial regions, while multi-head self-attention captures long-range spatial depende... More >
Graphical Abstract