ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 3, Issue 1: 11-20, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/TIS.2025.951370
Abstract
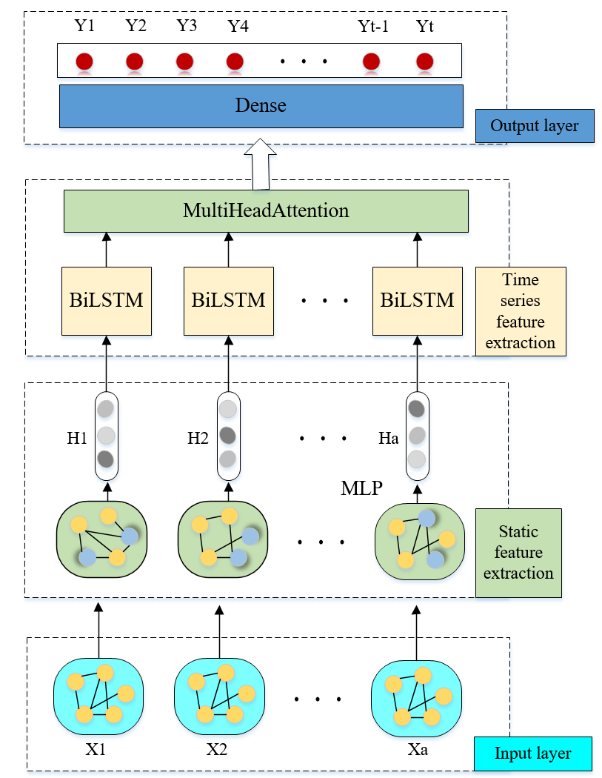
To address the challenge of traditional models in simultaneously capturing local fluctuations and global trends for air pollutant concentration prediction, this paper proposes a multimodal deep learning model named MLP-BiLSTM- MHAT. The model integrates static features via MLP, extracts temporal dependencies through bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM), and employs a Multi-head Attention mechanism (MHAT) to fuse local and global features while enhancing interactions between static and temporal characteristics. An improved Adam algorithm dynamically optimizes learning rates to balance the influence of heterogenous features. Validated on multi-site air quality data from Beijing, experimental results de... More >
Graphical Abstract