ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
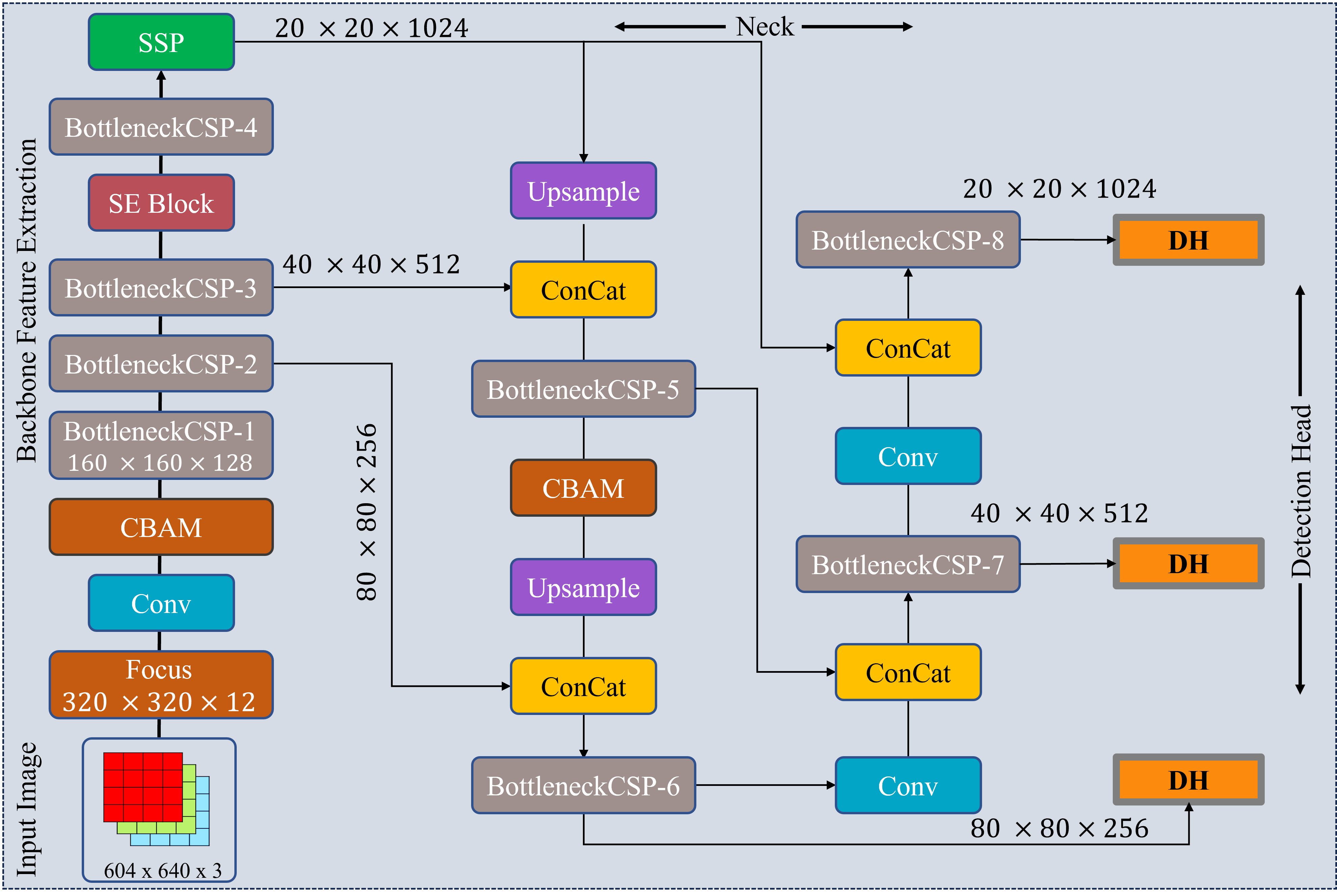
TY - JOUR AU - Ahmad, Muhammad Jamal AU - Khan, Arshad AU - Khan, Taimur Ali AU - Ahmad, Bilal PY - 2025 DA - 2025/11/26 TI - Dual Attention-Driven Optimized YOLOV5 Framework for Accurate Fall Detection in Visual Monitoring Systems JO - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics T2 - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics JF - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 1 EP - 10 DO - 10.62762/TIS.2025.559776 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.559776 KW - fall detection KW - optimized YOLOv5 KW - attention mechanism KW - healthcare monitoring KW - image analysis AB - Fall detection (FD) systems are an important part of healthcare monitoring, especially for elderly populations, where quick intervention can prevent serious injuries. This paper introduces an optimized YOLOV5-based framework that combines dual attention mechanisms for improved FD in real-time edge deployment situations. The proposed design integrates the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) blocks within the YOLOv5 backbone, along with an improved Focus module that uses slice-based feature extraction. These enhancements allow the model to effectively capture both spatial and channel-wise dependencies, which are essential for distinguishing fall events from normal human activities. Ablation studies confirm the individual contribution of each component, with more notable improvements observed on the challenging DiverseFALL10500 dataset, which features diverse environmental conditions. The framework maintains computational efficiency suitable for edge deployment while offering robust detection performance across different camera angles, lighting conditions, and complex backgrounds. A thorough evaluation on the CAUCAFall and DiverseFALL10500 benchmark datasets shows superior performance compared to existing YOLO variants. SN - 3068-5079 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Ahmad2025Dual,
author = {Muhammad Jamal Ahmad and Arshad Khan and Taimur Ali Khan and Bilal Ahmad},
title = {Dual Attention-Driven Optimized YOLOV5 Framework for Accurate Fall Detection in Visual Monitoring Systems},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics},
year = {2025},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {1-10},
doi = {10.62762/TIS.2025.559776},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.559776},
abstract = {Fall detection (FD) systems are an important part of healthcare monitoring, especially for elderly populations, where quick intervention can prevent serious injuries. This paper introduces an optimized YOLOV5-based framework that combines dual attention mechanisms for improved FD in real-time edge deployment situations. The proposed design integrates the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) and Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) blocks within the YOLOv5 backbone, along with an improved Focus module that uses slice-based feature extraction. These enhancements allow the model to effectively capture both spatial and channel-wise dependencies, which are essential for distinguishing fall events from normal human activities. Ablation studies confirm the individual contribution of each component, with more notable improvements observed on the challenging DiverseFALL10500 dataset, which features diverse environmental conditions. The framework maintains computational efficiency suitable for edge deployment while offering robust detection performance across different camera angles, lighting conditions, and complex backgrounds. A thorough evaluation on the CAUCAFall and DiverseFALL10500 benchmark datasets shows superior performance compared to existing YOLO variants.},
keywords = {fall detection, optimized YOLOv5, attention mechanism, healthcare monitoring, image analysis},
issn = {3068-5079},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/