ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 2, Issue 1: 25-41, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2025.570823
Abstract
Accurate state estimation for dynamic targets is essential in fields such as target tracking, navigation, and autonomous driving. However, traditional estimation models struggle to handle the nonlinear motion patterns and sensor noise prevalent in real-world environments. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel end-to-end estimation model named Variational Neural Network with Planar Flow (VNNPF). The model integrates a Bayesian Gated Recurrent Unit (BGRU) as the process model, a planar flow-based variational autoencoder (PFVAE) as the measurement model, and a Bayesian hyperparameter optimization module inspired by Kalman filtering. The BGRU captures nonlinear temporal depend... More >
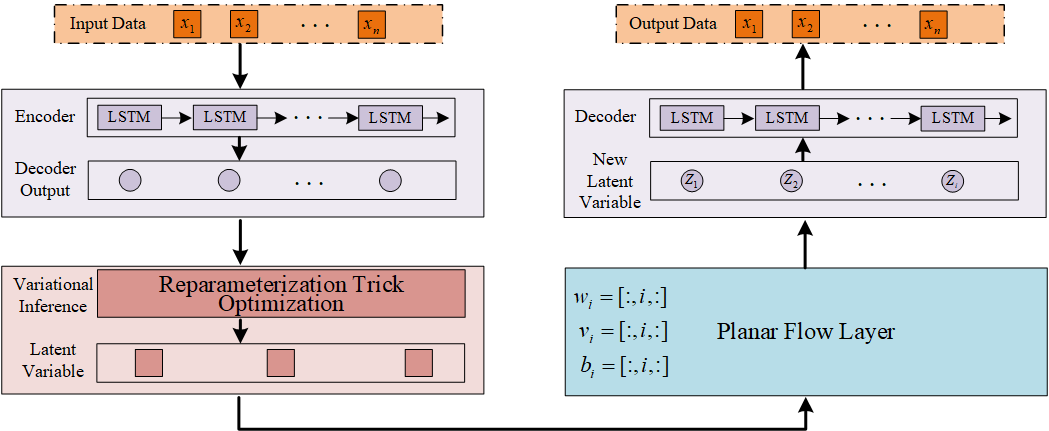
Graphical Abstract