Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
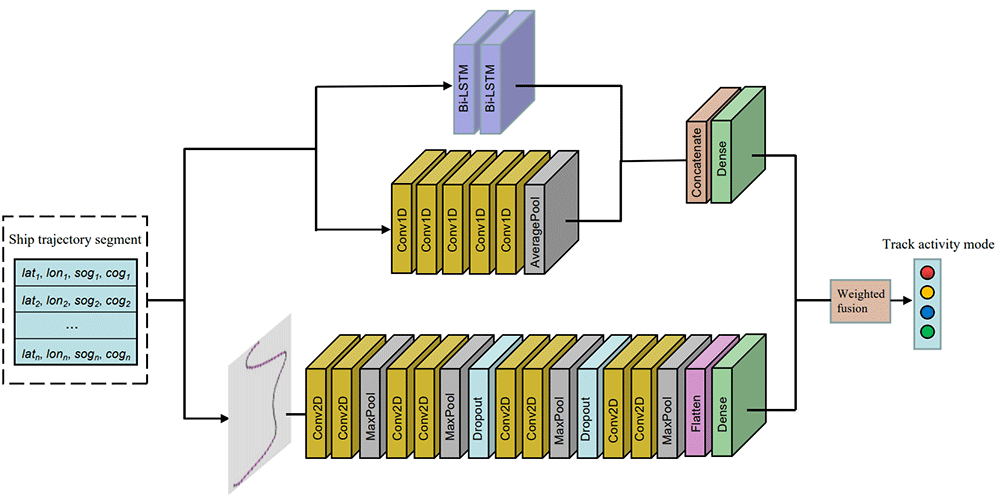
TY - JOUR AU - Liu, Jun AU - Chen, Zhen AU - Zhou, Jihao AU - Xue, Anke AU - Peng, Dongliang AU - Gu, Yu AU - Chen, Huajie PY - 2024 DA - 2024/05/25 TI - Research on A Ship Trajectory Classification Method Based on Deep Learning JO - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion T2 - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion JF - Chinese Journal of Information Fusion VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 3 EP - 15 DO - 10.62762/CJIF.2024.361873 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/CJIF.2024.361873 KW - deep learning KW - trajectory classification KW - AIS data KW - data fusion KW - ship monitoring AB - The unrestricted development and utilization of marine resources have resulted in a series of practical problems, such as the destruction of marine ecology. The wide application of radar, satellites and other detection equipment has gradually led to a large variety of large-capacity marine spatiotemporal trajectory data from a vast number of sources. In the field of marine domain awareness, there is an urgent need to use relevant information technology means to control and monitor ships and accurately classify and identify ship behavior patterns through multisource data fusion analysis. In addition, the increase in the type and quantity of trajectory data has produced a corresponding increase in the complexity and difficulty of data processing that cannot be adequately addressed by traditional data mining algorithms. Therefore, this paper provides a deep learning-based algorithm for the recognition of four main motion types of the ship from automatic identification system (AIS) data: anchoring, mooring, sailing and fishing. A new method for classifying patterns is presented that combines the computer vision and time series domains. Experiments are carried out on a dataset constructed from the open AIS data of ships in the coastal waters of the United States, which show that the method proposed in this paper achieves more than 95% recognition accuracy. The experimental results confirm that the method proposed in this paper is effective in classifying ship trajectories using AIS data and that it can provide efficient technical support for marine supervision departments. SN - 2998-3371 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Liu2024Research,
author = {Jun Liu and Zhen Chen and Jihao Zhou and Anke Xue and Dongliang Peng and Yu Gu and Huajie Chen},
title = {Research on A Ship Trajectory Classification Method Based on Deep Learning},
journal = {Chinese Journal of Information Fusion},
year = {2024},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {3-15},
doi = {10.62762/CJIF.2024.361873},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/CJIF.2024.361873},
abstract = {The unrestricted development and utilization of marine resources have resulted in a series of practical problems, such as the destruction of marine ecology. The wide application of radar, satellites and other detection equipment has gradually led to a large variety of large-capacity marine spatiotemporal trajectory data from a vast number of sources. In the field of marine domain awareness, there is an urgent need to use relevant information technology means to control and monitor ships and accurately classify and identify ship behavior patterns through multisource data fusion analysis. In addition, the increase in the type and quantity of trajectory data has produced a corresponding increase in the complexity and difficulty of data processing that cannot be adequately addressed by traditional data mining algorithms. Therefore, this paper provides a deep learning-based algorithm for the recognition of four main motion types of the ship from automatic identification system (AIS) data: anchoring, mooring, sailing and fishing. A new method for classifying patterns is presented that combines the computer vision and time series domains. Experiments are carried out on a dataset constructed from the open AIS data of ships in the coastal waters of the United States, which show that the method proposed in this paper achieves more than 95\% recognition accuracy. The experimental results confirm that the method proposed in this paper is effective in classifying ship trajectories using AIS data and that it can provide efficient technical support for marine supervision departments.},
keywords = {deep learning, trajectory classification, AIS data, data fusion, ship monitoring},
issn = {2998-3371},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2024 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. Chinese Journal of Information Fusion
ISSN: 2998-3371 (Online) | ISSN: 2998-3363 (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/