Abstract
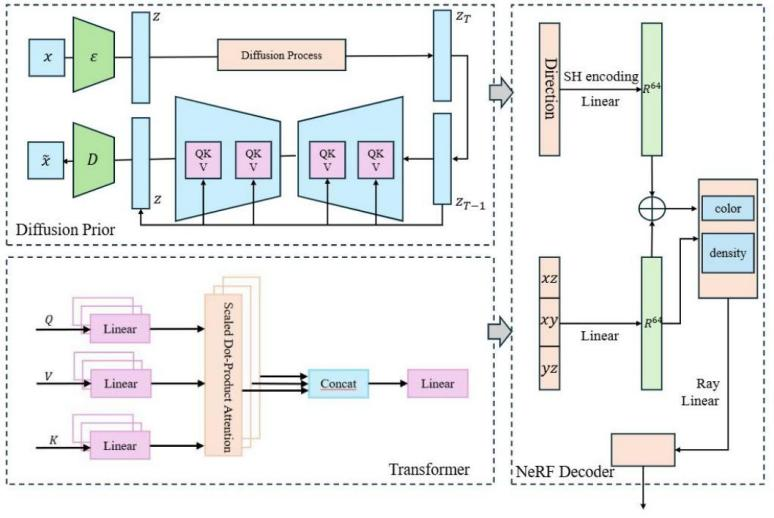
This paper proposes a Diffusion Model-Optimized Neural Radiance Field (DT-NeRF) method, aimed at enhancing detail recovery and multi-view consistency in 3D scene reconstruction. By combining diffusion models with Transformers, DT-NeRF effectively restores details under sparse viewpoints and maintains high accuracy in complex geometric scenes. Experimental results demonstrate that DT-NeRF significantly outperforms traditional NeRF and other state-of-the-art methods on the Matterport3D and ShapeNet datasets, particularly in metrics such as PSNR, SSIM, Chamfer Distance, and Fidelity. Ablation experiments further confirm the critical role of the diffusion and Transformer modules in the model's performance, with the removal of either module leading to a decline in performance. The design of DT-NeRF showcases the synergistic effect between modules, providing an efficient and accurate solution for 3D scene reconstruction. Future research may focus on further optimizing the model, exploring more advanced generative models and network architectures to enhance its performance in large-scale dynamic scenes.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Liu, B., Li, R., Zhou, L., & Zhou, Y. (2025). DT-NeRF: A Diffusion and Transformer-Based Optimization Approach for Neural Radiance Fields in 3D Reconstruction. ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 2(3), 190–202. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2025.874668
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue