ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
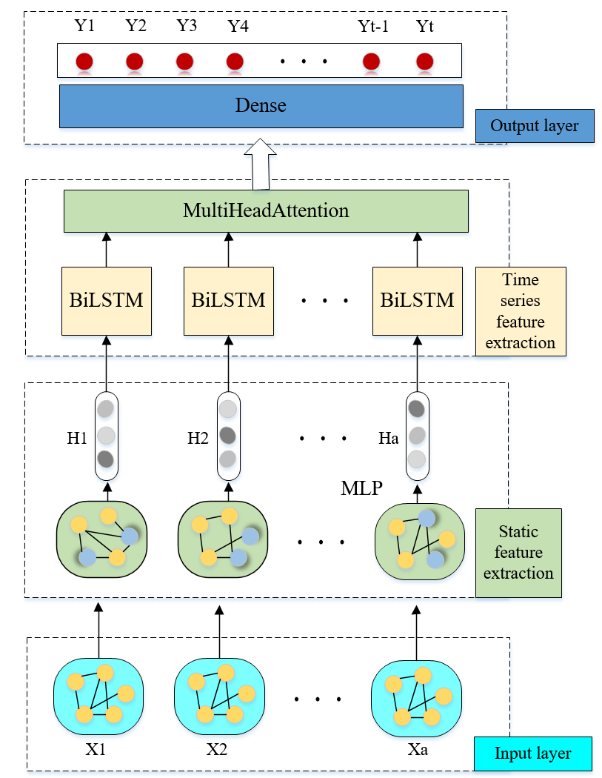
TY - JOUR AU - Gu, Chenbin AU - Tan, Yimi AU - Yin, Xiaoqi AU - Li, Xuejun AU - Yang, Yudong AU - Lv, Yan PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/29 TI - Enhanced Air Pollution Prediction via Adam-Optimized Multi-Head Attention and Hybrid Deep Learning JO - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics T2 - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics JF - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 11 EP - 20 DO - 10.62762/TIS.2025.951370 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.951370 KW - multimodal KW - deep learning network KW - improved Adam algorithm KW - air pollutant concentration prediction AB - To address the challenge of traditional models in simultaneously capturing local fluctuations and global trends for air pollutant concentration prediction, this paper proposes a multimodal deep learning model named MLP-BiLSTM- MHAT. The model integrates static features via MLP, extracts temporal dependencies through bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM), and employs a Multi-head Attention mechanism (MHAT) to fuse local and global features while enhancing interactions between static and temporal characteristics. An improved Adam algorithm dynamically optimizes learning rates to balance the influence of heterogenous features. Validated on multi-site air quality data from Beijing, experimental results demonstrate that MLP-BiLSTM-MHAT outperforms baseline models with an average reduction of 1.9% in RMSE, 4.2% in MAE, and a 1.8% improvement in R², showcasing superior accuracy and robustness across diverse pollutants and scenarios. SN - 3068-5079 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Gu2026Enhanced,
author = {Chenbin Gu and Yimi Tan and Xiaoqi Yin and Xuejun Li and Yudong Yang and Yan Lv},
title = {Enhanced Air Pollution Prediction via Adam-Optimized Multi-Head Attention and Hybrid Deep Learning},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {11-20},
doi = {10.62762/TIS.2025.951370},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.951370},
abstract = {To address the challenge of traditional models in simultaneously capturing local fluctuations and global trends for air pollutant concentration prediction, this paper proposes a multimodal deep learning model named MLP-BiLSTM- MHAT. The model integrates static features via MLP, extracts temporal dependencies through bidirectional LSTM (BiLSTM), and employs a Multi-head Attention mechanism (MHAT) to fuse local and global features while enhancing interactions between static and temporal characteristics. An improved Adam algorithm dynamically optimizes learning rates to balance the influence of heterogenous features. Validated on multi-site air quality data from Beijing, experimental results demonstrate that MLP-BiLSTM-MHAT outperforms baseline models with an average reduction of 1.9\% in RMSE, 4.2\% in MAE, and a 1.8\% improvement in R², showcasing superior accuracy and robustness across diverse pollutants and scenarios.},
keywords = {multimodal, deep learning network, improved Adam algorithm, air pollutant concentration prediction},
issn = {3068-5079},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/