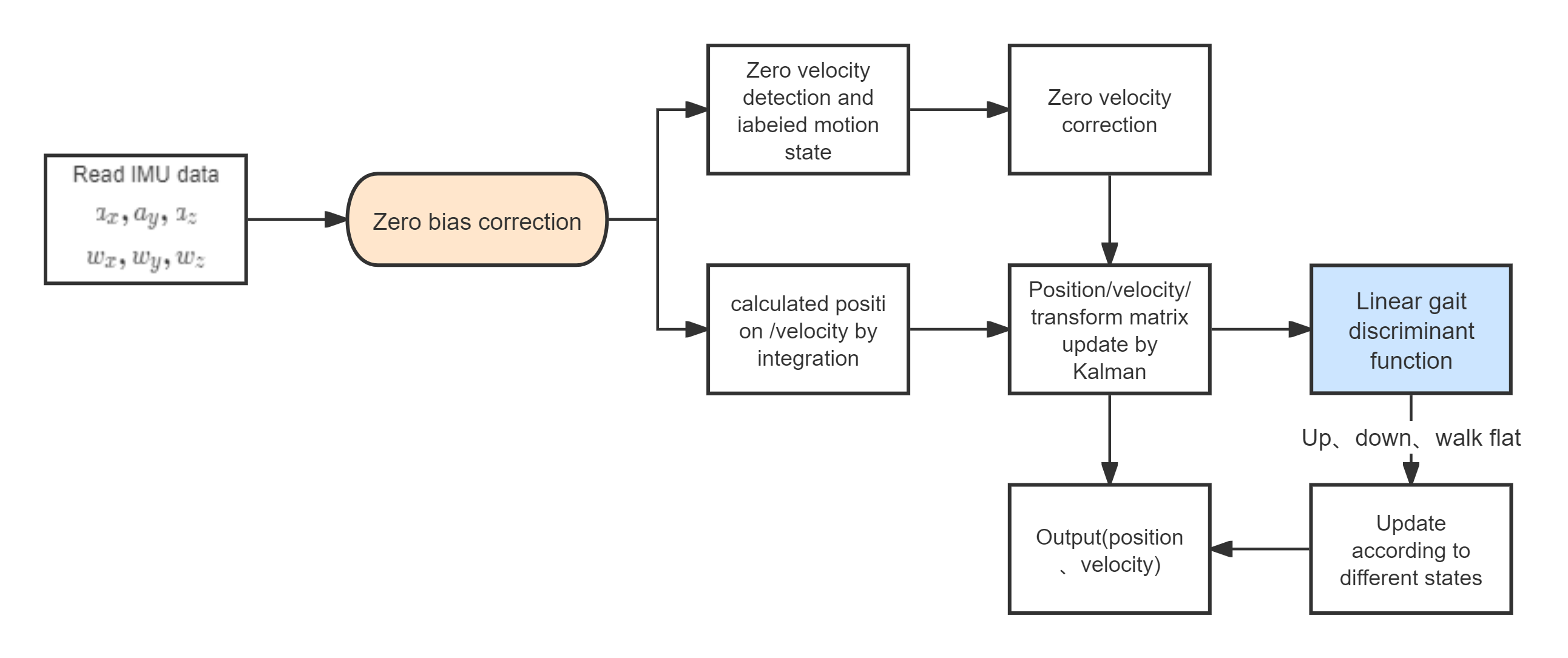
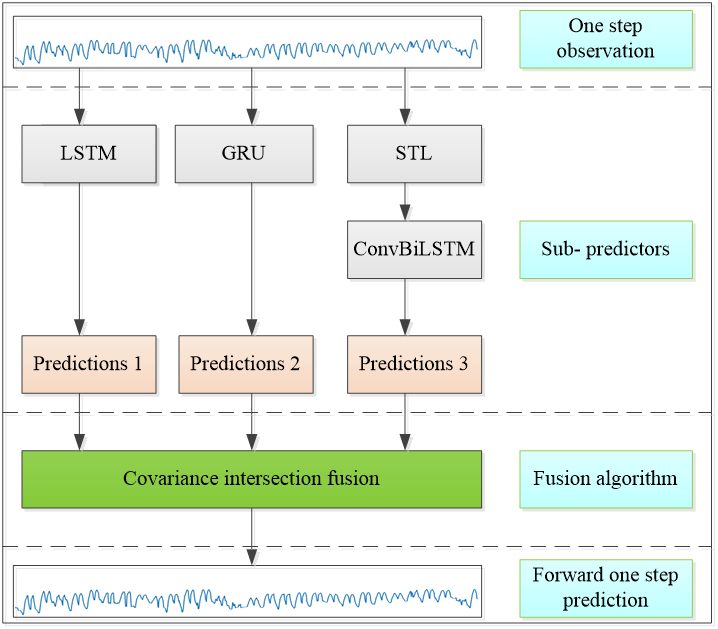
ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics | Volume 1, Issue 2: 102-111, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/TIS.2024.307219
Abstract
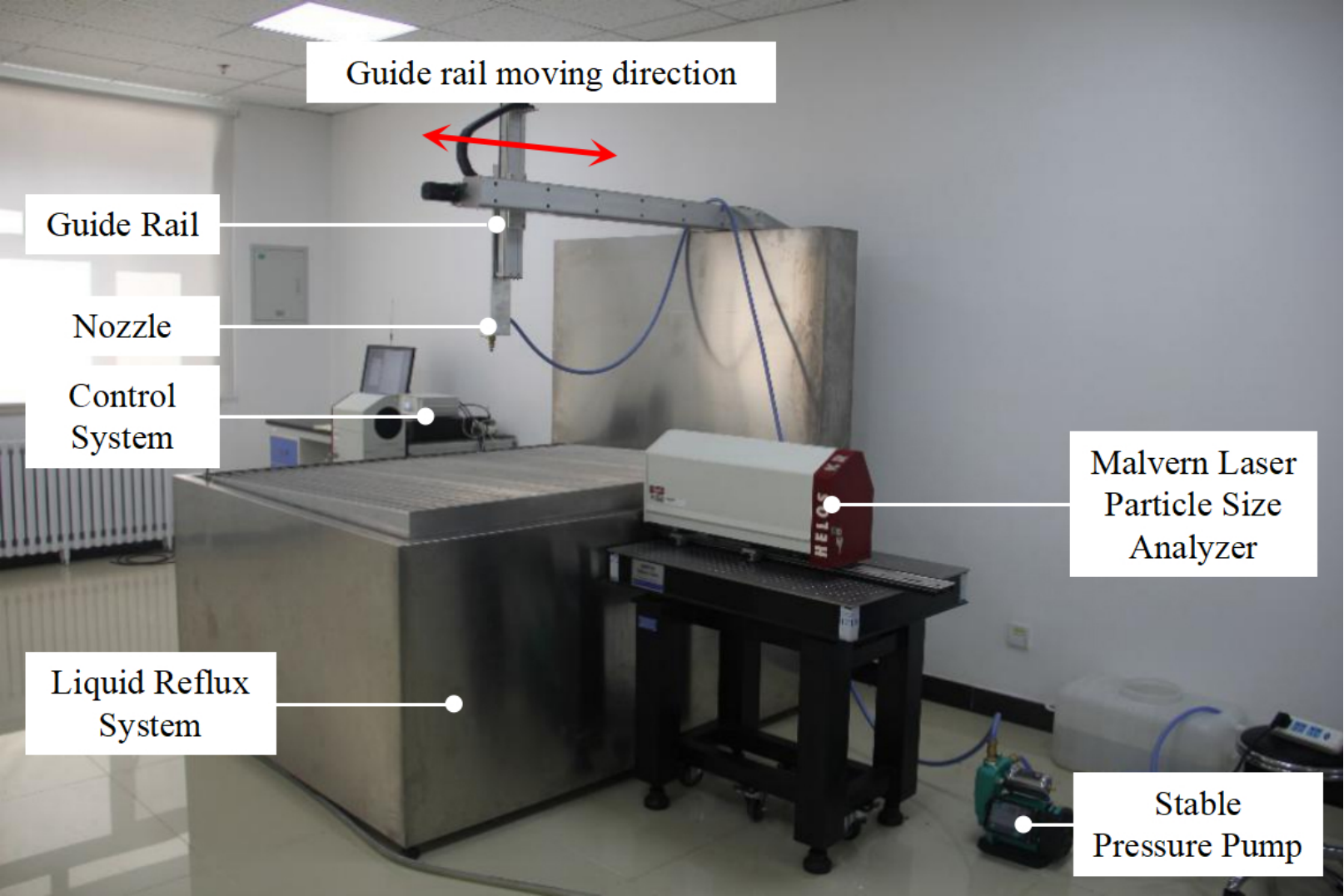
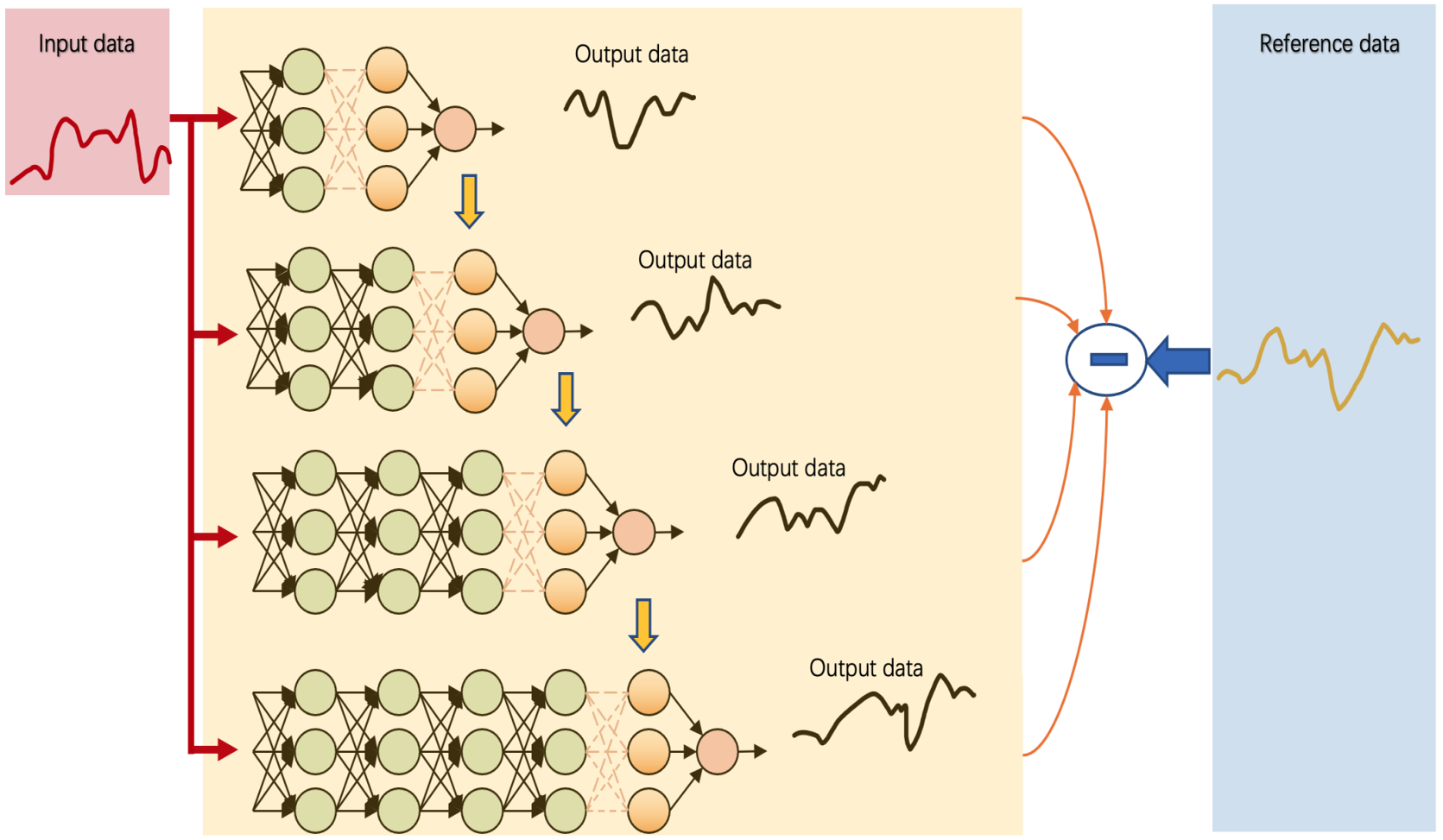
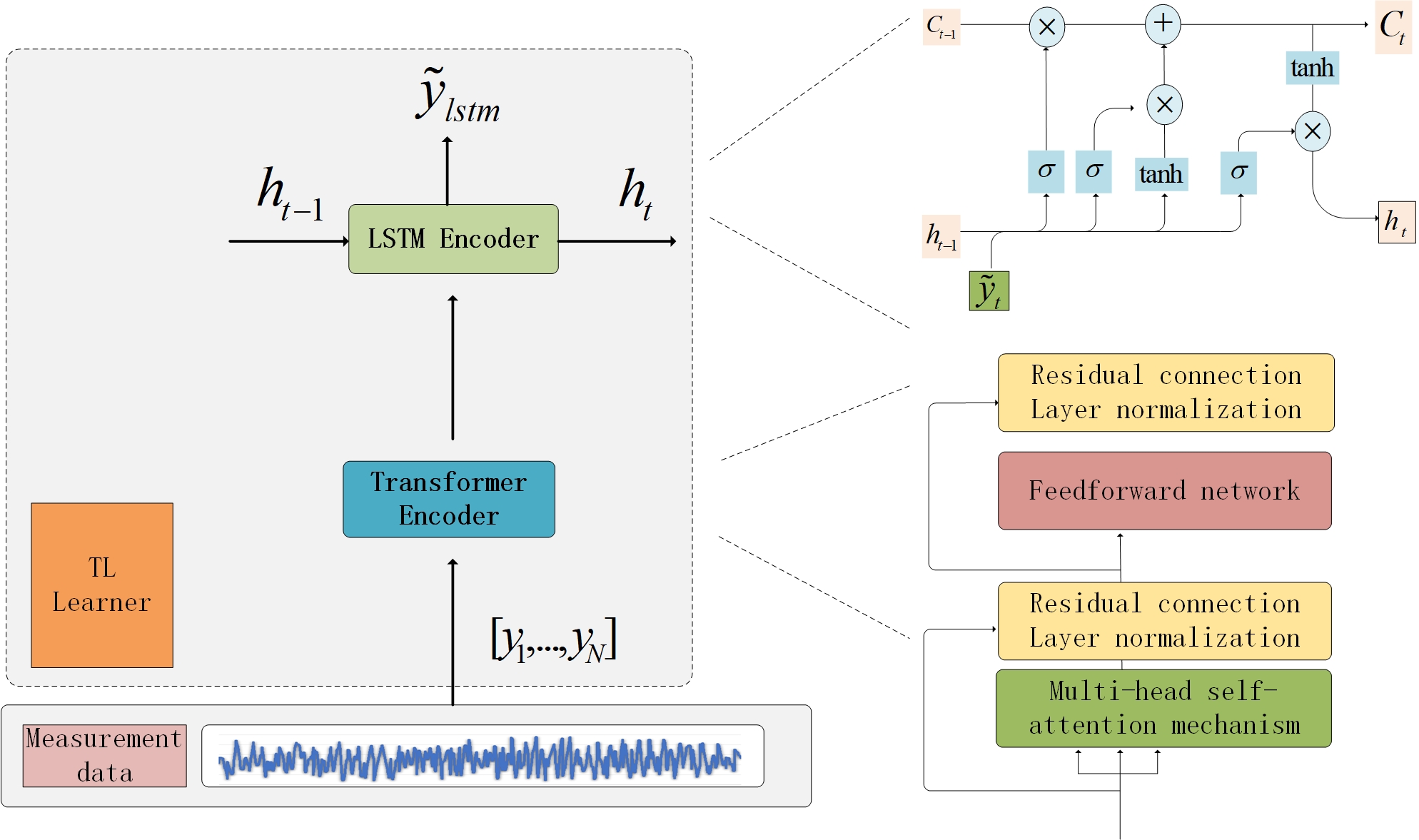
Precision plant protection involves a complex spray–droplet system in which atomization behavior is governed by the coupled effects of operating parameters and nozzle characteristics. However, a systematic understanding of how these parameters jointly influence droplet size and deposition performance remains limited in ground plant protection applications. In this study, a laser-based particle size measurement approach is employed to characterize the systematic dependence of atomized droplet size on spray pressure, nozzle flow rate (orifice), and spray angle under controlled conditions. The results reveal consistent parameter–response patterns: droplet size decreases with increasing spra... More >
Graphical Abstract