Abstract
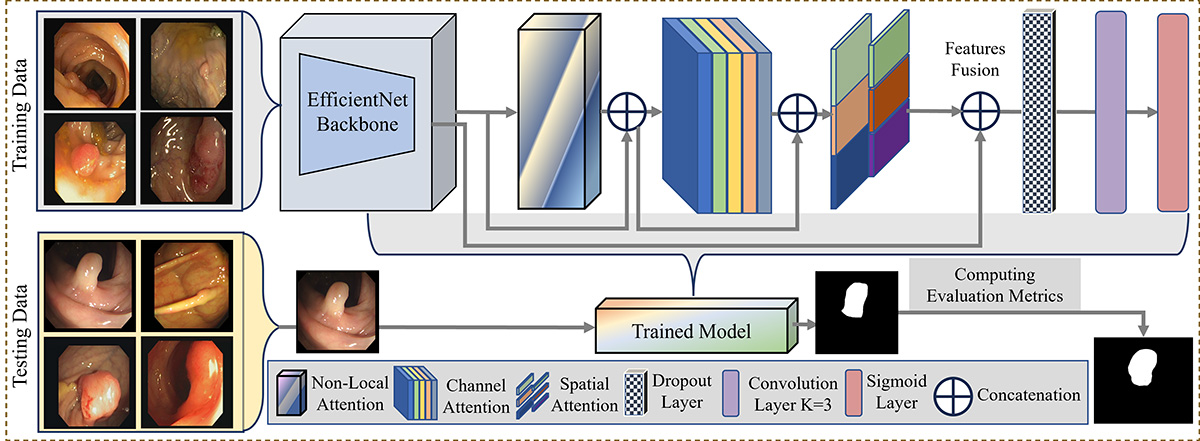
Accurate segmentation of colorectal cancer (CRC) from endoscopic images is crucial for computer-aided diagnosis. Visual intelligence enhances detection precision, supporting clinical decision-making. However, current segmentation methods often struggle with accurately delineating fine-grained lesion boundaries due to limited context comprehension and inadequate attention to optimal features. Additionally, the poor fusion of multi-scale semantic cues hinders performance, especially in complex endoscopic scenarios. To address these issues, we introduce ColoSegNet, a Visual Intelligence-Driven Triple Attention Feature Fusion Network designed for high-precision CRC segmentation. Our approach begins with an analysis of backbone networks to identify optimal intermediate-level feature extraction. The architecture includes a non-local attention module to capture long-range dependencies, enhanced by channel and spatial attention mechanisms for better feature selectivity across semantic hierarchies. Multi-scale fusion strategies are used to preserve both low-level details and high-level context, enabling accurate localization under challenging conditions. Extensive evaluations across four publicly available endoscopic datasets, along with cross-dataset assessments, demonstrate the effectiveness and generalizability of ColoSegNet, outperforming state-of-the-art segmentation methods.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
This study utilized only publicly available datasets (ClinicDB, ColonDB, Endoscene, ETIS) with pre-existing ethical approvals. No additional human or animal participation was involved, hence no further ethical approval was required.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Salman, T., Gazis, A., Ali, A. Khan, M. H., Ali, M., Khan, H., & Shah, H. A. (2025). ColoSegNet: Visual Intelligence Driven Triple Attention Feature Fusion Network for Endoscopic Colorectal Cancer Segmentation. ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 2(2), 125–136. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2025.385365
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue