Abstract
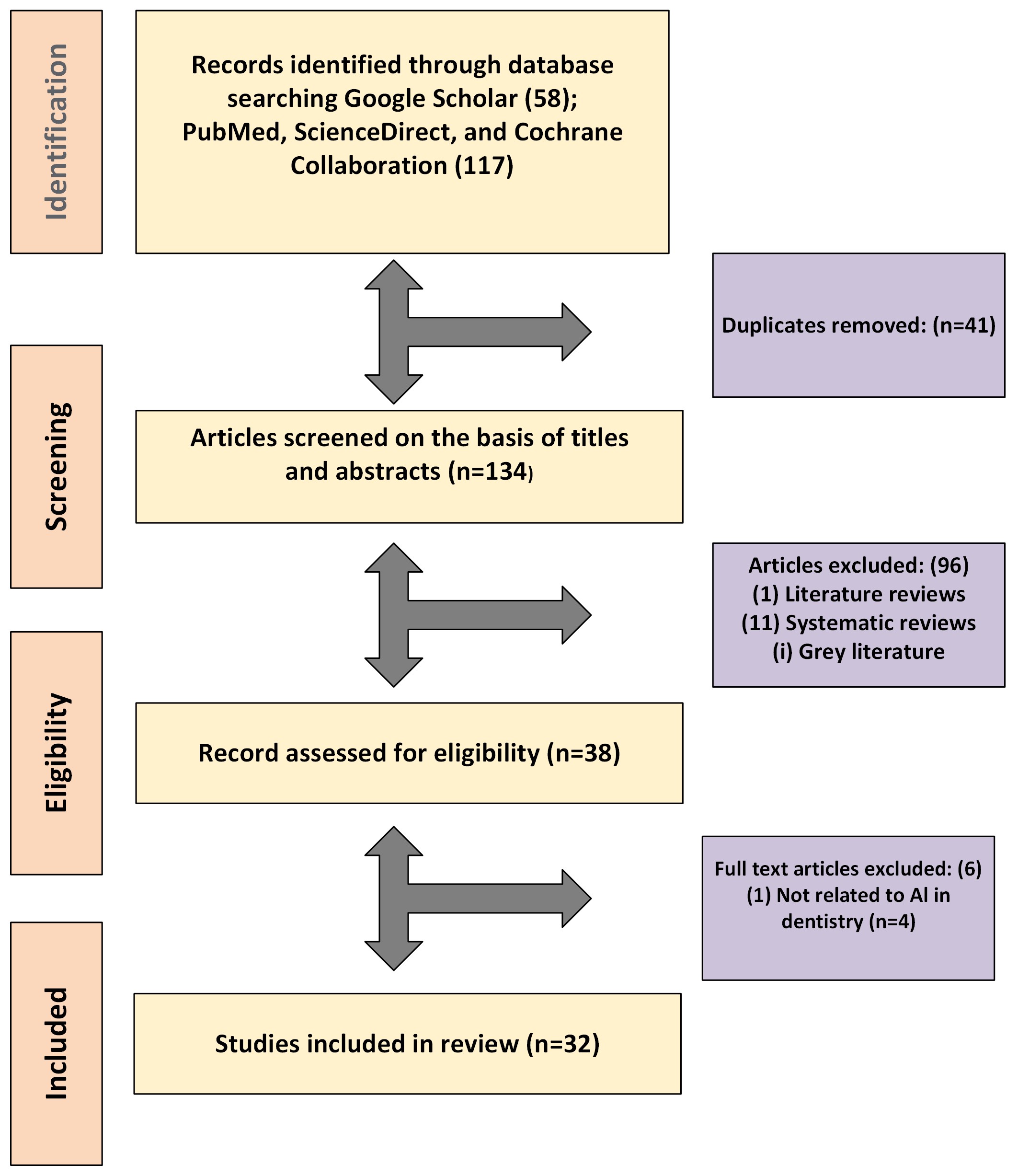
This systematic review and meta-analysis assesses the transformative effect of artificial intelligence (AI) on forensic odontology, concentrating on gains in identification accuracy and workflow efficiency. Traditionally, human identification in this specialty depends on meticulous comparison of dental charts and radiographs. The integration of AI-driven technologies—including machine-learning algorithms and image-recognition networks—has begun to expedite core tasks such as bite-mark interpretation, dental-age estimation and record reconciliation, while also limiting examiner bias and clerical error. Following PRISMA guidelines to ensure methodological rigour, we searched PubMed, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar and Cochrane, retrieving 175 papers; 32 fulfilled pre-established inclusion and exclusion criteria. Analytical performance was appraised with the K Vaal and Cameriere frameworks, chosen for their relevance to age and identity determination. Across studies, AI systems consistently processed large datasets at high speed and delivered accuracy that exceeded conventional approaches. Quantitative synthesis further demonstrated superior precision in automated dental charting and radiograph-based age assessment across diverse age brackets and tooth classes. As a group, pooled sensitivity and specificity averaged 0.93 and 0.95, respectively, underscoring robust diagnostic performance across both pediatric and adult cohorts. These findings highlight AI’s versatility and validate its role as a dependable decision-support tool for forensic odontologists, enhancing the reliability and timeliness of evidence presented in legal contexts.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Khan, M. S., Afridi, U., Ahmed, M. J., Zeb, B., Ullah, I., & Hassan, M. Z. (2024). Comprehensive Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence Applications in Forensic Odontology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics, 1(3), 176-189. https://doi.org/10.62762/TIS.2024.818917
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge (ICCK) or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue