ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
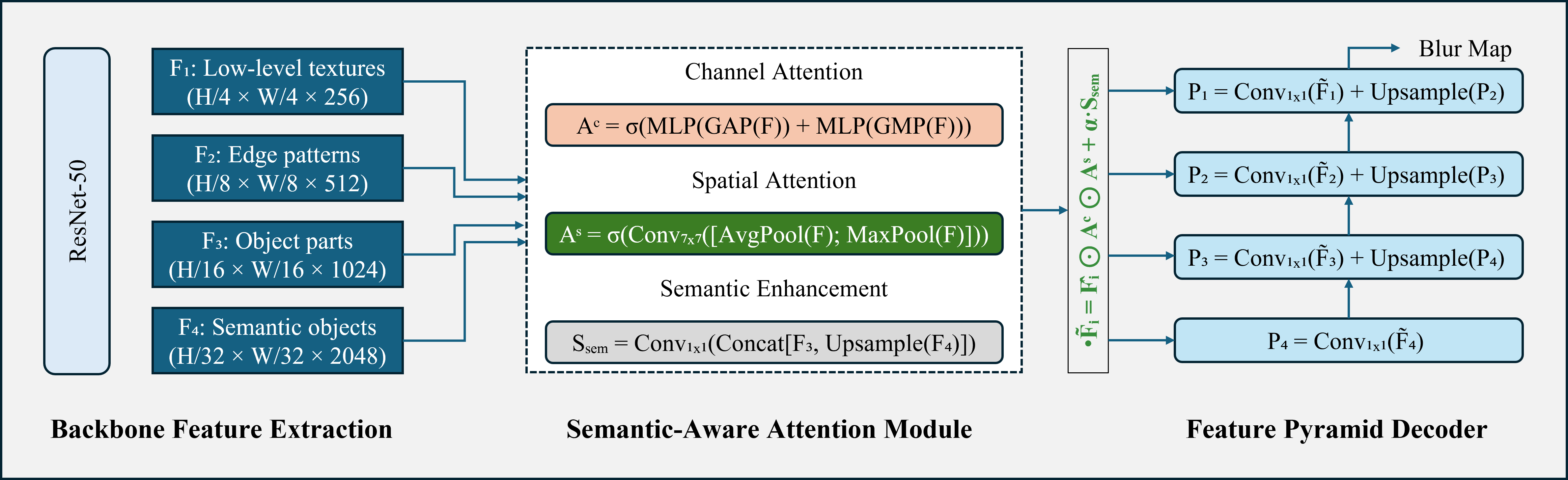
TY - JOUR AU - Haider, Asad Ullah AU - Gazis, Alexandros AU - Zahoor, Faryal PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/19 TI - SemanticBlur: Semantic-Aware Attention Network with Multi-Scale Feature Refinement for Defocus Blur Detection JO - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics T2 - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics JF - ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics VL - 3 IS - 1 SP - 21 EP - 31 DO - 10.62762/TIS.2025.879161 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.879161 KW - blur detection KW - semantic segmentation KW - attention mechanisms KW - deep neural networks KW - image analysis KW - multi-scale processing AB - Defocus blur detection is essential for computational photography applications, but existing methods struggle with accurate blur localization and boundary preservation. We propose SemanticBlur, a deep learning framework which integrates semantic understanding with attention mechanisms for robust defocus blur detection. Our semantic-aware attention module combines channel attention, spatial attention, and semantic enhancement to leverage high-level features for low-level feature refinement. The architecture employs a modified ResNet-50 backbone with dilated convolutions that preserves spatial resolution while expanding receptive fields, coupled with a feature pyramid decoder using learnable fusion weights for adaptive multi-scale integration. A combined loss function balancing binary cross-entropy and structural similarity achieves both pixel-wise accuracy and structural coherence. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets (CUHK, DUT, CTCUG, EBD) demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, with ablation studies confirming that semantic enhancement provides the most significant gains while maintaining computational efficiency. SemanticBlur generates visually coherent detection maps with sharp boundaries, validating its practical applicability for real-world deployment. SN - 3068-5079 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Haider2026SemanticBl,
author = {Asad Ullah Haider and Alexandros Gazis and Faryal Zahoor},
title = {SemanticBlur: Semantic-Aware Attention Network with Multi-Scale Feature Refinement for Defocus Blur Detection},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics},
year = {2026},
volume = {3},
number = {1},
pages = {21-31},
doi = {10.62762/TIS.2025.879161},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TIS.2025.879161},
abstract = {Defocus blur detection is essential for computational photography applications, but existing methods struggle with accurate blur localization and boundary preservation. We propose SemanticBlur, a deep learning framework which integrates semantic understanding with attention mechanisms for robust defocus blur detection. Our semantic-aware attention module combines channel attention, spatial attention, and semantic enhancement to leverage high-level features for low-level feature refinement. The architecture employs a modified ResNet-50 backbone with dilated convolutions that preserves spatial resolution while expanding receptive fields, coupled with a feature pyramid decoder using learnable fusion weights for adaptive multi-scale integration. A combined loss function balancing binary cross-entropy and structural similarity achieves both pixel-wise accuracy and structural coherence. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets (CUHK, DUT, CTCUG, EBD) demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance, with ablation studies confirming that semantic enhancement provides the most significant gains while maintaining computational efficiency. SemanticBlur generates visually coherent detection maps with sharp boundaries, validating its practical applicability for real-world deployment.},
keywords = {blur detection, semantic segmentation, attention mechanisms, deep neural networks, image analysis, multi-scale processing},
issn = {3068-5079},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Intelligent Systematics
ISSN: 3068-5079 (Online) | ISSN: 3069-003X (Print)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/