Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing | Volume 2, Issue 1: 27-38, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JRSC.2025.385825
Abstract
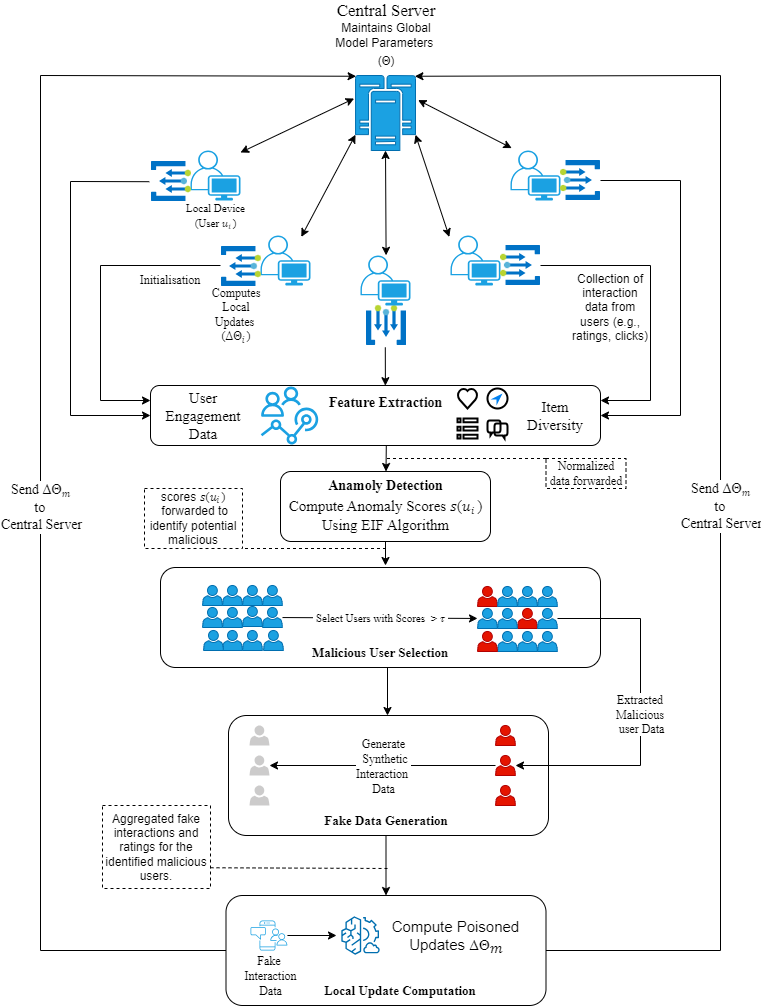
Federated learning (FL) enables decentralized model training and enhances user privacy by keeping data on local devices. Despite these advantages, FL remains vulnerable to sophisticated adversarial attacks. Federated recommender systems (FRS), an important application of FL, are particularly susceptible to threats such as model poisoning. In this paper, we propose DyMUSA, a novel model poisoning attack tailored for FRS. DyMUSA exploits systemic vulnerabilities through dynamic user selection and adaptive poisoning strategies. Specifically, it leverages the Isolation Forest algorithm to identify anomalous users and generate poisoned gradients that compromise the integrity of the recommender sy... More >
Graphical Abstract