Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing
ISSN: 3070-6424 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
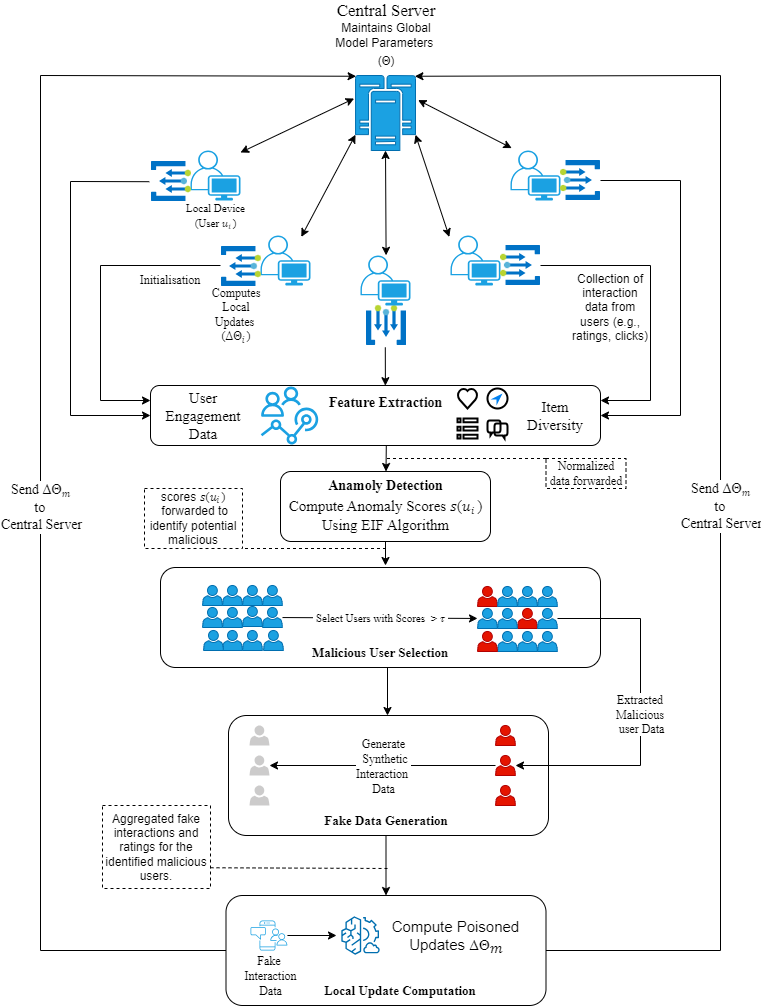
TY - JOUR AU - Singh, Jagdeep AU - Kumari, Saru AU - Agrawal, Seema PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/07 TI - A Novel System for Detecting Model Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning JO - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing T2 - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing JF - Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 27 EP - 38 DO - 10.62762/JRSC.2025.385825 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.385825 KW - federated learning KW - attacks KW - privacy KW - real world data KW - datasets AB - Federated learning (FL) enables decentralized model training and enhances user privacy by keeping data on local devices. Despite these advantages, FL remains vulnerable to sophisticated adversarial attacks. Federated recommender systems (FRS), an important application of FL, are particularly susceptible to threats such as model poisoning. In this paper, we propose DyMUSA, a novel model poisoning attack tailored for FRS. DyMUSA exploits systemic vulnerabilities through dynamic user selection and adaptive poisoning strategies. Specifically, it leverages the Isolation Forest algorithm to identify anomalous users and generate poisoned gradients that compromise the integrity of the recommender system. Experiments conducted on real-world datasets demonstrate that DyMUSA significantly increases the exposure of targeted items while maintaining minimal impact on overall system performance. SN - 3070-6424 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Singh2026A,
author = {Jagdeep Singh and Saru Kumari and Seema Agrawal},
title = {A Novel System for Detecting Model Poisoning Attacks in Federated Learning},
journal = {Journal of Reliable and Secure Computing},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {27-38},
doi = {10.62762/JRSC.2025.385825},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRSC.2025.385825},
abstract = {Federated learning (FL) enables decentralized model training and enhances user privacy by keeping data on local devices. Despite these advantages, FL remains vulnerable to sophisticated adversarial attacks. Federated recommender systems (FRS), an important application of FL, are particularly susceptible to threats such as model poisoning. In this paper, we propose DyMUSA, a novel model poisoning attack tailored for FRS. DyMUSA exploits systemic vulnerabilities through dynamic user selection and adaptive poisoning strategies. Specifically, it leverages the Isolation Forest algorithm to identify anomalous users and generate poisoned gradients that compromise the integrity of the recommender system. Experiments conducted on real-world datasets demonstrate that DyMUSA significantly increases the exposure of targeted items while maintaining minimal impact on overall system performance.},
keywords = {federated learning, attacks, privacy, real world data, datasets},
issn = {3070-6424},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/