ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing | Volume 1, Issue 4: 196-209, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/JIAP.2025.346328
Abstract
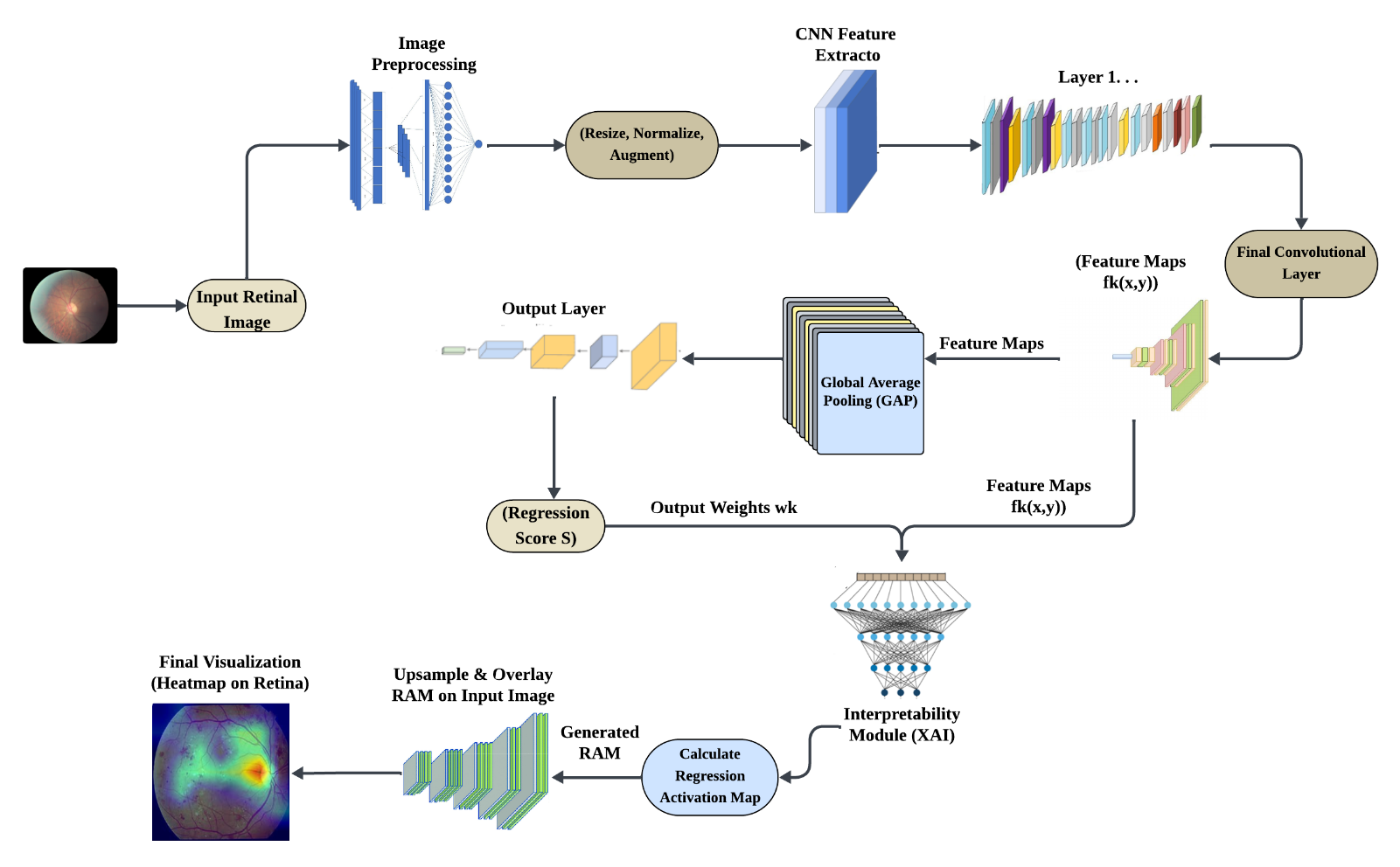
The escalating global prevalence of diabetes renders effective screening for Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) indispensable to prevent irreversible vision loss. Although deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), attain diagnostic accuracy comparable to that of human experts, their black-box nature erodes clinical trust. To harmonize accuracy with interpretability, this paper proposes a novel CNN architecture that reformulates DR grading as a regression task. By substituting traditional dense layers with a Global Average Pooling (GAP) layer, our approach substantially reduces model complexity and training time while enabling the generation of Regression Activation Maps... More >
Graphical Abstract