ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing
ISSN: 3068-6679 (Online)
Email: [email protected]


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
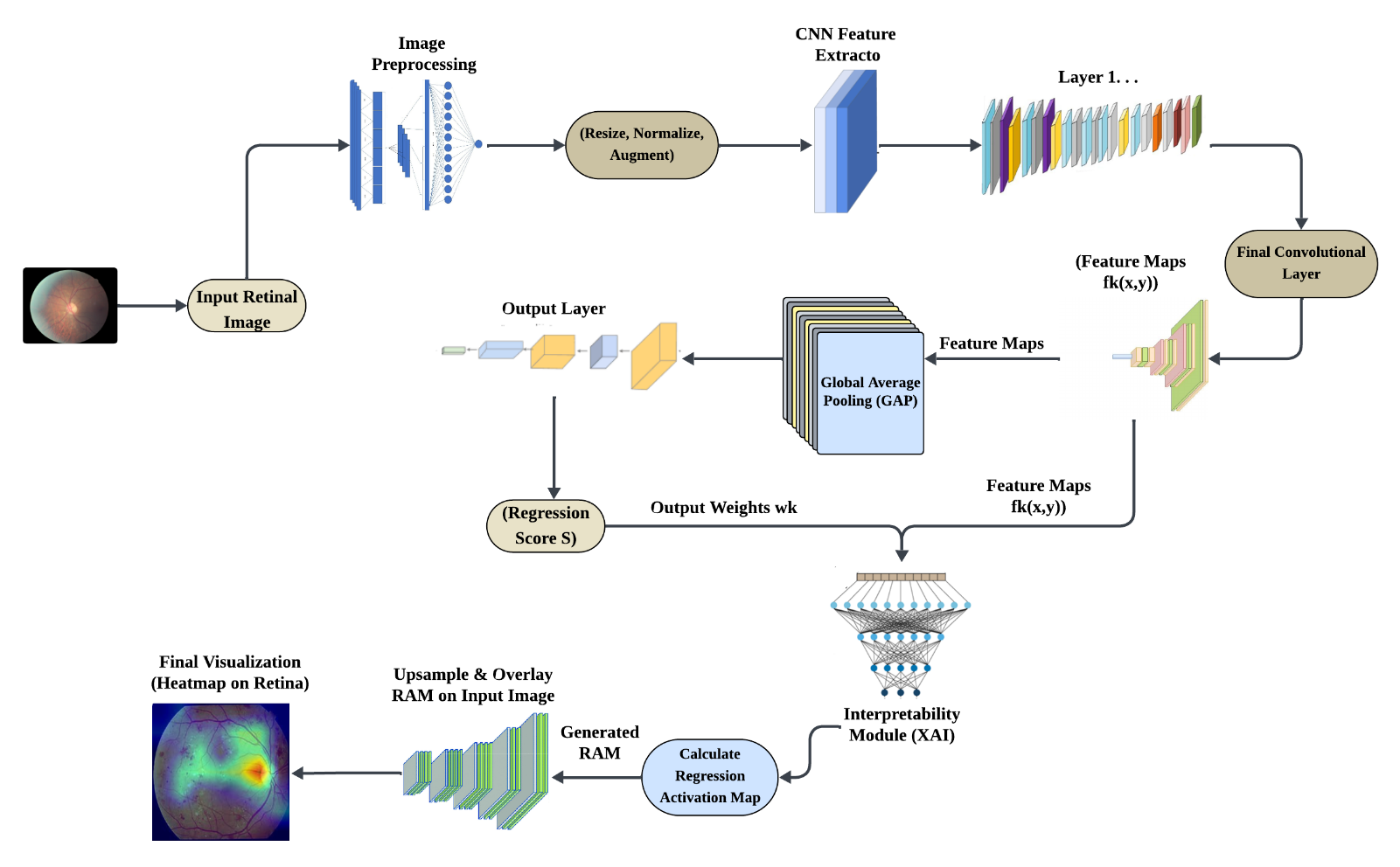
TY - JOUR AU - Khalid, Muhammad Imran AU - Ahmad, Israr AU - Saleem, Sohaibe AU - Hussain, Altaf AU - Hussain, Syed Akif AU - Waghan, Atif Ali AU - Khan, Muzamil PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/18 TI - Interpretable Deep Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading using Regression Activation Maps JO - ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing T2 - ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing JF - ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing VL - 1 IS - 4 SP - 196 EP - 209 DO - 10.62762/JIAP.2025.346328 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JIAP.2025.346328 KW - diabetic retinopathy KW - deep learning KW - explainable AI KW - regression activation maps (RAM) KW - global average pooling AB - The escalating global prevalence of diabetes renders effective screening for Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) indispensable to prevent irreversible vision loss. Although deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), attain diagnostic accuracy comparable to that of human experts, their black-box nature erodes clinical trust. To harmonize accuracy with interpretability, this paper proposes a novel CNN architecture that reformulates DR grading as a regression task. By substituting traditional dense layers with a Global Average Pooling (GAP) layer, our approach substantially reduces model complexity and training time while enabling the generation of Regression Activation Maps (RAMs). These RAMs deliver visual explanations by precisely highlighting the pathological regions that underpin the model's predictions. Evaluated on the Kaggle Diabetic Retinopathy Detection dataset, our model—through the replacement of dense layers with Global Average Pooling—markedly lowers model complexity while delivering diagnostic performance on par with baseline models employing fully-connected layers. The resulting system provides a simpler, more precise, and transparent alternative for automated medical screening, directly associating predictions with clinically relevant features. SN - 3068-6679 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Khalid2025Interpreta,
author = {Muhammad Imran Khalid and Israr Ahmad and Sohaibe Saleem and Altaf Hussain and Syed Akif Hussain and Atif Ali Waghan and Muzamil Khan},
title = {Interpretable Deep Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading using Regression Activation Maps},
journal = {ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {4},
pages = {196-209},
doi = {10.62762/JIAP.2025.346328},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JIAP.2025.346328},
abstract = {The escalating global prevalence of diabetes renders effective screening for Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) indispensable to prevent irreversible vision loss. Although deep learning models, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), attain diagnostic accuracy comparable to that of human experts, their black-box nature erodes clinical trust. To harmonize accuracy with interpretability, this paper proposes a novel CNN architecture that reformulates DR grading as a regression task. By substituting traditional dense layers with a Global Average Pooling (GAP) layer, our approach substantially reduces model complexity and training time while enabling the generation of Regression Activation Maps (RAMs). These RAMs deliver visual explanations by precisely highlighting the pathological regions that underpin the model's predictions. Evaluated on the Kaggle Diabetic Retinopathy Detection dataset, our model—through the replacement of dense layers with Global Average Pooling—markedly lowers model complexity while delivering diagnostic performance on par with baseline models employing fully-connected layers. The resulting system provides a simpler, more precise, and transparent alternative for automated medical screening, directly associating predictions with clinically relevant features.},
keywords = {diabetic retinopathy, deep learning, explainable AI, regression activation maps (RAM), global average pooling},
issn = {3068-6679},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/