ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability | Volume 1, Issue 2: 136-148, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TSSR.2025.657859
Abstract
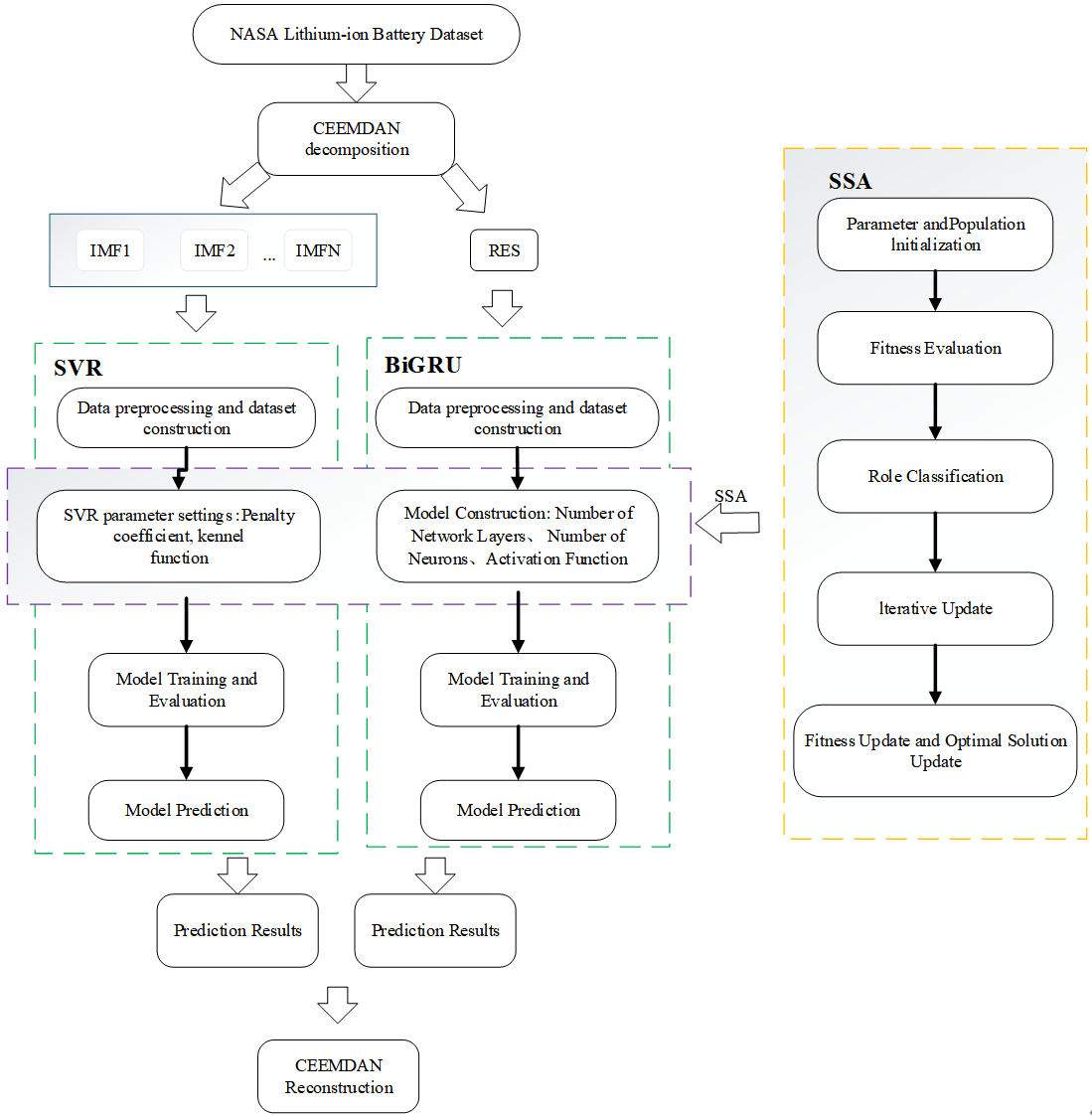
The capacity regeneration phenomenon in lithium-ion batteries is inevitable and leads to non-monotonic fluctuations in capacity degradation trajectories, significantly complicating accurate remaining useful life (RUL) prediction. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a hybrid prediction model based on CEEMDAN-SSA-SVR-BiGRU. The method first employs Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) to decompose the original capacity sequence into multiple Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) representing local regeneration fluctuations, and a residual component (RES) referring to the global degradation trend, thereby achieving effective signal decoupling. Subseq... More >
Graphical Abstract