ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability
ISSN: 3069-1087 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
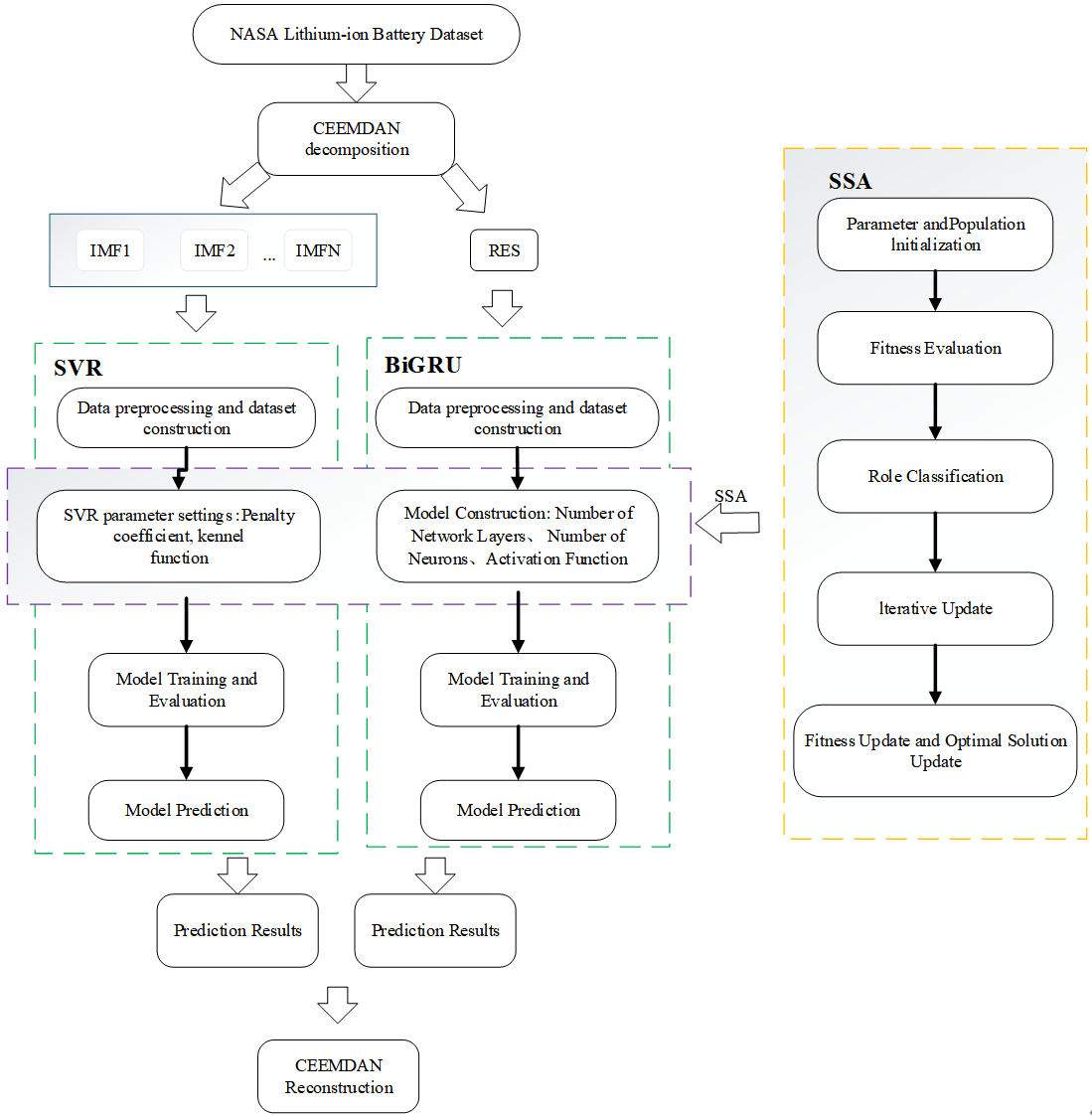
TY - JOUR AU - Zhao, Fei AU - Dai, Xinyu PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/30 TI - A Hybrid RUL Prediction Approach for Lithium-ion Batteries Based on CEEMDAN-SSA-SVR-BiGRU JO - ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability T2 - ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability JF - ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability VL - 1 IS - 2 SP - 136 EP - 148 DO - 10.62762/TSSR.2025.657859 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSSR.2025.657859 KW - remaining useful life KW - capacity regeneration KW - CEEMDAN KW - sparrow search algorithm KW - support vector regression KW - bidirectional gated recurrent unit AB - The capacity regeneration phenomenon in lithium-ion batteries is inevitable and leads to non-monotonic fluctuations in capacity degradation trajectories, significantly complicating accurate remaining useful life (RUL) prediction. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a hybrid prediction model based on CEEMDAN-SSA-SVR-BiGRU. The method first employs Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) to decompose the original capacity sequence into multiple Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) representing local regeneration fluctuations, and a residual component (RES) referring to the global degradation trend, thereby achieving effective signal decoupling. Subsequently, distinct prediction strategies are applied to different components after decomposition. Support Vector Regression (SVR) is utilized to capture nonlinear local fluctuations, while Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) models long-term dependencies. To further enhance the model performance, the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) is introduced to jointly optimize kernel parameters and penalty factors in SVR, as well as architectural hyperparameters in BiGRU. Experimental results on the NASA lithium battery dataset demonstrate that the proposed model achieves higher accuracy, with Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) no more than 0.0067, 0.0049, and 0.0094, respectively, significantly outperforming the ablated models and some baseline models. This study validates that the integration of signal decomposition, component-specific modeling, and hyperparameter optimization yields a significant improvement in the accuracy and robustness of the RUL prediction for lithium-ion batteries under capacity regeneration. SN - 3069-1087 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Zhao2025A,
author = {Fei Zhao and Xinyu Dai},
title = {A Hybrid RUL Prediction Approach for Lithium-ion Batteries Based on CEEMDAN-SSA-SVR-BiGRU},
journal = {ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {2},
pages = {136-148},
doi = {10.62762/TSSR.2025.657859},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/TSSR.2025.657859},
abstract = {The capacity regeneration phenomenon in lithium-ion batteries is inevitable and leads to non-monotonic fluctuations in capacity degradation trajectories, significantly complicating accurate remaining useful life (RUL) prediction. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a hybrid prediction model based on CEEMDAN-SSA-SVR-BiGRU. The method first employs Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (CEEMDAN) to decompose the original capacity sequence into multiple Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs) representing local regeneration fluctuations, and a residual component (RES) referring to the global degradation trend, thereby achieving effective signal decoupling. Subsequently, distinct prediction strategies are applied to different components after decomposition. Support Vector Regression (SVR) is utilized to capture nonlinear local fluctuations, while Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Unit (BiGRU) models long-term dependencies. To further enhance the model performance, the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) is introduced to jointly optimize kernel parameters and penalty factors in SVR, as well as architectural hyperparameters in BiGRU. Experimental results on the NASA lithium battery dataset demonstrate that the proposed model achieves higher accuracy, with Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) no more than 0.0067, 0.0049, and 0.0094, respectively, significantly outperforming the ablated models and some baseline models. This study validates that the integration of signal decomposition, component-specific modeling, and hyperparameter optimization yields a significant improvement in the accuracy and robustness of the RUL prediction for lithium-ion batteries under capacity regeneration.},
keywords = {remaining useful life, capacity regeneration, CEEMDAN, sparrow search algorithm, support vector regression, bidirectional gated recurrent unit},
issn = {3069-1087},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
ICCK Transactions on Systems Safety and Reliability
ISSN: 3069-1087 (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/