ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 1, Issue 2: 106-116, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2025.493945
Abstract
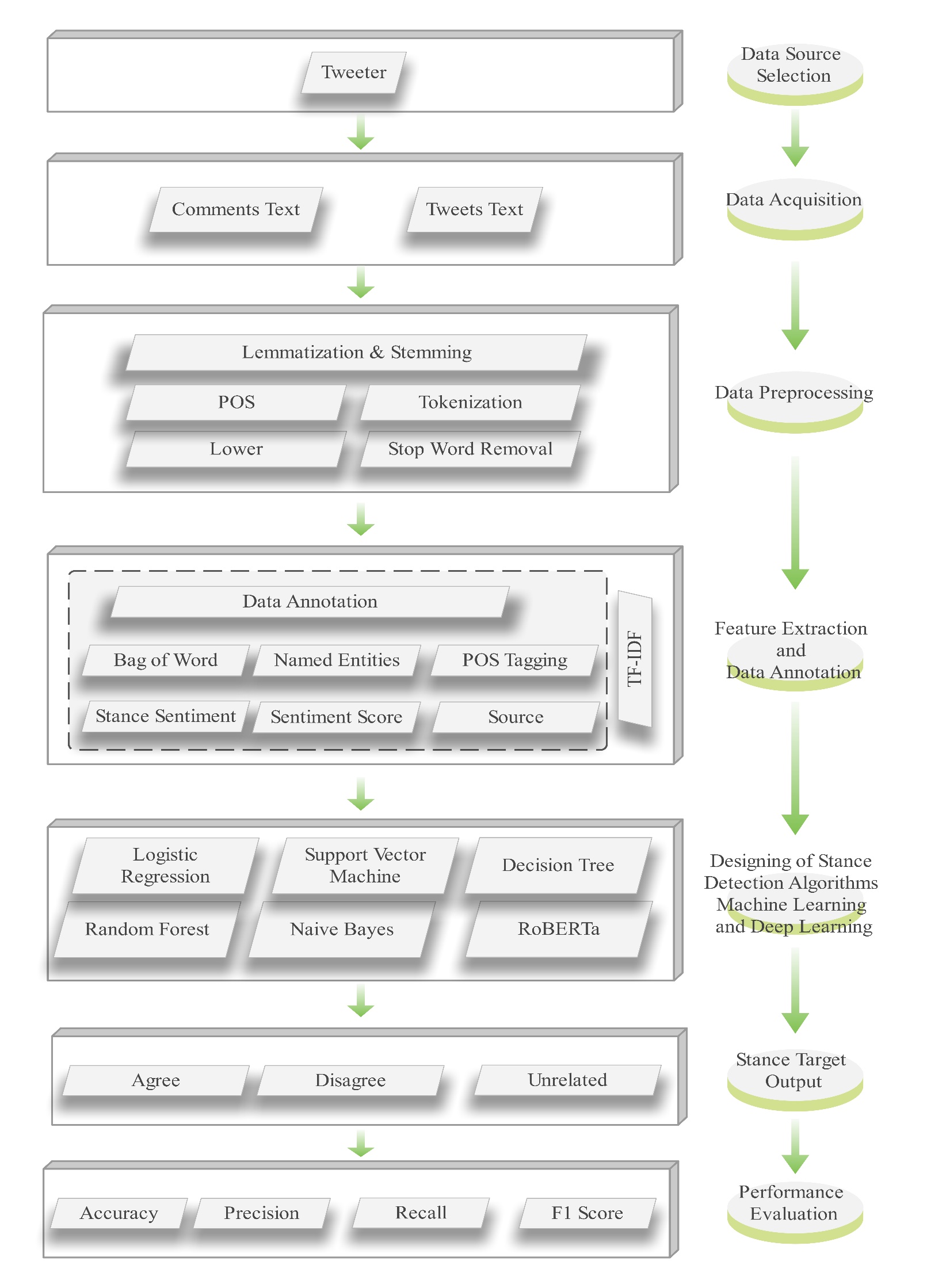
The process of assigning grammatical categories, such as ``Noun'' and ``Verb,'' to every word in a text corpus is known as part-of-speech (POS) tagging. This technique is widely used in applications like sentiment analysis, machine translation, and other linguistic and computational tasks. However, the unique features of the Pashto language and its limited resources present significant challenges for POS tagging. This study explores the critical role of POS tagging in the Pashto language by employing six popular deep-learning and machine-learning techniques. Experimental results demonstrate machine learning methods' effectiveness in capturing Pashto text's grammatical patterns. The evaluatio... More >
Graphical Abstract