ICCK Transactions on Applied Intelligence and Cybernetics | Volume 1, Issue 1: 1-4, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/TAIC.2025.516366
Academic Profile
Hazrat Bilal (Member of IEEE, CAS-TWAS Fellow) received his MS degree in Control Science and Engineering in 2018 from Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, and his PhD degree in Control Science and Engineering in 2024 from the University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui, respectively. He is currently a full-time Research Fellow at the College of Mechatronics and Control Engineering, Shenzhen University, China. His research interests include robotics, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, Internet of robotic things (IoRT), and artificial intelligence. In 2018, considering his research achievement, the Nanjing University of Science and Technology awarded him the Outstanding Graduate Award, while the University of Science and Technology of China awarded him the CAS-TWAS Fellow Award. He is currently a member of IEEE, IEEE Robotics and Automation Society, and IEEE Control Systems Society. Mr. Bilal has many publications in IEEE, Elsevier, and Springer brands.
Editorial Roles
No Editorial Roles
This user currently does not serve as an editor for any ICCK journals.
ICCK Publications
Total Publications: 5
Bridging Minds and Machines: TAIC’s Vision for Next-Gen AI and Cybernetic Revolutions
Open Access
|
Research Article
| 30 June 2025
| Cited:
1
,
1
Comparison of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models for Part-of-Speech Tagging
by
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 1, Issue 2: 106-116, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2025.493945
Abstract
The process of assigning grammatical categories, such as ``Noun'' and ``Verb,'' to every word in a text corpus is known as part-of-speech (POS) tagging. This technique is widely used in applications like sentiment analysis, machine translation, and other linguistic and computational tasks. However, the unique features of the Pashto language and its limited resources present significant challenges for POS tagging. This study explores the critical role of POS tagging in the Pashto language by employing six popular deep-learning and machine-learning techniques. Experimental results demonstrate machine learning methods' effectiveness in capturing Pashto text's grammatical patterns. The evaluatio... More >
Graphical Abstract

Free Access
|
Research Article
| 19 May 2025
Optimizing Cloud Security with a Hybrid BiLSTM-BiGRU Model for Efficient Intrusion Detection
by
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 2, Issue 2: 106-121, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2024.433246
Abstract
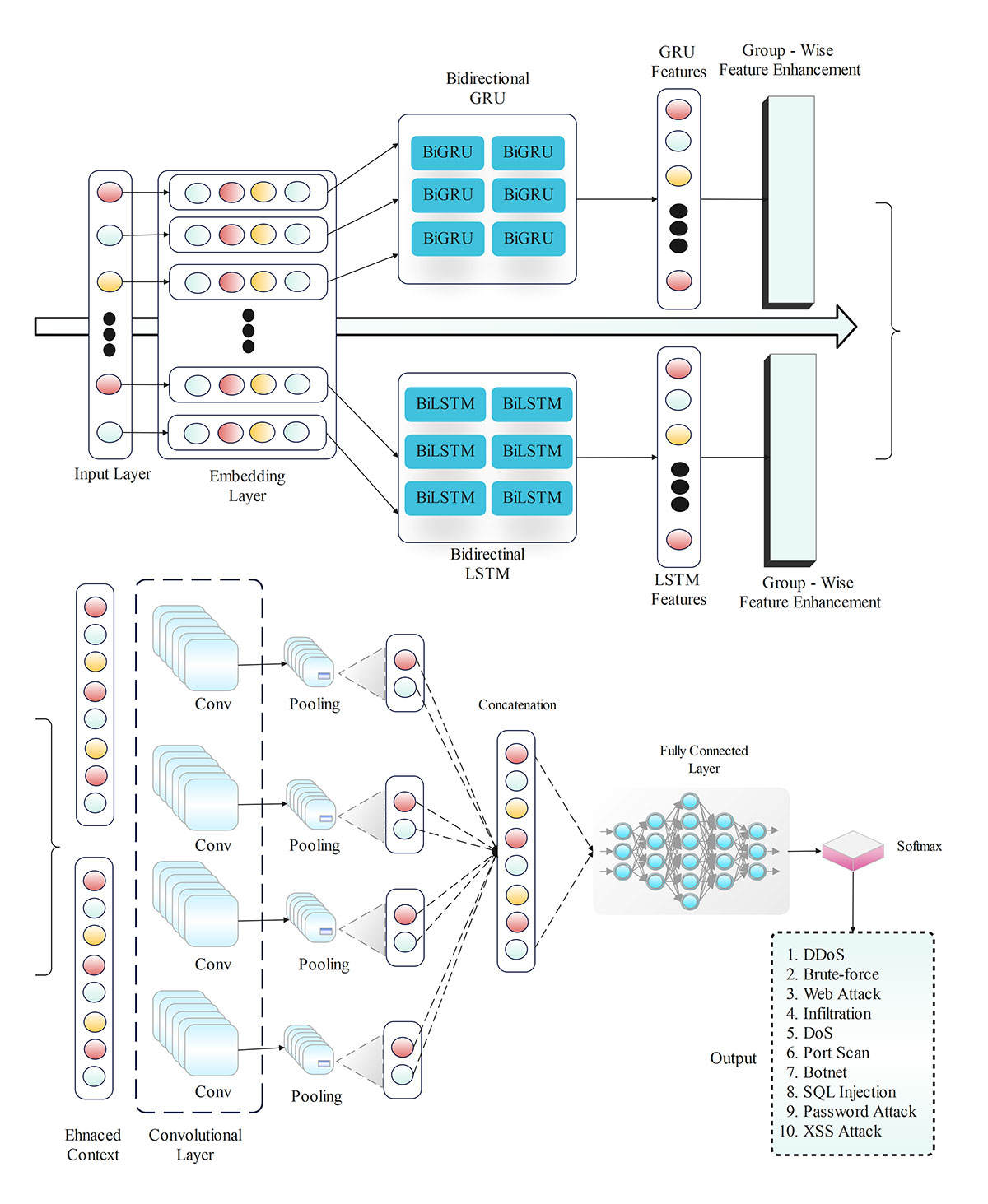
To address evolving security challenges in cloud computing, this study proposes a hybrid deep learning architecture integrating Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) and Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Units (BiGRU) for cloud intrusion detection. The BiLSTM-BiGRU model synergizes BiLSTM's long-term dependency modeling with BiGRU's efficient gating mechanisms, achieving a detection accuracy of 96.7% on the CIC-IDS 2018 dataset. It outperforms CNN-LSTM baselines by 2.2% accuracy, 3.3% precision, 3.6% recall, and 3.6% F1-score while maintaining 0.03% false positive rate. The architecture demonstrates operational efficiency through 20% reduced computational latency and 15% lower memory foo... More >
Graphical Abstract
Open Access
|
Research Article
| 31 March 2025
| Cited:
4
,
4
ViTDroid and Hybrid Models for Effective Android and IoT Malware Detection
ICCK Transactions on Advanced Computing and Systems | Volume 1, Issue 1: 32-47, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/TACS.2024.521915
Abstract
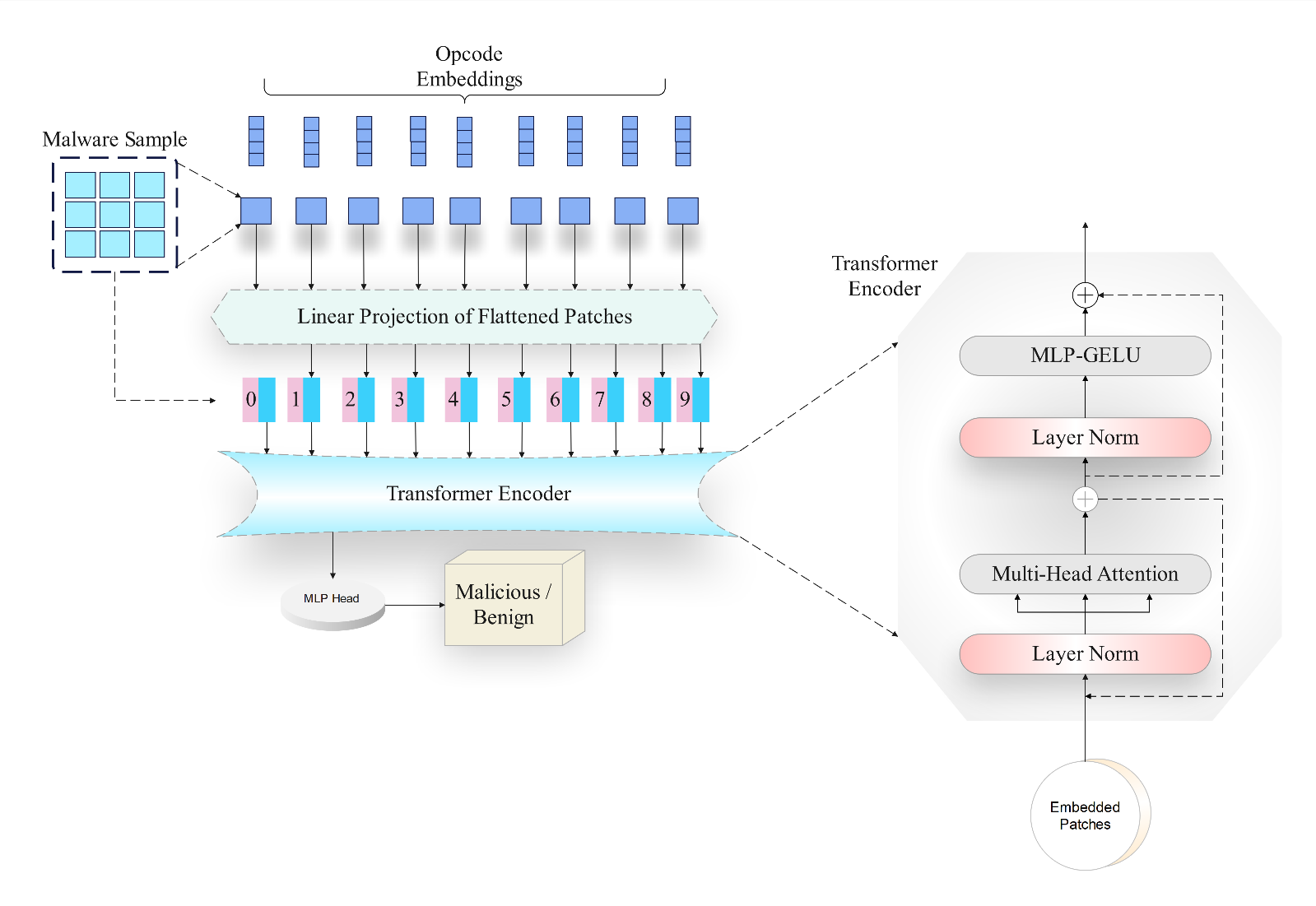
This paper introduces ViTDroid, a novel hybrid model that combines Vision Transformers (ViTs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to enhance Android and IoT malware detection. ViTDroid addresses critical challenges by leveraging ViTs to capture global spatial dependencies and RNNs (LSTM and GRU) to model temporal patterns, enabling comprehensive analysis of complex malware behaviors. Additionally, the model integrates explainability tools, such as LIME and SHAP, to enhance transparency and trustworthiness, essential for real-world cybersecurity applications. The study evaluates ViTDroid's performance against conventional models, including RNN, LSTM, and GRU, using accuracy, precision, recal... More >
Graphical Abstract
Free Access
|
Research Article
| 31 December 2024
| Cited:
1
,
1
Vehicular Network Security Through Optimized Deep Learning Model with Feature Selection Techniques
by
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
ICCK Transactions on Sensing, Communication, and Control | Volume 1, Issue 2: 136-153, 2024 | DOI: 10.62762/TSCC.2024.626147
Abstract
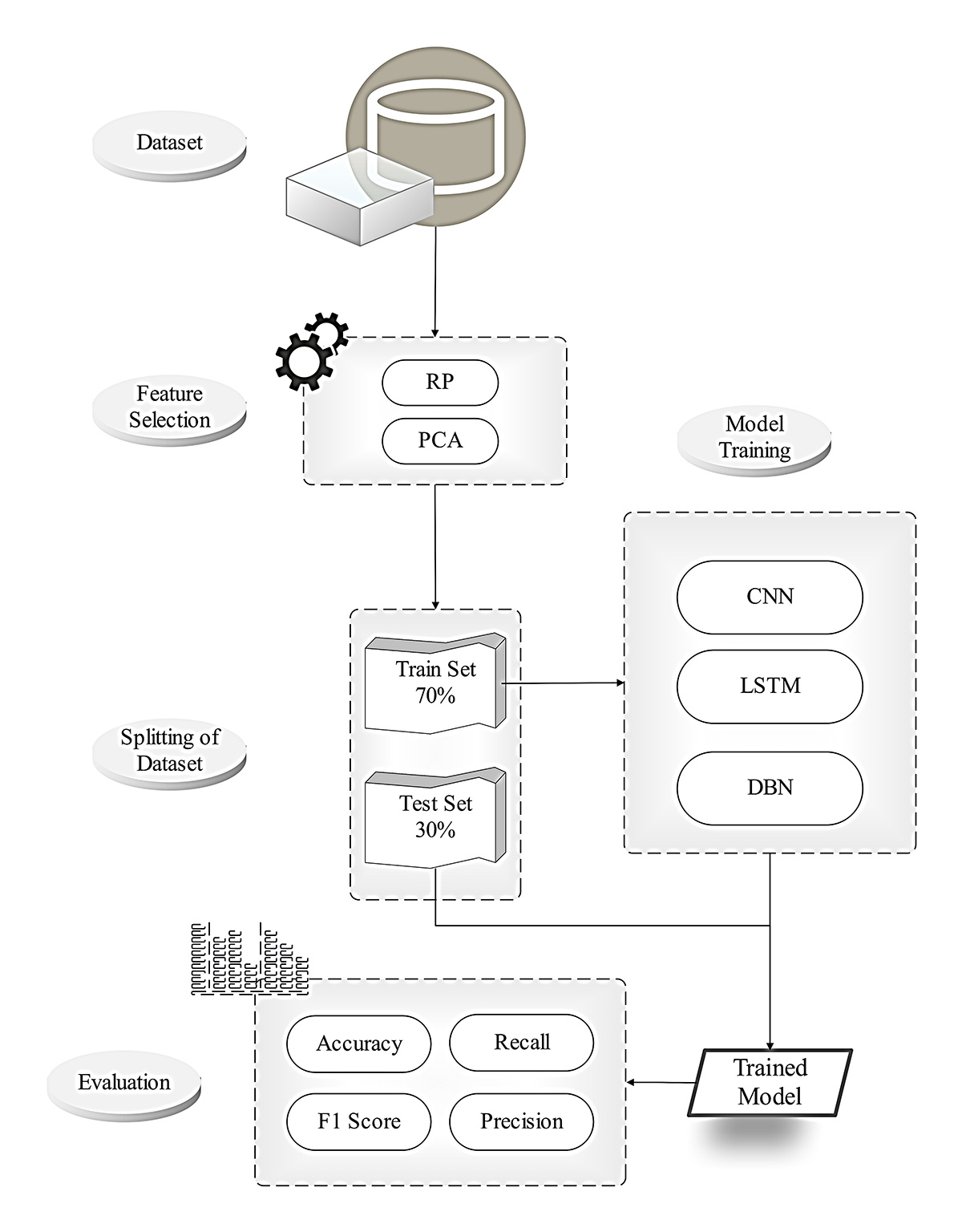
In recent years, vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs) have faced growing security concerns, particularly from Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. These attacks flood the network with malicious traffic, disrupting services and compromising resource availability. While various techniques have been proposed to address these threats, this study presents an optimized framework leveraging advanced deep-learning models for improved detection accuracy. The proposed Intrusion Detection System (IDS) employs Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), and Deep Belief Networks (DBN) alongside robust feature selection techniques, Random Projecti... More >
Graphical Abstract