Frontiers in Biomedical Signal Processing | Volume 1, Issue 1: 24-36, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/FBSP.2025.954863
Abstract
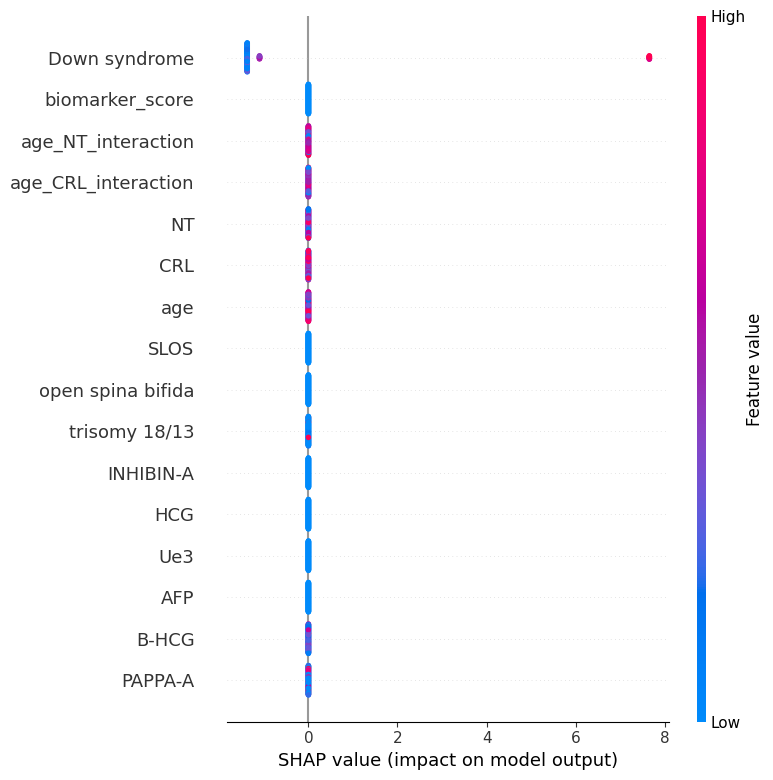
This study developed a machine learning model for early risk stratification of Down syndrome by integrating maternal serum biomarkers and ultrasound measurements. A retrospective multicentre dataset was used, including maternal age, AFP, HCG, INHIBIN-A, and ultrasound parameters (NT, CRL). After imputing missing data and engineering features (e.g., Age_NT_interaction), a Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) was trained and evaluated using AUROC, precision, recall, and F1-score. The model achieved high performance (AUROC: 0.9921; precision: 1.00; F1-score: 0.91; accuracy: 0.97). SHAP analysis identified key interactions—particularly Age_NT, Age_HCG, and Age_PAPP-A—as major contributors. High m... More >
Graphical Abstract