Abstract
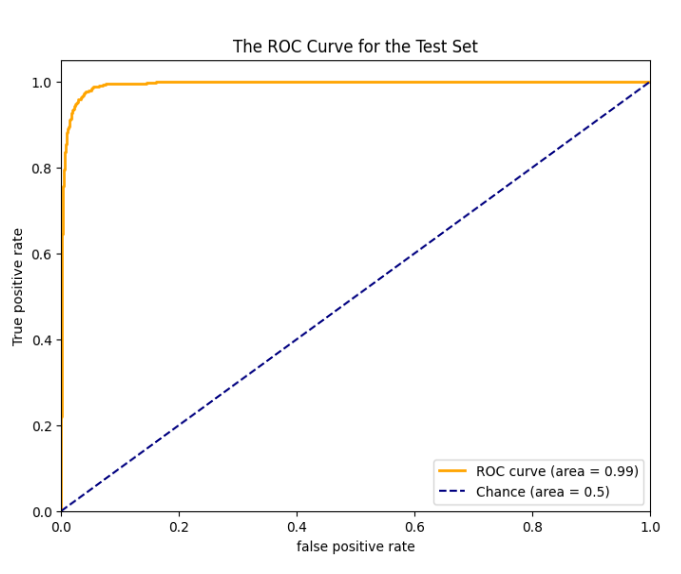
This work investigates the effectiveness of incorporating paralinguistic feature extraction in audio deepfake detection models. The proposed model extracts paralinguistic features from audio clips and represents them as 1024-dimensional vector embeddings. These embeddings are then used as input for a logistic regression model, which performs binary classification to distinguish between real and deepfake audio samples. The ASVspoof2019 dataset, comprising both genuine and spoofed audio clips, is used to evaluate the model's performance. The results are assessed using evaluation metrics such as Equal Error Rate (EER) and accuracy, which provide insight into the model's effectiveness compared to state-of-the-art methods. The proposed model achieves an EER of 3.04% and an accuracy of 97.9%, indicating that paralinguistic feature extraction is a promising approach for audio deepfake detection. These results suggest that incorporating paralinguistic features can improve the performance of audio deepfake detection systems, making it a valuable tool for future research in this area. Overall, the study demonstrates the potential of paralinguistic feature extraction in enhancing the accuracy and reliability of audio deepfake detection methods.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Ahmed, Z., Khan, G. S. A., & Vavekanand, R. (2025). AUDD: Audio Deepfake Detection Using Paralinguistic Feature Extraction Techniques. Journal of Computing Intelligence, 1(1), 3–8. https://doi.org/10.62762/JCI.2024.667518
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 