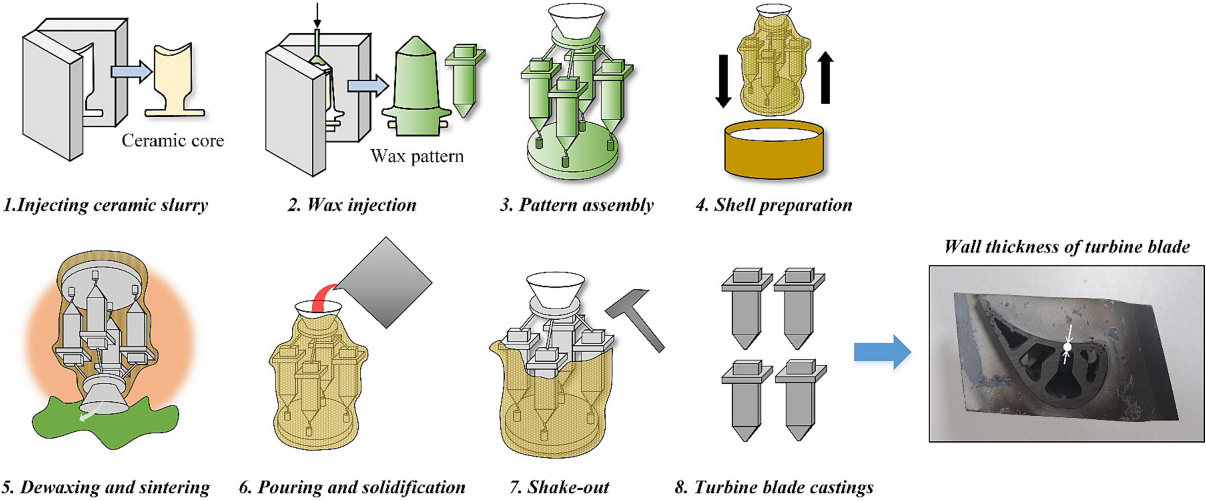
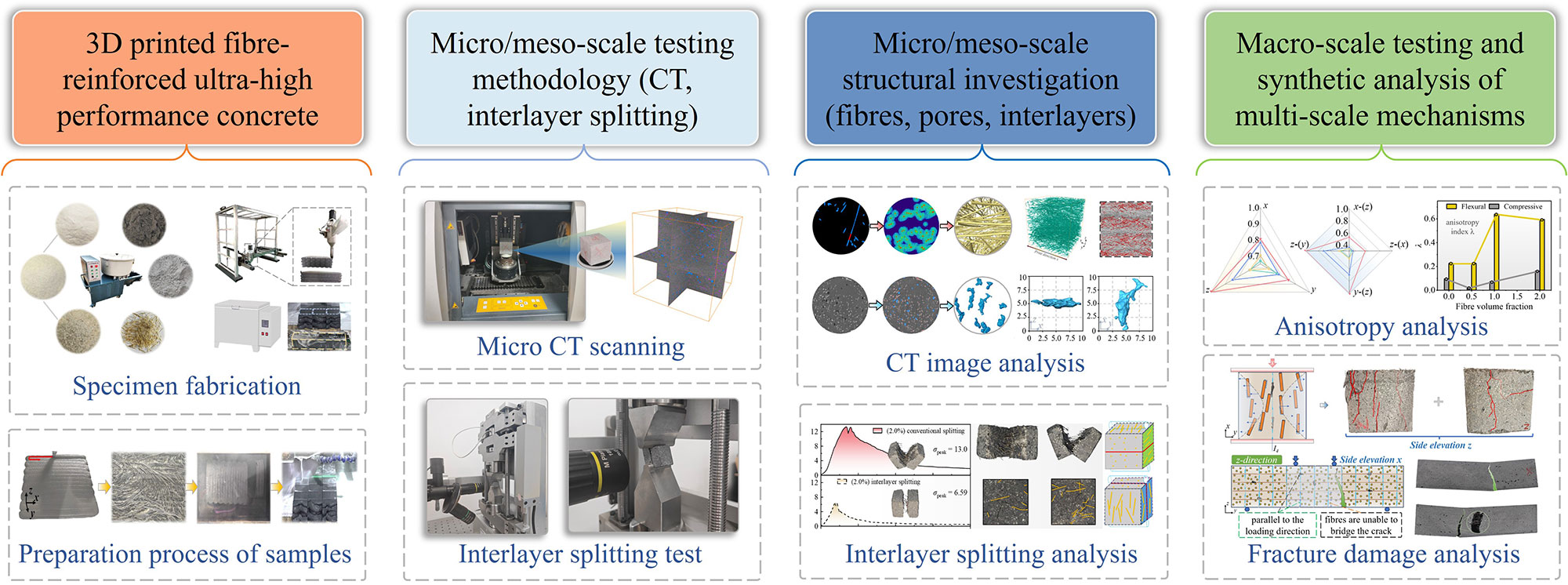
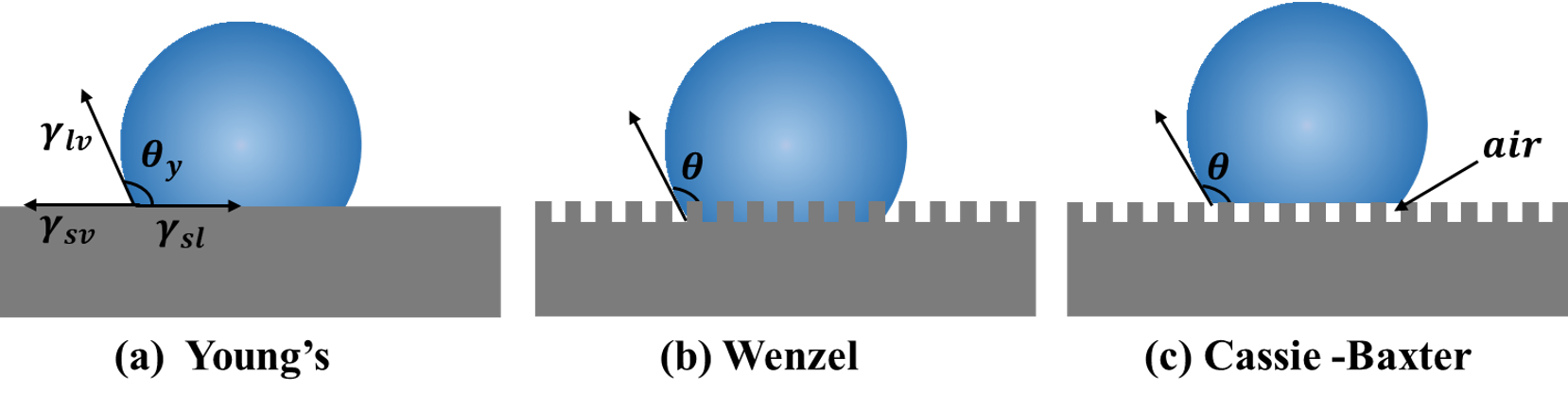
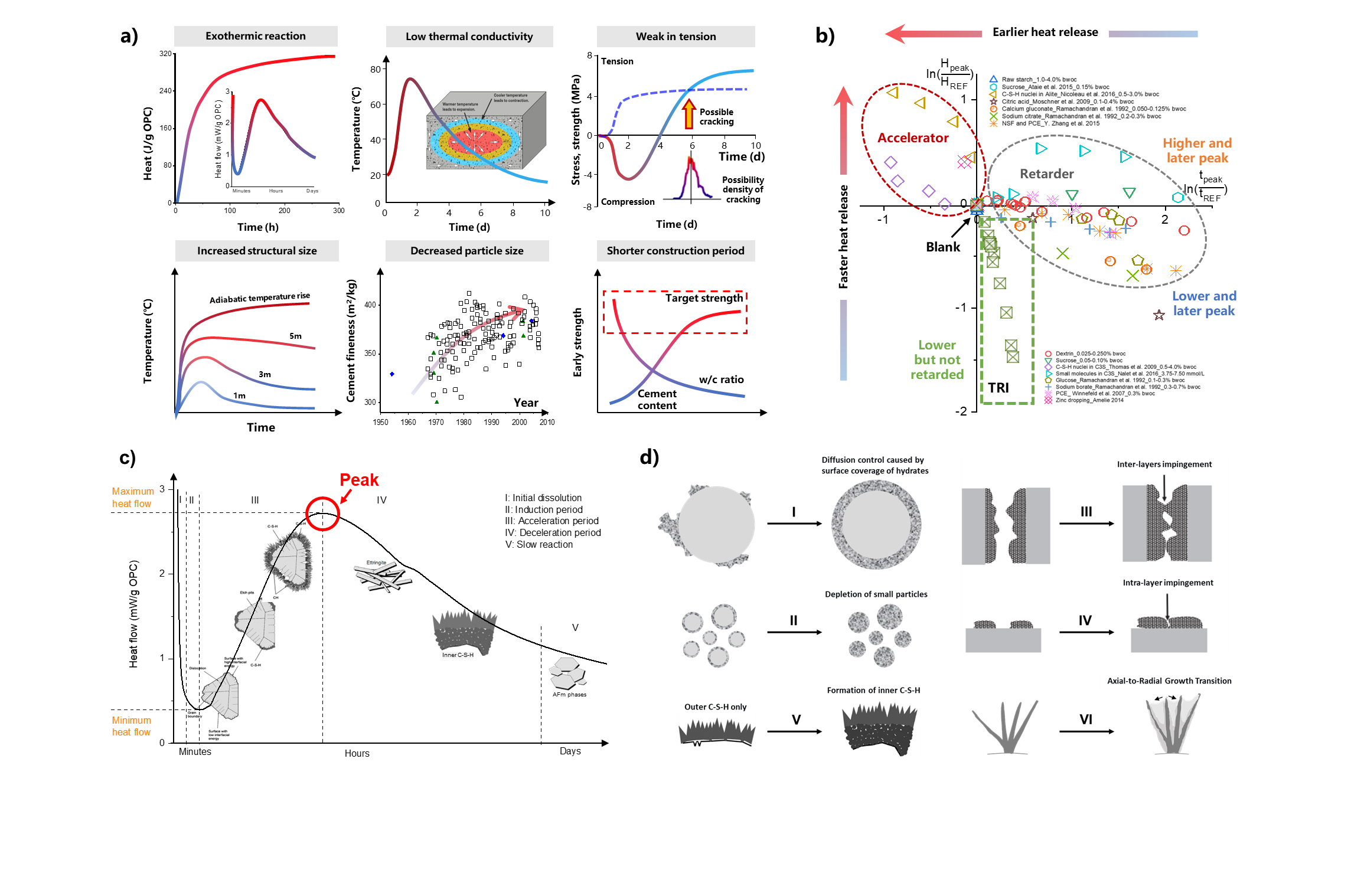
Journal of Advanced Materials Research | Volume 2, Issue 1: 55-85, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JAMR.2025.827155
Abstract
Additive manufacturing (AM) is redefining the limits of directional solidification (DS) and single-crystal (SX) fabrication for nickel-based superalloys. By reconciling classical Bridgman theory with the extreme thermal gradients (G) and solidification velocities (V) inherent to AM, this review establishes a unified framework for controlled epitaxy. It dissects the kinetics of grain competition and the columnar-to-equiaxed transition (CET), highlighting how scan strategies and thermal management dictate melt pool geometry and the G/V ratio. A comparative assessment of laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF), electron beam powder bed fusion (EB-PBF), and directed energy deposition (DED) delineates di... More >
Graphical Abstract