Journal of Advanced Materials Research | Volume 2, Issue 2: 86-96, 2026 | DOI: 10.62762/JAMR.2026.672409
Abstract
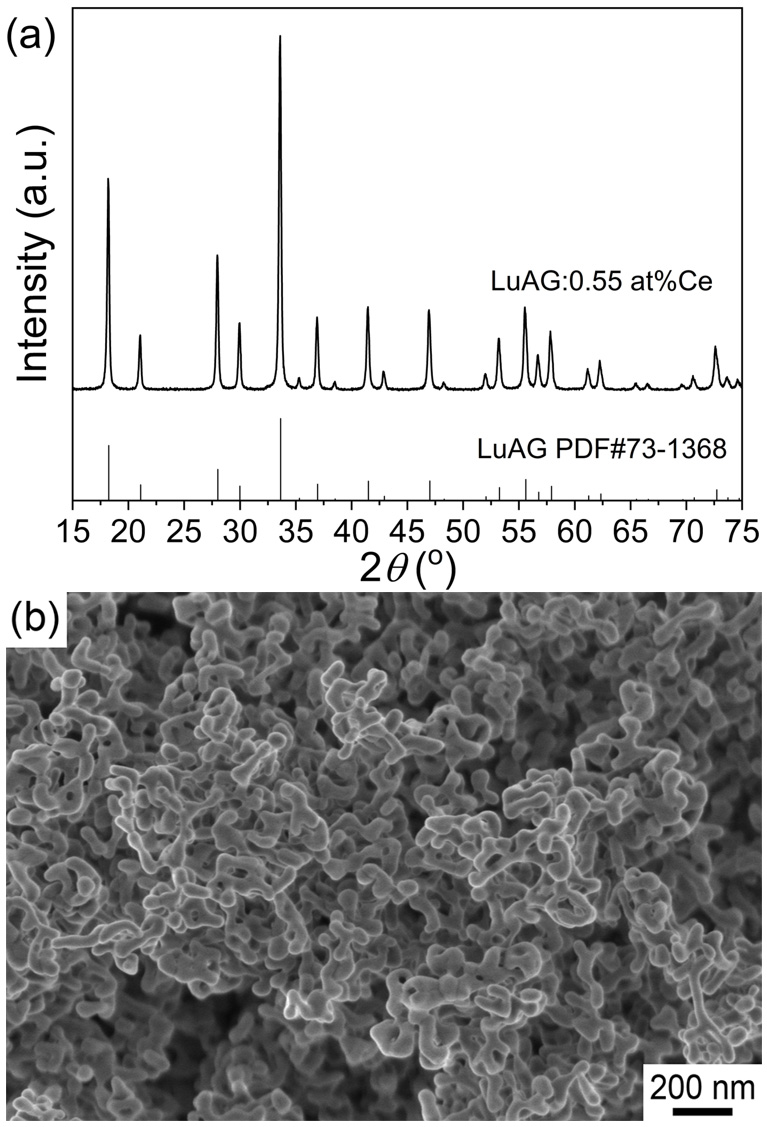
The generation of high-brightness white light in laser-illuminated devices is achieved by exciting yellow-green phosphors with a blue laser source. This configuration offers advantages such as high energy density and strong central luminous intensity. Among luminescent materials, LuAG:Ce phosphor ceramics (PCs) are notable for their high thermal stability and luminous output. In this study, LuAG:Ce PCs were produced from co-precipitated monophase nanopowders. The effects of vacuum sintering and air annealing temperatures on their porosity and luminescent properties were investigated. The sample, sintered at 1550°C and subsequently annealed at 1350°C, exhibited 3.5 vol.% porosity, highest r... More >
Graphical Abstract