Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare | Volume 1, Issue 3: 118-137, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/BISH.2025.212535
Abstract
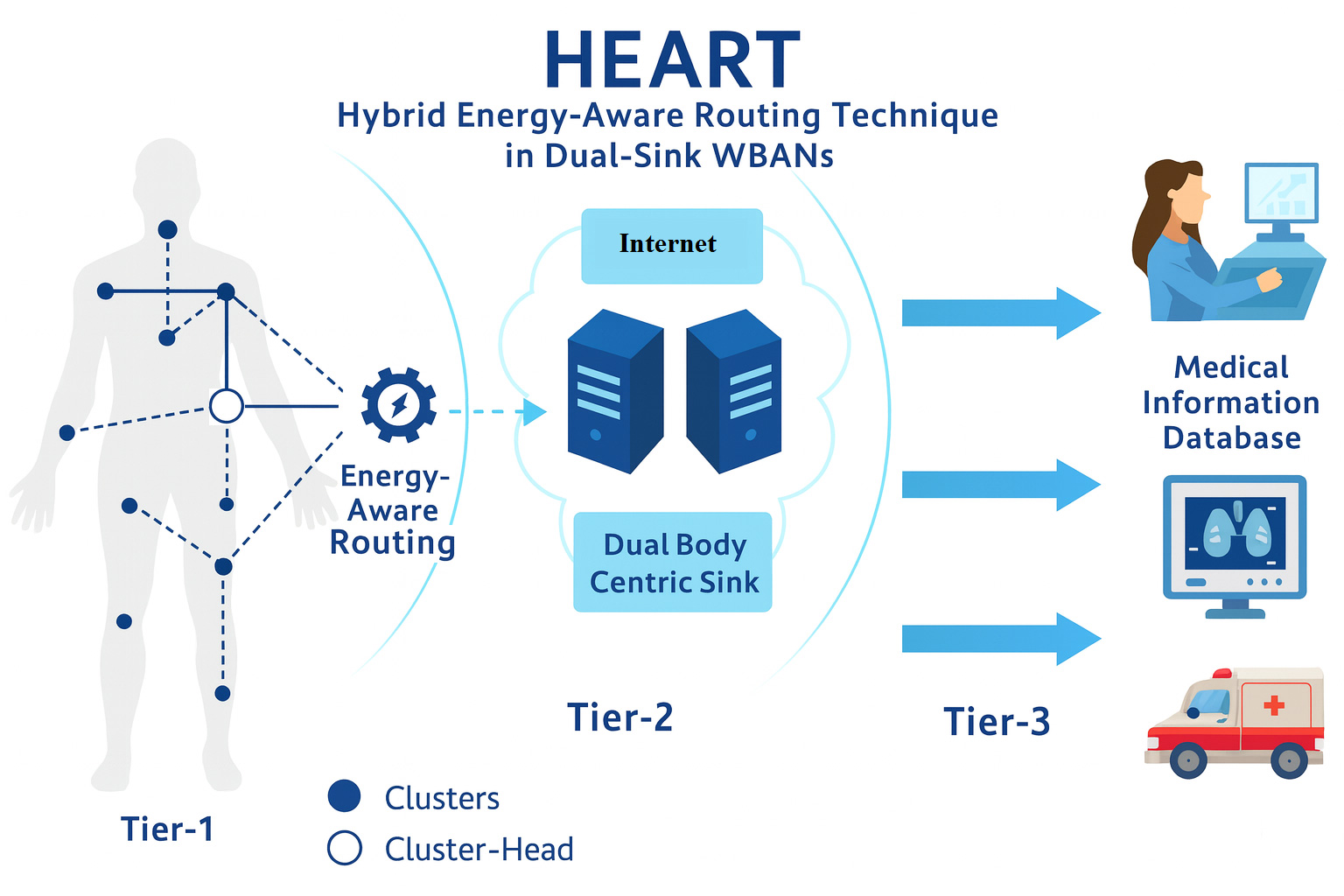
The rapid evolution of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has enabled pervasive patient monitoring through Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs). However, energy depletion, high path-loss, link instability, and latency remain major barriers to achieving reliability in real-time healthcare applications. Existing schemes, such as Distance Aware Relaying Energy-efficient (DARE) and Link Aware and Energy Efficient Scheme for Body Area Networks (LAEEBA), mitigate individual constraints, distance and link quality respectively, but lack holistic optimization across energy, distance, and reliability dimensions. This paper proposes HEART (Hybrid Energy-Aware Routing Technique), a dual-sink, clusteri... More >
Graphical Abstract