Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare
ISSN: 3068-5524 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
TY - JOUR
AU - Hussain, Altaf
PY - 2025
DA - 2025/12/23
TI - HEART: Hybrid Energy-Aware Routing Technique for Dual-Sink Body Area Networks in Smart Healthcare IoT Systems
JO - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare
T2 - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare
JF - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare
VL - 1
IS - 3
SP - 118
EP - 137
DO - 10.62762/BISH.2025.212535
UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/BISH.2025.212535
KW - smart IoMT
KW - WBANs
KW - real-time monitoring
KW - node deployment
KW - path-loss
KW - energy consumption
KW - network lifetime
KW - DARE
KW - LAEEBA
KW - HEART scheme
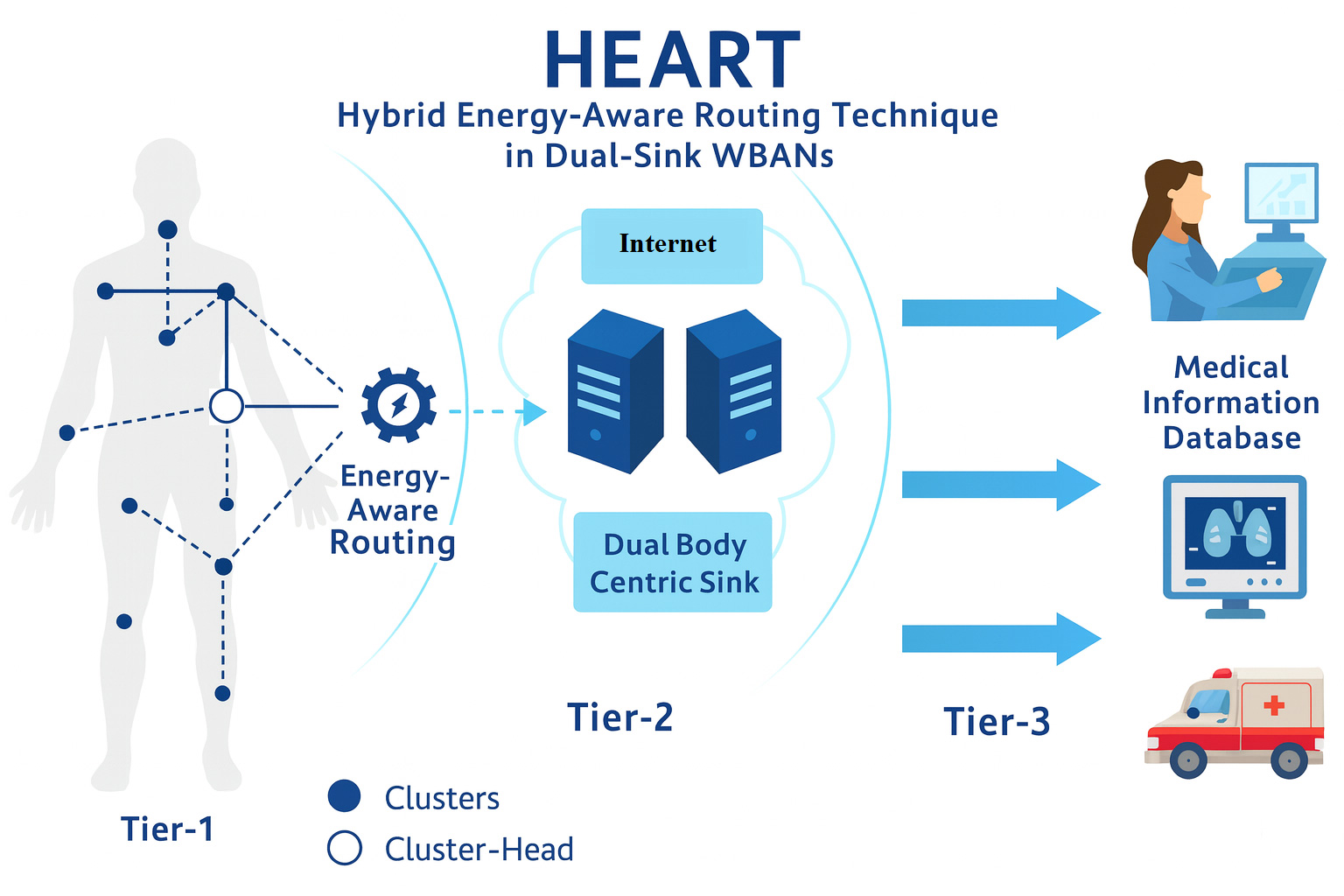
AB - The rapid evolution of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has enabled pervasive patient monitoring through Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs). However, energy depletion, high path-loss, link instability, and latency remain major barriers to achieving reliability in real-time healthcare applications. Existing schemes, such as Distance Aware Relaying Energy-efficient (DARE) and Link Aware and Energy Efficient Scheme for Body Area Networks (LAEEBA), mitigate individual constraints, distance and link quality respectively, but lack holistic optimization across energy, distance, and reliability dimensions. This paper proposes HEART (Hybrid Energy-Aware Routing Technique), a dual-sink, clustering-based protocol designed to minimize path-loss and balance energy consumption in smart healthcare IoMT environments. HEART employs a cost function combining residual energy and link distance for adaptive Cluster-Head (CH) selection and integrates dual-sink coordination to enhance data reliability and reduce latency. Simulation results (0--\(10^5\) rounds) demonstrate that HEART outperforms DARE and LAEEBA across all performance metrics: achieving \(35.5_{\text{dB}}\) average path-loss, \(1.53_{\text{J}}\) residual energy, \(0.77_{\text{s}}\) end-to-end delay, and \(1.16_{\frac{packets}{s}}\) throughput, while improving packet delivery ratio, data generation rate, and reducing packet/bit error rates. Cumulative distribution analyses further confirm HEART's statistical stability and robustness under dynamic body postures. The proposed protocol significantly prolongs network lifetime and ensures dependable, energy-efficient transmission for continuous medical data acquisition—making it a strong candidate for next-generation smart IoMT healthcare systems.
SN - 3068-5524
PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge
LA - English
ER -
@article{Hussain2025HEART,
author = {Altaf Hussain},
title = {HEART: Hybrid Energy-Aware Routing Technique for Dual-Sink Body Area Networks in Smart Healthcare IoT Systems},
journal = {Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {3},
pages = {118-137},
doi = {10.62762/BISH.2025.212535},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/BISH.2025.212535},
abstract = {The rapid evolution of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) has enabled pervasive patient monitoring through Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs). However, energy depletion, high path-loss, link instability, and latency remain major barriers to achieving reliability in real-time healthcare applications. Existing schemes, such as Distance Aware Relaying Energy-efficient (DARE) and Link Aware and Energy Efficient Scheme for Body Area Networks (LAEEBA), mitigate individual constraints, distance and link quality respectively, but lack holistic optimization across energy, distance, and reliability dimensions. This paper proposes HEART (Hybrid Energy-Aware Routing Technique), a dual-sink, clustering-based protocol designed to minimize path-loss and balance energy consumption in smart healthcare IoMT environments. HEART employs a cost function combining residual energy and link distance for adaptive Cluster-Head (CH) selection and integrates dual-sink coordination to enhance data reliability and reduce latency. Simulation results (0--\(10^5\) rounds) demonstrate that HEART outperforms DARE and LAEEBA across all performance metrics: achieving \(35.5\_{\text{dB}}\) average path-loss, \(1.53\_{\text{J}}\) residual energy, \(0.77\_{\text{s}}\) end-to-end delay, and \(1.16\_{\frac{packets}{s}}\) throughput, while improving packet delivery ratio, data generation rate, and reducing packet/bit error rates. Cumulative distribution analyses further confirm HEART's statistical stability and robustness under dynamic body postures. The proposed protocol significantly prolongs network lifetime and ensures dependable, energy-efficient transmission for continuous medical data acquisition—making it a strong candidate for next-generation smart IoMT healthcare systems.},
keywords = {smart IoMT, WBANs, real-time monitoring, node deployment, path-loss, energy consumption, network lifetime, DARE, LAEEBA, HEART scheme},
issn = {3068-5524},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/