Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare | Volume 1, Issue 3: 149-154, 2025 | DOI: 10.62762/BISH.2025.444143
Abstract
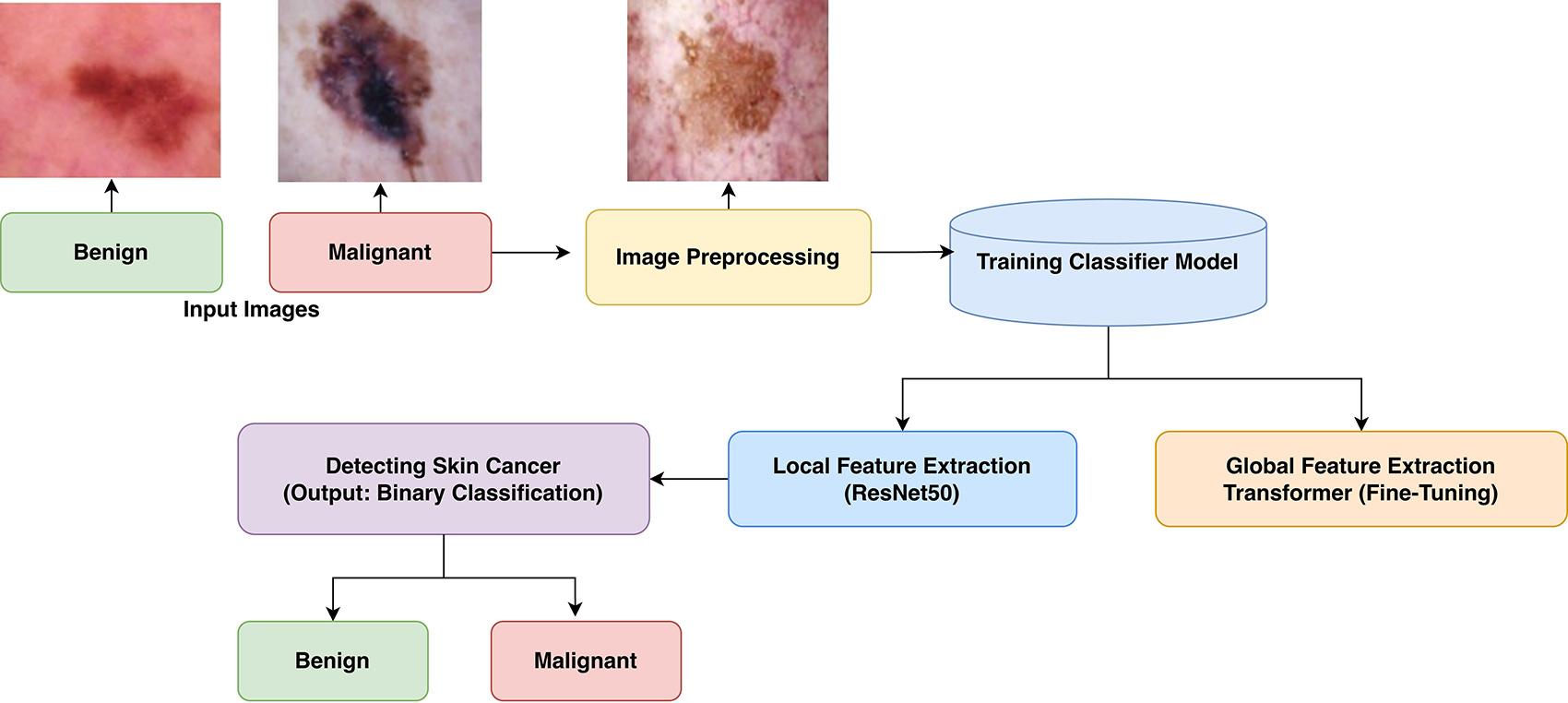
Early diagnosis plays a critical role in the successful skin cancer treatment. To classify skin lesions as benign or malignant, this study suggested a deep learning-enabled method that combines a Transformer module with ResNet50. At first ResNet50, a powerful convolutional neural network, to extract the image features and then enhance the model with a Transformer layer to improve the model accuracy is used. The final model is fine-tuned to achieve better accuracy. This approach shows improved classification results compared to the traditional model. The results signify that combining CNN-based feature extraction with Transformer-enabled global attention suggestively improves skin lesion clas... More >
Graphical Abstract