Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare
ISSN: 3068-5524 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
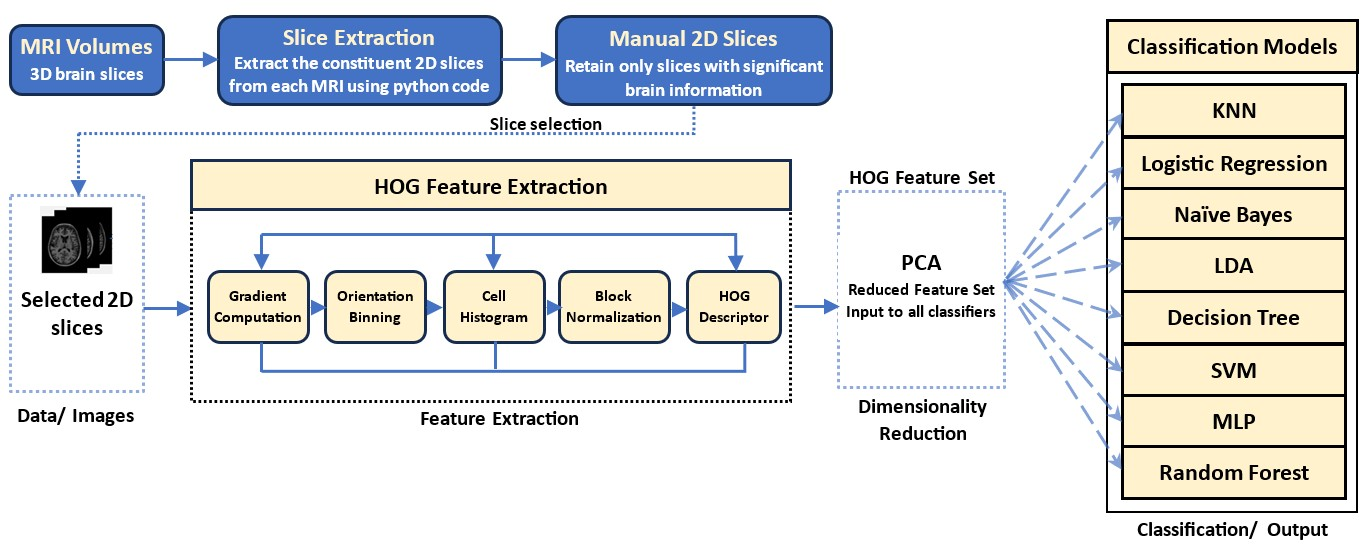
TY - JOUR AU - Kumar, Neeraj AU - Akram, Waseem AU - Bhushan, Megha AU - Lakhnotra, Ajay AU - Manhas, Jatinder PY - 2025 DA - 2025/12/28 TI - Empirical Analysis of the Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms in Classifying 2D MR Images from PCA Reduced HOG and LBP Features JO - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare T2 - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare JF - Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare VL - 1 IS - 3 SP - 138 EP - 148 DO - 10.62762/BISH.2025.993395 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/BISH.2025.993395 KW - medical imaging KW - feature extraction KW - ensemble techniques KW - histogram of oriented gradients KW - local binary patterns KW - PCA AB - This study investigates the role of feature extraction and dimensionality reduction techniques in addressing high-dimensional image data, with a particular focus on Alzheimer's disease classification using 2D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) and Local Binary Patterns (LBP) are employed to extract discriminative features from MRI images; however, due to the high dimensionality of the extracted features, dimensionality reduction is required. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is utilized to reduce feature dimensionality while preserving most of the relevant information, as reflected in the improved performance of the underlying machine learning (ML) classifiers. Two feature extraction pipelines are evaluated: (i) HOG combined with PCA, and (ii) LBP combined with PCA. The reduced feature sets are subsequently used for classification. Experimental results demonstrate that ML algorithms consistently achieve superior performance using features derived from the HOG+PCA pipeline compared to those obtained from the LBP+PCA pipeline. Although the LBP+PCA approach exhibits certain advantages, HOG+PCA proves to be more effective for the problem under consideration, while acknowledging that performance may vary across applications. Furthermore, the study confirms that ensemble learning methods generally outperform individual classifiers by leveraging complementary strengths, and that larger datasets tend to enhance model performance by enabling the learning of richer patterns. In contrast, memory-intensive algorithms such as k-nearest neighbors (KNN) may be suitable for smaller datasets but are typically less scalable for large-scale applications. SN - 3068-5524 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Kumar2025Empirical,
author = {Neeraj Kumar and Waseem Akram and Megha Bhushan and Ajay Lakhnotra and Jatinder Manhas},
title = {Empirical Analysis of the Performance of Machine Learning Algorithms in Classifying 2D MR Images from PCA Reduced HOG and LBP Features},
journal = {Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare},
year = {2025},
volume = {1},
number = {3},
pages = {138-148},
doi = {10.62762/BISH.2025.993395},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/BISH.2025.993395},
abstract = {This study investigates the role of feature extraction and dimensionality reduction techniques in addressing high-dimensional image data, with a particular focus on Alzheimer's disease classification using 2D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) and Local Binary Patterns (LBP) are employed to extract discriminative features from MRI images; however, due to the high dimensionality of the extracted features, dimensionality reduction is required. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is utilized to reduce feature dimensionality while preserving most of the relevant information, as reflected in the improved performance of the underlying machine learning (ML) classifiers. Two feature extraction pipelines are evaluated: (i) HOG combined with PCA, and (ii) LBP combined with PCA. The reduced feature sets are subsequently used for classification. Experimental results demonstrate that ML algorithms consistently achieve superior performance using features derived from the HOG+PCA pipeline compared to those obtained from the LBP+PCA pipeline. Although the LBP+PCA approach exhibits certain advantages, HOG+PCA proves to be more effective for the problem under consideration, while acknowledging that performance may vary across applications. Furthermore, the study confirms that ensemble learning methods generally outperform individual classifiers by leveraging complementary strengths, and that larger datasets tend to enhance model performance by enabling the learning of richer patterns. In contrast, memory-intensive algorithms such as k-nearest neighbors (KNN) may be suitable for smaller datasets but are typically less scalable for large-scale applications.},
keywords = {medical imaging, feature extraction, ensemble techniques, histogram of oriented gradients, local binary patterns, PCA},
issn = {3068-5524},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/