Abstract
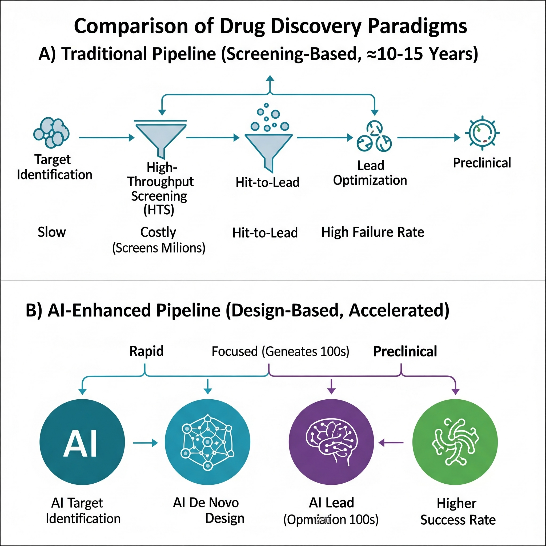
Exorbitant expenses, lengthy development periods, and a high incidence of drug candidate attrition plague the conventional pharmaceutical R&D pipeline---a problem sometimes referred to as ``Eroom's Law.'' By radically reorganizing the discovery process, generative artificial intelligence (AI), which has emerged as a transformational force, promises to buck this tendency. Through data synthesis on key performance metrics, this review offers a thorough analysis of the effects of AI-enhanced methodologies. We explore how a new set of tools is changing the paradigm from experimental screening to in silico design. These tools include graph neural networks (GNNs)—a class of neural architectures that operate directly on graph-structured data by recursively aggregating information from neighbouring nodes—for molecular modelling. Additionally, large language models (LLMs)—Transformer-based neural networks trained on massive text corpora that learn contextual representations of biological sequences and scientific literature—are revolutionizing target identification. According to our analysis, integrating AI results in previously unheard-of benefits: clinical success rates for AI-discovered candidates are expected to rise from a baseline of 7.9% to as high as 90%, costs are predicted to be cut by 45--80%, and early-stage discovery timelines are compressed by up to 62.5% (e.g., reducing target-to-lead time from 24 to 9 months). These improvements stem from a sharp rise in molecular-level prediction accuracy. We come to the conclusion that generative AI is a crucial tool for accelerating the development of new treatments, allowing for a quicker, more economical, and more successful strategy that will characterize the next phase of pharmaceutical innovation.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Saurabh Sarkar is an employee of Chicory AI, Greater Seattle, United States.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Mishra, A., Sarkar, S., Chandan, R. R., Bhushan, S., & Shivahare, B. D. (2025). Accelerating Pharmaceutical R&D: The Role of Generative Artificial Intelligence in Modern Drug Discovery. Biomedical Informatics and Smart Healthcare, 1(2), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.62762/BISH.2025.789201
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 