Abstract
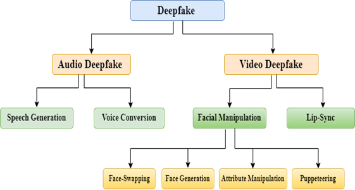
The rapid advancement in machine learning and artificial intelligence has significantly enhanced capabilities in multimedia content creation, particularly in the domain of deepfake generation. Deepfakes leverage complex neural networks to create hyper-realistic manipulated audio-visual content, raising profound ethical, societal, and security concerns. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of contemporary trends in deepfake video research, focusing on both generation and detection methodologies. The study categorizes deepfakes into three primary types: facial manipulation, lip-synchronization, and audio deepfakes, further subdividing them into face swapping, face generation, attribute manipulation, puppeteering, speech generation, and voice conversion. For each type, the paper reviews cutting-edge generation techniques, including StyleGANs, variational autoencoders, and various speech synthesis models. It also presents an in-depth analysis of detection methods, highlighting both traditional handcrafted feature-based approaches and modern deep learning frameworks utilizing CNNs, RNNs, attention mechanisms, and hybrid transformer models. The paper evaluates these methods in terms of performance, generalization, robustness, and limitations against evolving deepfake techniques. The survey identifies significant challenges such as vulnerability to adversarial attacks, lack of generalized models, and dependency on high-quality training data. The insights provided aim to aid researchers and practitioners in developing more robust detection mechanisms and understanding the landscape of deepfake threats and countermeasures. Ultimately, this study contributes to the growing body of literature by mapping current trends and suggesting potential avenues for future research in combating deepfake proliferation.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported without any funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Cite This Article
APA Style
Khan, I., Khan, K., & Ahmad, A. (2025). A Comprehensive Survey of DeepFake Generation and Detection Techniques in Audio-Visual Media. ICCK Journal of Image Analysis and Processing, 1(2), 73–95. https://doi.org/10.62762/JIAP.2025.431672
Publisher's Note
ICCK stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and Permissions

Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.


 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
 Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2025 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 