PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
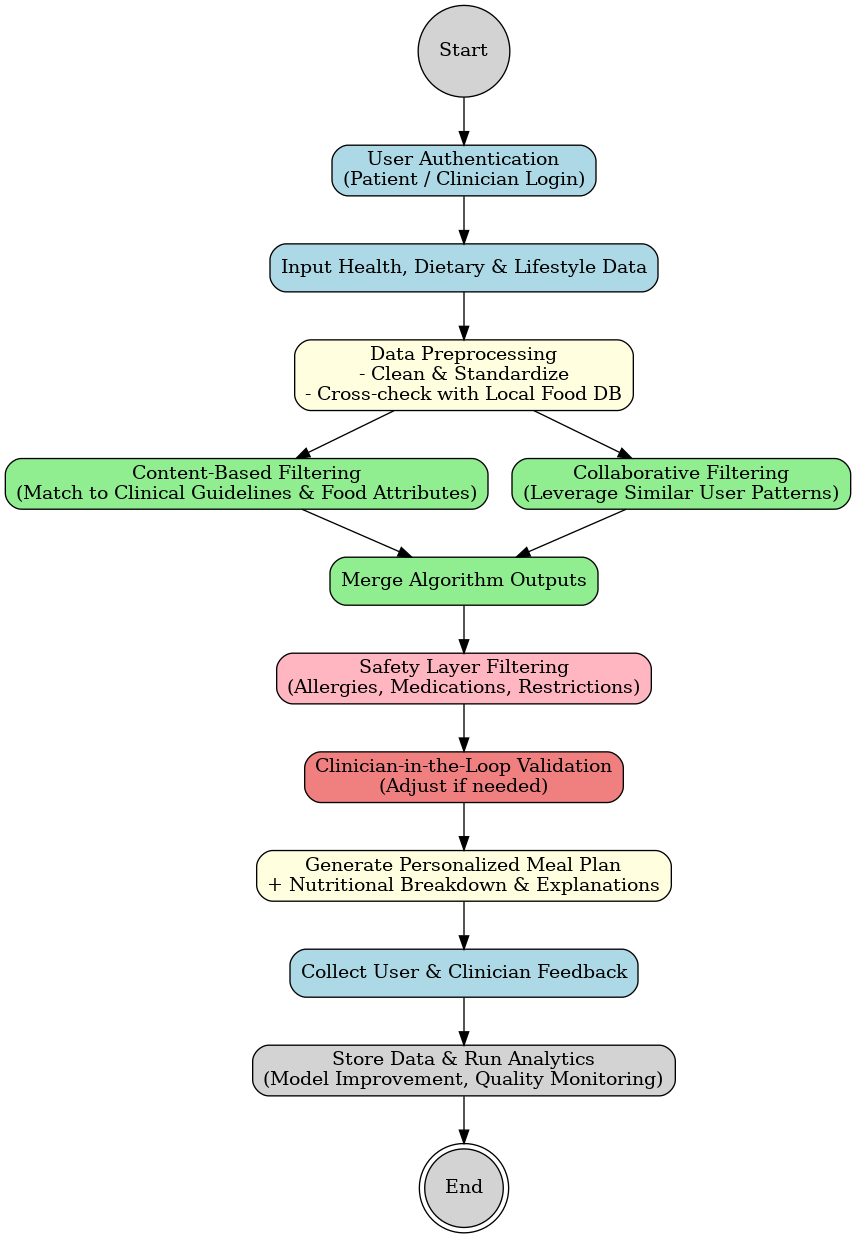
TY - JOUR AU - Soliman, Marvic Alejo AU - Dumlao, Menchita F. PY - 2026 DA - 2026/02/10 TI - Cardiovascular Patient’s Nutrition Assessment Web Application with Hybrid Recommender System for Malabon Hospital and Medical Clinic JO - PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation T2 - PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation JF - PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation VL - 1 IS - 1 SP - 12 EP - 27 DO - 10.62762/JRIT.2025.397682 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRIT.2025.397682 KW - nutrition assessment KW - hybrid recommender system KW - Web application AB - This paper presents the design and development of a Cardiovascular Patients’ Nutrition Assessment Web Application with a Hybrid Recommender System, developed for Malabon Hospital and Medical Clinic. The primary objective of the system is to support both patients and healthcare providers in monitoring nutritional status and improving dietary management for individuals with cardiovascular conditions. The application was implemented using the Laravel framework and features a simple, user-friendly interface that facilitates interaction among patients, clinicians, and nutritionists. The recommender system integrates rule-based logic with intelligent recommendation techniques to generate personalized meal plans that align with clinical guidelines and individual patient profiles. The evaluation of the system focused on black box testing conducted under controlled conditions using simulated data. While this approach confirms the reliability, efficiency, and functional correctness of key system features—such as user registration, authentication, survey processing, and recommendation generation—it is important to note that the results reflect performance in a simulated environment rather than real-world clinical deployment. Overall, the study demonstrates the feasibility of a technology-supported nutrition management system tailored to a local healthcare setting, highlighting its potential to enhance patient engagement, support clinical decision-making, and contribute to more effective, localized cardiovascular nutrition management in clinical practice. SN - pending PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Soliman2026Cardiovasc,
author = {Marvic Alejo Soliman and Menchita F. Dumlao},
title = {Cardiovascular Patient’s Nutrition Assessment Web Application with Hybrid Recommender System for Malabon Hospital and Medical Clinic},
journal = {PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation},
year = {2026},
volume = {1},
number = {1},
pages = {12-27},
doi = {10.62762/JRIT.2025.397682},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/JRIT.2025.397682},
abstract = {This paper presents the design and development of a Cardiovascular Patients’ Nutrition Assessment Web Application with a Hybrid Recommender System, developed for Malabon Hospital and Medical Clinic. The primary objective of the system is to support both patients and healthcare providers in monitoring nutritional status and improving dietary management for individuals with cardiovascular conditions. The application was implemented using the Laravel framework and features a simple, user-friendly interface that facilitates interaction among patients, clinicians, and nutritionists. The recommender system integrates rule-based logic with intelligent recommendation techniques to generate personalized meal plans that align with clinical guidelines and individual patient profiles. The evaluation of the system focused on black box testing conducted under controlled conditions using simulated data. While this approach confirms the reliability, efficiency, and functional correctness of key system features—such as user registration, authentication, survey processing, and recommendation generation—it is important to note that the results reflect performance in a simulated environment rather than real-world clinical deployment. Overall, the study demonstrates the feasibility of a technology-supported nutrition management system tailored to a local healthcare setting, highlighting its potential to enhance patient engagement, support clinical decision-making, and contribute to more effective, localized cardiovascular nutrition management in clinical practice.},
keywords = {nutrition assessment, hybrid recommender system, Web application},
issn = {pending},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. PWU Journal of Research, Innovation, and Transformation
ISSN: pending (Online)
Email: [email protected]

Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/