Reservoir Science
ISSN: 3070-2356 (Online)
Email: [email protected]
 Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
Submit Manuscript
Edit a Special Issue
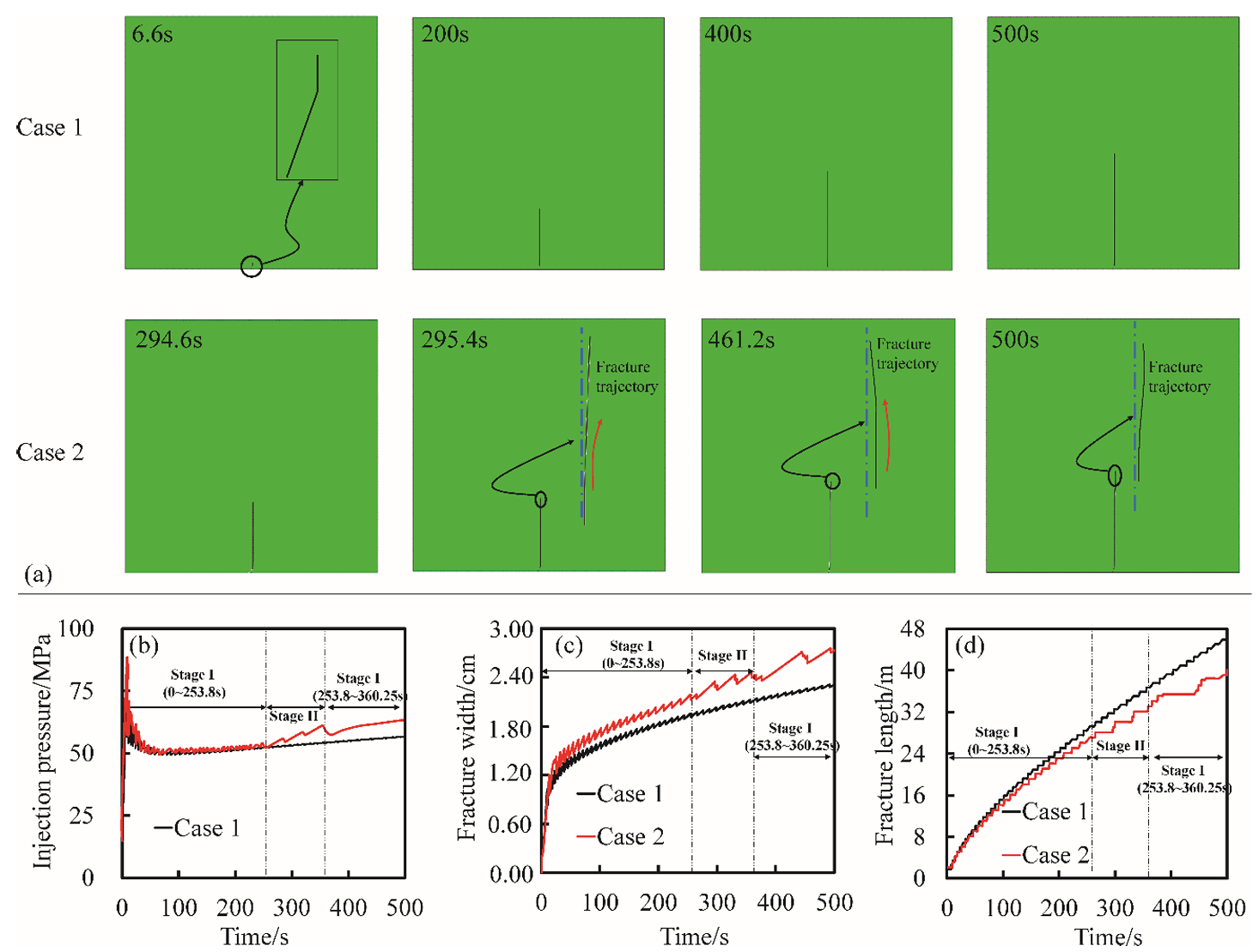
TY - JOUR AU - Tahir, Muhammad Usman AU - Guo, Shenglan PY - 2026 DA - 2026/01/18 TI - Preliminary Investigation of Fracture Behavior during Carbon Dioxide Fracturing of Natural Hydrogen Reservoir with Hard-Core Imperfections JO - Reservoir Science T2 - Reservoir Science JF - Reservoir Science VL - 2 IS - 1 SP - 34 EP - 51 DO - 10.62762/RS.2025.759326 UR - https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.759326 KW - natural hydrogen KW - carbon dioxide-based fracturing KW - reservoir imperfection KW - fracture initiation KW - fracture propagation AB - The low concentration and poor reservoir properties of natural hydrogen suggest that reservoir stimulation measures such as fracturing is required for its efficient development. Nevertheless, the presence of reservoir imperfections, including hard and soft cores, can significantly affect fracture behavior during the fracturing operations. Moreover, there is currently a lack of relevant simulation and experimental studies addressing these effects. In the present work, the effects and mechanisms of hard cores on fracture propagation in natural hydrogen reservoirs in the Songliao basin were numerically simulated. In addition, various factors affecting propagation behavior of fracture were also analyzed. The investigation results indicate that the presence of hard cores induces the fracture propagation mode from “straight-line dominated” to “path optimization” (obstacle-avoidance) pattern, which consequently decreases propagation efficiency. The final fracture length exhibits a reduction of 12.63% compared with that in the homogeneous reservoir case, accompanied by an increase of 18.49% in the final fracture width. Furthermore, higher hard core strength and leakage coefficients significantly decrease fracture propagation efficiency, promoting the development of wide, short fractures. This research offers a preliminary theoretical framework to support the stimulation and efficient development of imperfection-bearing natural hydrogen reservoirs. SN - 3070-2356 PB - Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge LA - English ER -
@article{Tahir2026Preliminar,
author = {Muhammad Usman Tahir and Shenglan Guo},
title = {Preliminary Investigation of Fracture Behavior during Carbon Dioxide Fracturing of Natural Hydrogen Reservoir with Hard-Core Imperfections},
journal = {Reservoir Science},
year = {2026},
volume = {2},
number = {1},
pages = {34-51},
doi = {10.62762/RS.2025.759326},
url = {https://www.icck.org/article/abs/RS.2025.759326},
abstract = {The low concentration and poor reservoir properties of natural hydrogen suggest that reservoir stimulation measures such as fracturing is required for its efficient development. Nevertheless, the presence of reservoir imperfections, including hard and soft cores, can significantly affect fracture behavior during the fracturing operations. Moreover, there is currently a lack of relevant simulation and experimental studies addressing these effects. In the present work, the effects and mechanisms of hard cores on fracture propagation in natural hydrogen reservoirs in the Songliao basin were numerically simulated. In addition, various factors affecting propagation behavior of fracture were also analyzed. The investigation results indicate that the presence of hard cores induces the fracture propagation mode from “straight-line dominated” to “path optimization” (obstacle-avoidance) pattern, which consequently decreases propagation efficiency. The final fracture length exhibits a reduction of 12.63\% compared with that in the homogeneous reservoir case, accompanied by an increase of 18.49\% in the final fracture width. Furthermore, higher hard core strength and leakage coefficients significantly decrease fracture propagation efficiency, promoting the development of wide, short fractures. This research offers a preliminary theoretical framework to support the stimulation and efficient development of imperfection-bearing natural hydrogen reservoirs.},
keywords = {natural hydrogen, carbon dioxide-based fracturing, reservoir imperfection, fracture initiation, fracture propagation},
issn = {3070-2356},
publisher = {Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge}
}
 Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made.
Copyright © 2026 by the Author(s). Published by Institute of Central Computation and Knowledge. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. 
Portico
All published articles are preserved here permanently:
https://www.portico.org/publishers/icck/